Aarab Jihan*, Moukasse Yasmina, Sfaoua Hasnae, Allam Asma, Lahlali Fatima Zahra, El-Majjaoui Sanae, Kebdani Tayeb, El-Kacemi Hanan and Benjaafar Noureddine
Department of Radiotherapy and Radiation Oncology, National Institute of Oncology in Rabat, Mohammed 5 University, Rabat, Morroco
*Corresponding Author:
Aarab Jihan
Department of Radiation therapy
National Institute of Oncology in Rabat
Mohammed V University in Rabat, Morocco.
Tel: 00212662436121
E-mail: jihanaarab@gmail.com
Received Date: May 02, 2018; Accepted Date: May 07, 2018; Published Date: May 12, 2018
Citation: Jihan A, Yasmina M, Hasnae S, Asma A, Zahra LF, et al. (2018) A Rare Case of Submandibular Gland Metastasis as the First Sign of Adenocarcinoma of the Lung. Arch Cancer Res. Vol.6 No.2:9 DOI: 10.21767/2254-6081.100175
The current study document is an unusual case of submandibular metastasis as the first sign of adenocarcinoma of the lung. We report a 57-year-old male chronic smoker presented with a tumefaction in the submandibular gland. The patient had a complete excision. At the histological examination, the diagnosis of an undifferentiated carcinoma of the submandibular gland was retained. A systemic work-up was performed, which unexpectedly detected a tumor in the right lung and was confirmed by histopathological examination. Despite their rarity, submandibular lesions should be considered as possible manifestations of underlying malignancies.
Keywords
Submandibular gland; Metastasis; Adenocarcinoma; Lung
Introduction
Lung carcinomas are aggressive malignancies, characterized by early metastatic spread and poor prognosis at the time of presentation. Metastasis of non-small cell lung carcinoma to submandibular gland is rare. The diagnosis of a metastatic lesion is challenging, both to the clinician and to the pathologist. This case is a rare condition, in our knowledge it is the fourth of the literature. We present a 57-year-old male patient with lung adenocarcinoma reveleated by a tumefaction of the submandibular gland.
Case Presentation
Our patient is a chronic smoker, presented with a 4-month history of a tumefaction in the left submandibular region that was slowly increasing in size, without any other associated signs. Cervical ultrasound revealed a suspect mandibular mass measuring 20 × 34 mm, without any cervical adenopathy. The patient had a complete excision of the submandibular gland with a lymphadenectomy of group IA. At the histological examination, the diagnosis of an undifferentiated carcinoma of the submandibular gland was retained. A chest radiograph unexpectedly revealed right pulmonary opacity. A thoracic computerized tomography scan (CT) identified a lesional process of the right upper lobe, measuring 72 mm of main axis, without hilar or mediastinal lymphadenopathy (Figure 1). A pulmonary biopsy was recommended. Anatomopathological and immunohistochemical evaluation confirmed the diagnosis of an undifferentiated adenocarcinoma infiltrating bronchopulmonary origin was retained. Comparison was made between the submandibular left lesion and pulmonary carcinoma, we conclude that the patient was suffering from pulmonary adenocarcinoma with a metastasis in the left submandibular gland. The patient underwent an 18 fluorodeoxyglucose-based positron emission tomography scan that showed a large necrotic hyper metabolic mass in the right lower lobe, with hyper metabolic lesion in the left adrenal gland (Figures 2 and 3). The patient underwent a chemotherapy regimen of platinum and navelbine. He received 6 cycles the CT showed progression with brain metastasis, the patient was referred for radiotherapy. He received a dose of 30 Gray to the whole brain and he still in good condition one year after the diagnosis.
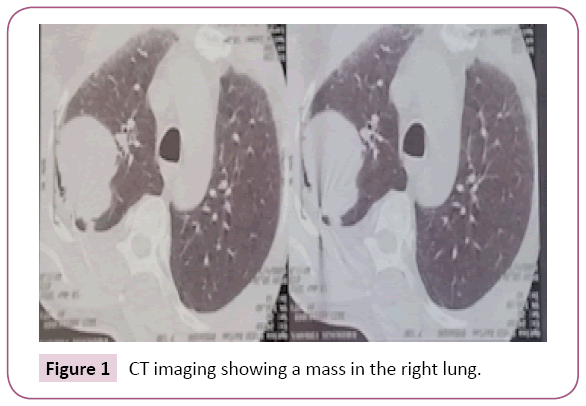
Figure 1: CT imaging showing a mass in the right lung.
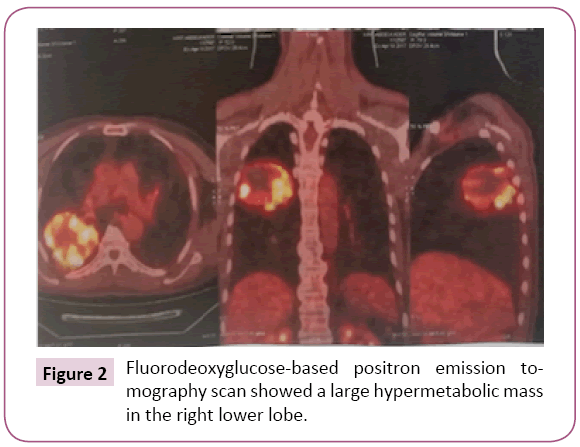
Figure 2: Fluorodeoxyglucose-based positron emission tomography scan showed a large hypermetabolic mass in the right lower lobe.
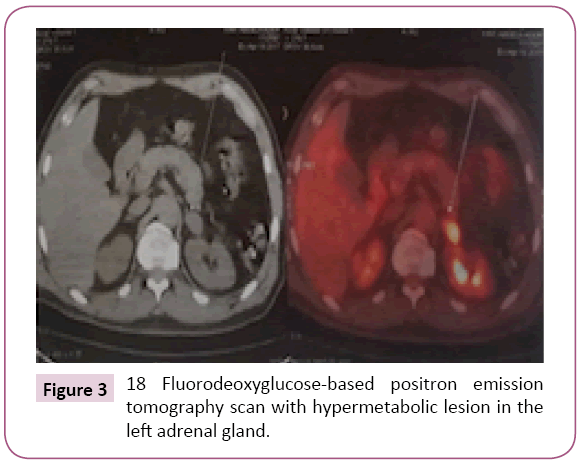
Figure 3: 18 Fluorodeoxyglucose-based positron emission tomography scan with hypermetabolic lesion in the left adrenal gland.
Discussion
Pulmonary adenocarcinoma is an aggressive malignancies tumor, initially metastatic at the time of diagnosis in 56% [1]. The pre-selective site of the metastasis is at the ganglionic, hepatic, bone and adrenal gland levels in 75%, 47%, 41% and 30% of cases, respectively [2]. Localization at the level of the submandibular gland is very rare, and reported in only 3 cases according to our knowledge; this appears to be the fourth case of adenocarcinoma metastatic to the submandibular gland. There was a clear predominance of submandibulary gland metastasis in men versus women, these results are not surprising since lung cancer is more frequent in men, and with the consequence that submandibulary gland metastasis is more common in male patients [1]. The tumefaction of the submandibular gland revealed pulmonary neoplasia in a single patient, in the other two cases swelling appeared during the evolution of the disease [3-5]. In the three cases the histological type was an anaplasique and poorly differentiated carcinoma in two cases and small cell lung cancer in the third. There are no reports of adenocarcinoma of the lung cancer metastasis to the submandibular gland [3-5]. Our case is the first. Lung cancer can be revealed by metastasis at the level of the submandibular gland, a chest radiograph should be made before any excision especially in elderly patients with a history of smoking. The diagnosis by biopsy of the lesion is required to establish the correct diagnosis.
Conclusion
The current document is an atypical case of submandibular gland metastasis as the first sign of adenocarinoma of the lung and he still in good control despite the poor prognosis of similar cases.
22737
References
- Howlader N,Krapcho M(2016) SEER stat factsheets: Lung and bronchus. National Cancer Institute, Rockville, Maryland, USA.
- Line DH, Deeley T(1971) The necropsyfindings in carcinoma of the bronchus. BrJDisChest 65:238-242.
- Brodsky G, Arnold BR (1984) Metastasis to the submandibular gland as the initial presentation of smallcell ("oatcell") lungcarcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 58: 76-80.
- Januska JR, LebanSG (1978) Pulmonarymetastasis to the submandibular gland. J Oral Surg 36: 50-51.
- Shaikh T, Ehya H, TurakaP (2015) A smallcelllung cancer metastatic to the sub-mandibulargland. J RadiotherPract 14: 84-87.