Case Report - (2022) Volume 13, Issue 1
An Interesting Case of Intracranial Tuberculoma
with Spinal Tuberculous Spondylitis in a Patient
with Muscular Dystrophy
Kalyani J*,
Saravanan S and
Narayanan S
Department of Neurology, Tirunelveli Medical College, Palayamkottai, Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu, India
*Correspondence:
Kalyani J, Department of Neurology, Tirunelveli Medical College, Palayamkottai, Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu,
India,
Tel: 9442370976,
Email: ,
Received: 20-Oct-2021, Manuscript No. ipjnn-21-11193;
Editor assigned: 22-Oct-2021, Pre QC No. P-11193;
Reviewed: 15-Jan-2022, QC No. Q-11193;
Revised: 21-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. R-11193;
Published:
28-Jan-2022
Abstract
This case describes an unusual or novel occurrence. An unexpected association between intracranial tuberculoma and spinal tuberculosis. This is an unexpected event in the course observing and treating a patient with muscular dystrophy. We report a case combination of spinal tuberculous spondylitis and intracranial tuberculoma which is extremely rare. So far only five cases have been reported in the literature. 32-year-old female who is a known case of muscular dystrophy presenting with fever, diplopia, low back ache and motor weakness of both upper and lower extremities based on magnetic resonance imaging and polymerase chain reaction, we diagnosed as tuberculoma. She was started with conventional antituberculous treatment and steroids. The association of potts spine with intracranial tuberculomas is extremely rare. Up to date, there are only few cases which have been reported in the literature. Intracranial tuberculomas associated with intramedullary tuberculomas only about 5 cases has been reported worldwide.
Keywords
Intracranial tuberculoma; Brain; Spine; Weakness and magnetic resonance
imaging
Introduction
Tuberculosis which is a catastrophic infectious disease caused
by Mycobacterium tuberculosis presents with extra pulmonary
forms with drug resistance in the recent days [1-7]. Most
common manifestations of tuberculosis in the CNS [8] are
tuberculous meningitis [9] and intracranial tuberculoma. Brain is
far more commonly affected than the spinal cord. Infratentorial
tuberculomas [10] are more frequent in children, whereas lesions
are mostly supratentoria [11] in adults. Tuberculous spondylitis,
also known as Pott disease, refers to vertebral body osteomyelitis
and intervertebral discitis from tuberculosis (TB). The spine is the
most frequent location of musculoskeletal tuberculosis almost
50%. In spinal tuberculosis, characteristically, there is destruction
of the intervertebral disk space and the adjacent vertebral bodies,
collapse of the spinal elements, and anterior wedging leading
to the characteristic angulation and gibbus. Discitis [12] and/or
osteomyelitis usually affects the lower thoracic and upper lumbar
levels of the spine.
Spine is involved due to hematogenous spread [13] that can
occur via both arteries and veins, resulting in different patterns of infection.
Spread through the anterior arterial arcade that richly supplies the
subchondral paradiscal bone results in infection anterosuperiorly
and anteroinferior, adjacent to the disc [14]. In adults and
particularly older individuals the disc is conspicuously spared
due to its sparse vascularity. In contrast, in younger individuals,
especially children, the disc may be involved early as it has a far
richer blood supply.
Infection then spreads beneath the longitudinal ligaments and can
lead to infection of adjacent vertebral bodies. Gradual anterior
collapse typically results in an acute kyphotic or gibbus deformity
[15]. This angulation, coupled with epidural granulation tissue and
bony fragments, can lead to cord compression [16,17]. Central
involvement: Spread via the venous plexus of Batson typically
results in infection arising centrally within the vertebral body. This
is more common in older individuals [18]. Gradual collapse can
result in vertebra plana and acute kyphotic or gibbus deformity.
This angulation, coupled with epidural granulation tissue and
bony fragments, can lead to cord compression.
Posterior involvement, also known as an appendiceal [19] is also due to venous hematogenous spread via the posterior venous
plexuspattern. Synovial involvement is relatively rare but can be
seen involving facet joints and atlantoaxial and atlanto-occipital
joints. In late-stage spinal tuberculosis, large paraspinal abscesses
can develop without severe pain or frank pus or prominent
inflammatory signs and symptoms; thus "cold abscess.
Incidence of neurologic complications in spinal tuberculosis
varies from 10 to 43%.
Clinical Presentation
A 32-year-old female immunocompetent patient who is a known
case of muscular dystrophy came with signs of headache, diplopia,
and weakness in both upper and lower limbs. She had severe low
back ache and progressive weakness of both lower limbs. There
was also the history of the evening rise of temperature, loss of
weight and appetite. On examination, she had quadriparesis with
a power 2/5 proximally and 4/5 distally in upper limbs and 2/5 in
the lower limbs both proximally and distally.
Both superficial and deep tendon reflexes were absent and
plantar was extensor. Tone was hypotonia in both lower limbs.
Generalised wasting was present. She presented with sensory
involvement in the form of reduced perception of all modalities
from T10 segmental level. There was excruciating radiating pain
from the lower back down to both legs which was aggravated
by movement, coughing and straining at stools. Regarding higher
mental function she was conscious, oriented, memory, speech
and behaviour were normal. She had right lateral rectus palsy.
On evaluation, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) was
40mm/h, chest X-ray was normal. Sputum examination for acid
fast-bacilli (AFB) could not be done as a patient had no cough.
Mantoux test was positive and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was
clear, with 4 white blood cell/dL (100% lymphocytes), sugar 52
mg/dL, proteins 37 mg/dL, chloride 89mmol/L. AFB staining
was negative in CSF with adenosine deaminase activity levels of
7 IU/L. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain showed welldefined
ring-enhancing lesions with perilesional edema in pons,
suggestive of tuberculoma (Figure 1). X-Ray spine showed bony
destruction of D12 and anterior wedge fracture of L1 (Figure 2).
Spine CT showedspondylotic destruction of D12 to L1 vertebral
bodies, compression of conus medullaris and Rt sacroiliitis.
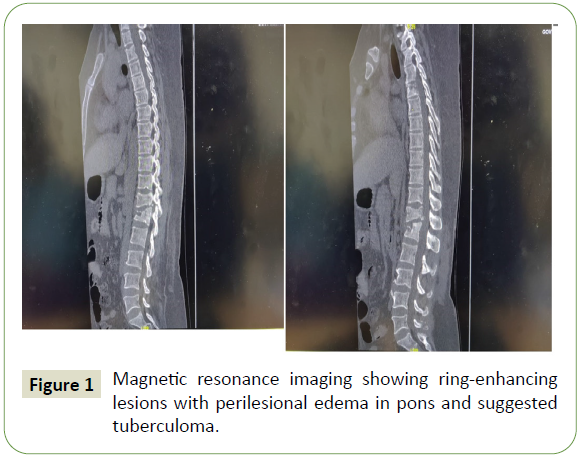
Figure 1: Magnetic resonance imaging showing ring-enhancing lesions with perilesional edema in pons and suggested tuberculoma.
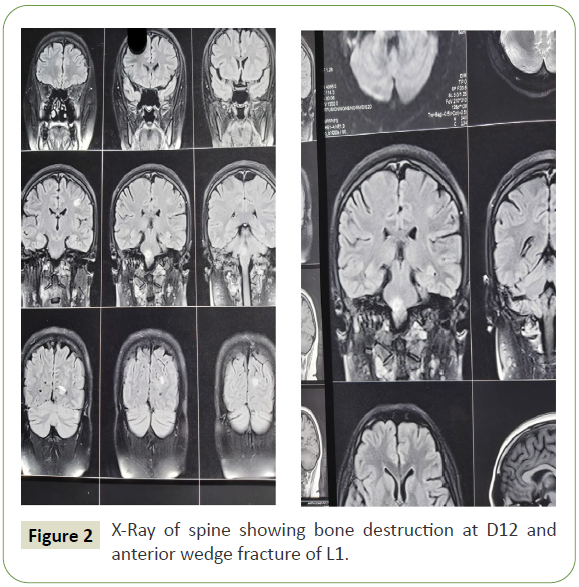
Figure 2: X-Ray of spine showing bone destruction at D12 and anterior wedge fracture of L1.
Discussion
Central nervous system tuberculosis is rare, affecting 0.5-2% of
patients with systemic tuberculosis.
Tuberculoma is a peculiar manifestation of tuberculosis that
might occur in any solid organ of the body. It is, usually, formed by
conglomeration of several miliary tubercles [20], with the centre
of the conglomeration becoming caseous. Caseous material gets
inspissated and sometimes liquefied. A thick capsule may form
around these lesions. Concurrent occurrence of intracranial
tuberculomas along with spinal tuberculosis is extremely rare.
The case presented here was diagnosed in the background of
muscular dystrophy. The chest X-ray of this patient was normal.
The patient had elevated ESR and was symptomatic in the form
of loss of weight and appetite with occasional evening rise of temperature. Magnetic resonance imaging is the optimal
measure because it shows location, size, and number of lesions
and the presence of degeneration and necrosis.
The differential diagnosis of tuberculomas includes granulomas
such as cysticercal granulomas and neoplastic lesions such as
astrocytoma, metastasis or lymphoma. In this case, the clinical
presentation and size of the lesion combined with the classical ring
enhancement and surrounding edema was thought to be typical
of a tuberculous granuloma. Associatedpotts spine also confirms
the aetiology. Paraplegia is the devastating complication found in
this patient, Hodgson, in his classical paper on Pott's paraplegia,
classified paraplegia into two groups according to the activity of
the tuberculous infection. These two groups were paraplegia of
active disease (early-onset paraplegia) and paraplegia of healed
disease (late-onset paraplegia). Early-onset paraplegia develops
in the active stage of spinal tuberculosis and requires active treatment. This type of paraplegia has a better prognosis and is
frequently seen in adults with Pott's spine.
Late-onset paraplegia may develop two to three decades
after active infection. It is often associated with marked spinal
deformities.
Conclusion
We report a case of concurrent occurrence of spinal tuberculous
spondylitis and intracranial tuberculomas in a patient with
muscular dystrophy. This case is being presented because of
extreme rarity. Medical therapy is generally advocated as the
initial treatment. High index of suspicion is needed to diagnose
extrapulmonary tuberculosis particularly in a developing country
like India where the prevalence of all forms of tuberculosis is
very high 5.05/1000 before considering other etiologies like
demyelination.
REFERENCES
- Mercuri E, Bönnemann CG, Muntoni F (2019) Muscular dystrophies. The Lancet 394: 2025-2038.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
- Hartung MP (2021) Tuberculous spondylitis (Pott disease) with large psoas abscesses.
- Garg RK (1999) Tuberculosis of the central nervous system. Postgrad Med J 75: 133-140.
Google Scholar
- Tomioka H, Namba K (2006) Development of antituberculous drugs: Current status and future prospects. Kekkaku 81: 753-774.
Google Scholar, Indexed at
- Shubin H, Lambert RE, Heiken CA, Sokmensuer A, Glaskin A (1959) Steroid therapy and tuberculosis. J Am Med Assoc 170: 1885-1890.
Google Scholar
- Keklikoğlu HD, Çoruh Y, Yoldaş TK, Keskin S (2008) Central nervous system tuberculoma and Pott's disease: Case report. J Neurol Sci (Turkish) 25: 142-147.
- Wilkinson RJ, Rohlwink U, Misra UK, Van Crevel R, Mai NT, et al. (2017) Tuberculous meningitis. Nature Rev Neurol 13: 581-598.
Google Scholar
- Tuberculoma: Tuberculomas are conglomerate caseous foci within the substance of the brain that develop from deep-seated tubercles acquired during a recent or remote period of bacillemia. From: Aminoff's Neurology and General Medicine (5th Edition), 2014.
- Winarno AN (2018) Multiple intracranial tuberculomas: A rare case of CNS TB. JKKI: Jurnal Kedokteran dan Kesehatan Indonesia 9: 53-59.
Google Scholar
- Rajasekaran S, Soundararajan DC, Shetty AP, Kanna RM (2018) Spinal tuberculosis: Current concepts. Global Spine J 8: 96-108.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
- Clark RA, Blakley SL, Greer D, Smith MH, Brandon W (1991) Hematogenous dissemination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in patients with AIDS. Rev Infect Dis 13: 1089-1092.
Google Scholar, Crossref
- Burrill J, Williams CJ, Bain G, Conder G, Hine AW, et al. (2007) Tuberculosis: A radiologic review. Radiographics 27: 1255-1273.
Google Scholar, Crossref
- Rajasekaran S, Shanmugasundaram TK (1987) Prediction of the angle of gibbus deformity in tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69: 503-509.
Google Scholar
- Sobti S, Grover A, John BP, Grewal SS, George UB (2018) Prospective randomized comparative study to evaluate epidural fibrosis and surgical outcome in patients undergoing lumbar laminectomy with epidural autologous free fat graft or gelfoam: A preliminary study. Int J Appl Basic Med Res 8: 71-75.
Google Scholar, Crossref
- Garg RK, Somvanshi DS (2011) Spinal tuberculosis: a review. J Spinal Cord Med 34: 440-454.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
- Zhen P, Li XS, Lu H (2013) Single vertebra tuberculosis presenting with solitary localized osteolytic lesion in young adult lumbar spines. Orthopaedic Surg 5: 105-111.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
- Chandra BS, Girish TU, Thrishuli PB, Vinay HG (2013) Primary tuberculosis of the appendix: A rare cause of a common disease. J Sur Tech Case Rep 5: 32-34.
Google Scholar, Crossref
- Fujimoto N, Gemba K, Yao A, Ozaki S, Ono K, et al. (2010) Tuberculosis diagnosed by PCR analysis of synovial fluid. J Infect Chemother 16: 53-55.
Google Scholar, Crossref
- Patel R, Gannamani V, Shay E, Alcid D (2016) Spinal tuberculosis and cold abscess without known primary disease: Case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Infect Dis 2016: 1780153.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
- Sharma SK, Mohan A, Sharma A (2016) Miliary tuberculosis: A new look at an old foe. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis 3: 13-27.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
Citation: Kalyani J, Saravanan S, Narayanan S (2022) An Interesting Case of Intracranial Tuberculoma with Spinal Tuberculous Spondylitis in a Patient with Muscular Dystrophy. J Neurol Neurosci Vol.13 No.1:405