Keywords
Quinoxalines, 2-Chloro-N-(substituted- aryl/alkyl)-acetamides, 2-(2-methylquinoxalin-3-ylthio)-Nsubstituted- aryl/alkyl)-acetamides, anti-inflammatory activity.
Introduction
Quinoxaline is commonly called 1, 4-diazanaphthalene or, bezopyrazine. Quinoxaline and its derivatives are mostly of synthetic origin. They have been described as a part of bicyclic desipeptide antibiotic having activity against gram positive bacteria and certain tumors by acting through inhibition of RNA synthesis. Quinoxaline ring structure is also found in the antibiotic such as Echinomycin, Levomycin and actinoleutin. It has been used in the synthesis of dyes, azo dyes, fluorescein dyes and pigments. Compounds containing the quinoxaline nucleus exhibit a broad spectrum of biological activity such as antibacterial [1- 3], antifungal [4, 5], antiviral [6], anticancer [7], antituberculosis [8], antimalarial [9] and antiinflammatory [10]. Thioethers have also been reported for their bactericidal, fungicidal, anti-inflammatory anticholestemic, hypolipidemic and neurotropic activities [11, 12], therefore in continuation of our previous work on 2-chloro-3- methylquinoxaline,”Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some thioether derivatives of quinoxaline,” it was thought worthwhile to evaluate their antiinflammatory activity too.
Material and Methods
The chemical synthesis (scheme I) was initiated with the reaction of o-phenylenediamine (1) with ethyl pyruvate in n-butanol to yield 2-hydroxy-3-methyl quinoxaline (2), which on treatment with POCl3 ,yielded 2-chloro-3-methylquinoxaline(3).A mixture of the compound(3) and sodium sulphide in DMF was refluxed to yield 3-methylquinoxalin-2- thiosodium(4),which on treatment with different Nsubstituted aryl and cyclohexyl chloroacetamides afforded the one pot synthesis of 2-(2- methylquinoxalin-3-ylthio)-N-substituted-aryl) and cyclohexyl -acetamides(5a-k). 2-chloro-N-substituted acetamides (the list of these compounds is shown in the Table 1) were prepared by treating substituted anilines in glacial acetic acid with chloroacetylchloride, warming on the water bath for half an hour and then precipitating, 2-chloro-N-substituted acetamides by addition of saturated aqueous solution of anhydrous sodium acetate. A compound 2-(benzylthio)-3- methylquinoxaline 5l was also prepared. All these compounds (5a-l) are depicted in Table 2. The compounds were purified by recrystallization from appropriate solvents. Purity of the compounds was checked by thin layer chromatography using silica gel- G on micro slide glass plates and spots were detected under iodine vapor.
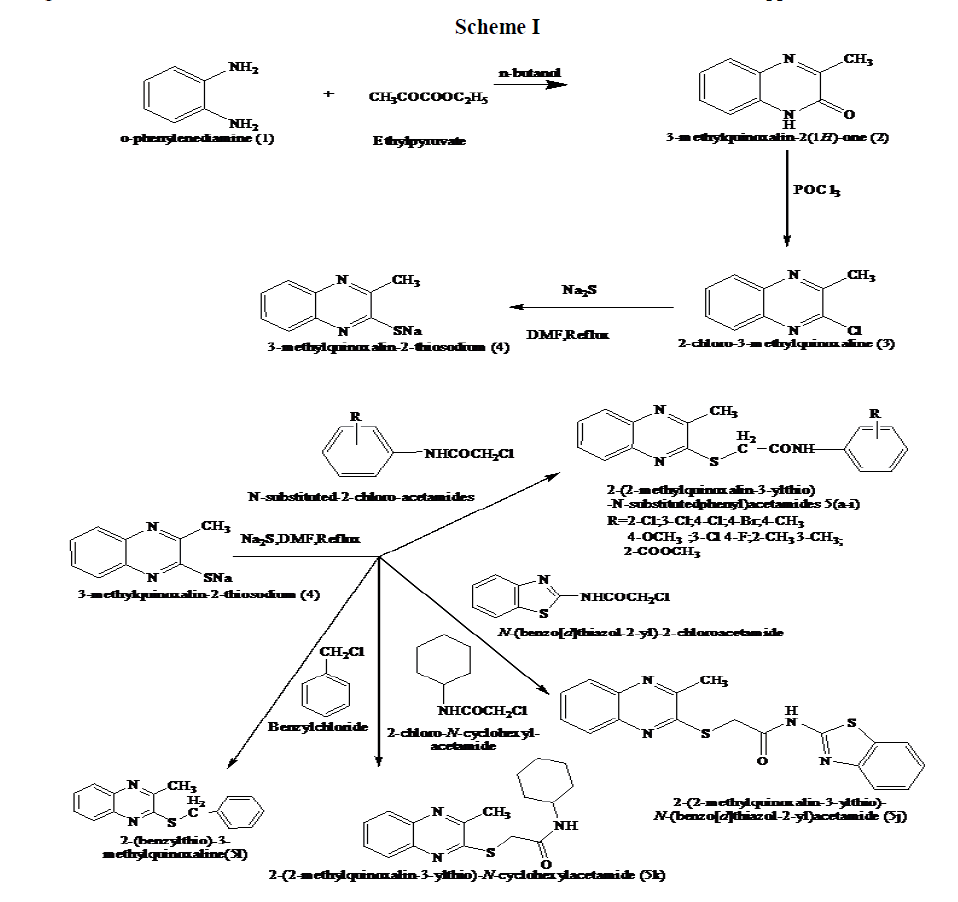
Scheme I
The melting points were determined in laboratory melting point apparatus using capillary method and are uncorrected. IR spectra were recorded in KBr disk on a Simadzu FTIR- 8400 spectrophotometer and 1HNMR spectra on JEOL FTNMR Spectrometer (300 MHz) using TMS as an internal standard. All chemical shift values were recorded as ä (ppm).
Anti inflammatory activity
Carrageenan induced rat paw edema method [13] was employed for screening of the anti inflammatory activity of the synthesized compounds.
Wistar rats of albino rats of either sex weighing 180- 250g were used for the experiments. They were housed in clean polypropylene cages and kept under room temperature (25± 2ºC) relative humidity 60-70% in a 12:12 hr natural light-dark cycle. The animals were given standard laboratory food and water. Food was withdrawn 12 hr before and during experimental hour.
The animals were divided in to several groups of six each. The control group received 2% gum acacia suspension orally, while the other groups received different drug treatment as detailed bellow. One hr after oral administration of the drug, acute inflammation was produced by sub plantar injection of 0.1 mL of 1% suspension of carrageenan with 2% gum acacia in normal saline, in the right hind paw of the rats. A mark was applied on the leg at the malleolus to facilitate subsequent readings. The paw volume was measured plythysmometrically at 30min, 1, 2, 3 and 4 hr after the injection of carrageenan. The % inhibition was calculated by applying
Newbould formula [14] - %Inhibition = (1-Vt/Vc) x100 Where Vt and Vc are the mean change in paw volume of treated and control rats respectively.
Statistical analysis
The results were expressed as mean ± SEM and were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Dunnett’s t-test .The probability of 0.05 or less was considered statistically significant.
The results of inflammatory activity are shown in the table1.
| Treatment |
Dose mg/Kg |
Mean changes in paw edema (ml) (Mean ± SEM)
(% Inhibition) |
| 30min |
1hr |
2hr |
3hr |
4hr |
| Group-I, Control(5% Acacia solution) |
- |
0.611±0.031 |
0.698±0.033 |
0.732±0.028 |
0.621±0.037 |
0.654±0.040 |
| Group-II, Standard (Indomethacin)p.o |
25 mg/kg |
0.264±0.012 (56.79) |
0.266±0.016 (61.89) |
0.267±0.017 (63.52) |
0.267±0.016 (57.00) |
0.268±0.017 (59.02) |
| Group-VII 5a |
100 mg/kg |
0.417±0.008 (31.75) |
0.424±0.008 (39.26) |
0.548±0.015 (25.14) |
0.451±0.019 (27.37) |
0.576±0.029 (11.93) |
| Group-VIII 5b |
100 mg/kg |
0.418±0.007 (31.59) |
0.424±0.008 (39.26) |
0.431±0.007 (41.12) |
0.372 ±0.007 (40.09) |
0.546±0.01 (16.51) |
| Group-IX 5c |
100 mg/kg |
0.469±0.012 (23.24) |
0.564±0.016 (19.18) |
0.568±0.012 (22.40) |
0.612±0.034 (1.45) |
0.602±0.037 (7.95) |
| Group-X 5d |
100 mg/kg |
0.465±0.008 (23.86) |
0.482±0.009 (30.95) |
0.579±0.008 (20.90) |
0.473±0.015 (23.83) |
0.418±0.024 (26.45) |
| Group-V 5e |
100 mg/kg |
0.430±0.014 (29.62) |
0.469±0.014 (32.81) |
0.541±0.023 (26.09) |
0.446±0.019 (28.34) |
0.701±0.017 (-) |
| Group-VI 5f |
100 mg/kg |
0.426±0.012 (30.28) |
0.558±0.014 (20.06) |
0.637±0.016 (12.99) |
0.697±0.013 (-) |
0.690±0.021 (-) |
| Group-XI 5g |
100 mg/kg |
0.483±0.006 (20.95) |
0.599±0.011 (14.18) |
0.593±0.021 (18.99) |
0.633±0.023 (30.27) |
0.680±0.024 (2.75) |
| Group-VI 5h |
100mg/kg |
0.555±0.019 (9.17) |
0.571±0.025 (18.19) |
0.659±0.024 (9.97) |
0.709±0.023 (-) |
0.744±0.025 (-) |
| Group-XII 5i |
100 mg/kg |
0.470±0.001 (23.08) |
0.485±0.005 (30.52) |
0.699±0.017 (4.51) |
0.707±0.015 (-) |
0.726±0.021 (-) |
| Group-XIII 5j |
100 mg/kg |
0.464±0.015 (24.06) |
0.505±0.022 (27.65) |
0.623±0.012 (14.89) |
0.623±0.015 (-) |
0.757±0.018 (-) |
| Group-XIV 5k |
100 mg/kg |
0.475±0.004 (22.26) |
0.487±0.008 (30.23) |
0.539±0.012 (26.37) |
0.466±0.007 (24.96) |
0.599±0.011 (. 8.41) |
| Group-III 5l |
100 mg/kg |
0.483±0.009 (20.95) |
0.574±0.091 (17.77) |
0.685±0.014 (6.42) |
0.682±0.011 (-) |
0.670±0.009 (-) |
Table 1. The results of inflammatory activity.
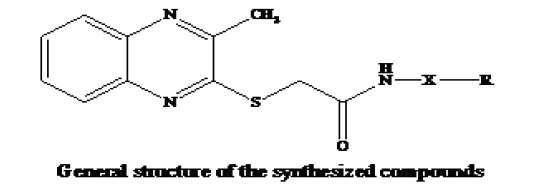
| Compounds |
X ; R |
Reaction Time |
M.P. (°C) |
Rf value |
| 5a. |
C6H4 ; 2-Cl |
6 Hr |
138 |
0.90 |
| 5b. |
C6H4 ; 3-Cl |
6 Hr |
109 |
0.83 |
| 5c. |
C6H4 ; 4-Cl |
6 Hr |
144-145 |
0.84 |
| 5d. |
C6H4 ; 4-Br |
6 Hr |
166-167 |
0.80 |
| 5e. |
C6H4 ; 4-CH3 |
5 Hr |
176 |
0.66 |
| 5f. |
C6H4 ; 4-OCH3 |
7 Hr |
160 |
0.79 |
| 5g. |
C6H3 ; 3-Cl, 4-F |
9 Hr |
159-160 |
0.81 |
| 5h. |
C6H3 ; 2- CH3 , 3-CH3 |
6 Hr |
182-183 |
0.78 |
| 5i |
C6H4 ; 2-COOCH3 |
6 Hr |
130 |
0.86 |
| 5j. |
 |
6 Hr |
180 |
0.57 |
| 5k. |
 |
6 Hr |
168-169 |
0.60 |
| 5l. |
R-X-NHCO = C6H5 |
2 Hr |
170-171 |
0.80 |
Physical data of compounds (5a-l) and structures are shown in the Table 2.
Physical data of compounds (5a-l) and structures are shown in the Table 2.
Result and Discussion
The attachment of various substituent groups in the synthesized compounds were also validated by their respective IR and 1HNMR spectra. The structures of all newly synthesized compounds were elucidated on the basis of their spectral and analytical data.
The anti-inflammatory activity of the compounds (5a-k) was evaluated by carrageenan induced rat paw edema method. The compounds were tested at 100 mg/kg dose and the results were compared with that of Indomethacin as a reference drug. The results are summarized in the table 1; suggest that the anti-inflammatory activity screening are in the range of 23.34 to 40.09% inhibition, whereas the standard drug Indomethacin showed an activity of 57% inhibition after 3 hrs. Among the compounds, screened for antiinflammatory activity, compounds 5a,5d,5e, and 5k are having moderate activity (23-28% inhibition) whereas the compound 5b,showed best anti-inflammatory activity (40.09% inhibition) and compound 5g showed good anti-inflammatory activity(30.27% inhibition).None of the compounds other than 5b(16.51) and 5d(26.47% inhibition) was found active after 4 hrs. It may be concluded that methyl (5e), chlorine (5a, 5b), bromine (5d), chlorine and fluorine (5g) substituted aromatic amines have enhancing effect on anti-inflammatory activity and in the case of compound(5k) the enhanced activity may be attributed due to presence of 2-aminobenzothiazole nucleus which is reported to have similar activity. Carrageenaninduced paw edema is believed to be biphasic and is commonly used to screen anti-inflammatory agents. The first phase is due to release of histamine or serotonin and the second phase is due to release of prostaglandin. Therefore, the anti-inflammatory activity of the synthesized compounds may be due to inhibition of histamine, serotonin or prostaglandin synthesis.
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to Director, college of pharmacy and Managing Director, I.F.T.M. Moradabad for providing research facilities. We extend our thanks to Director, National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms, National Chemical Laboratory, Pune for providing microbial strains.
Conflict of Interest: NIL Source of Support: NONE
5474
References
- Badran MM, Abonzid KA and Hussein MH: Synthesis of certain substituted quinoxalines as antimicrobials agents. Part II. Archibes of Pharmacal Research 2003; 26(2): 107-13.
- Griffith RK, Chittur SV and Chen YC: Inhibition of glucosamine-6-Phosphate synthase from candida albicans by quinoxaline-2, 3-diones. Medicinal Chemistry Research 1992; 2: 467-473.
- E-lGendy AA, El-Meligie S, El-Ansry A and Ahmedy AM:Synthesis of some quinoxaline derivatives containing Indoline-2,3-dione or, thiazolidine residue as potential antimicrobials agents. Archibes of Pharmacal Research 1995; 18: 44-47.
- Reddy-Sastry CV, Shrinivas-Rao K, Krishanan VSH, Rastogi K, Jain ML and Narayanan GKASS: Synthesis and biological activity of some new tetrazolobenzoxazines as bis-tetrazoloquinoxalines Indian Jouranal of Chemistry 1990; 29B:396-403.
- El-Hawash SA, Habib NS and Franki NH: Synthesis and antimicrobial testing of 1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a] quinoxalines,1,2,4-triazino[4,3- a] quinoxalines and 2-pyrazolylquinoxalines. Pharmazil 1990; 34(11): 808-815.
- Westphal G, Wasiki H, Zielinski U ,Weberr FG, Tonew M and Tonew E: Potentielle virostatica.Pharmazie 1977; 32: 570-571.
- Monge A, Martinez-Crespo FJ, Cerai AL, Palop JA, Narro S, Senador V, Marin A, Sainz,Y, Gonzalez M, Hamilton E and Barker AJ: Hypoxia selective agents derived from 2-quinoxalinecarbonitrile 1,2-di-N- oxides. Jouranal of Medicinal Chemistry 1995; 38: 4488-4495.
- Michael JW, Taibi Ben-Hadda, Ann TK, Ramdani A, Touzani R, Elkadiri S, Hakkou A, Boukka M and Elli T: 2,3-Bifunctionalized Quinoxalines: Synthesis, DNA Interactions and Evaluation of Anticancer, Anti- tuberculosis and Antifungal Activity Molecule 2002; 7: 641.
- Rangisetty JB, Gupta CNVHB, Prasad AL, Srinavas P, Sridhar N, Perimoo, P and Veeranjaneyulu, A: Synthesis of new arylaminoquinoxalines and their antimalarial activity in mice Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2001; 53(10): 1409-1413.
- Wagle S, Adhikari AV and Kumari NS: Synthesis of some new 2-(3-methyl-7- substituted-2- oxoquinoxalinyl)-5-(aryl)-1,3,4-oxadiazolesas potential non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Indian journal of chemistry 2008; 47B: 439-448.
- Silvia Schenone , Olga Bruno, Angelo Ranise, Francesco Bondavalli, Walter Filippelli, Francesca Rossi and Giuseppe Falcone: Synthesis and anti- inflammatory activity of esters derived from 5-aryl- 1,2-dihydro-2-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3- thiones. IIFarmaco 1998; 53(8-9): 590-593.
- Gulerman NN, Doan HN, Rollas S, Johnsson C and Colik C : Synthesis and structure elucidation of some new thioether derivatives of 1,2,4-triazoline-3-thiones and their antimicrobial activities, II Farmaco1998; 53(8-9): 590-593.
- Winter, CA, Risley, EA and Nuss, GA, Proc Sos Exptl Biol,1962,3,544.Newbould, BB. Brit J Pharmacol. 1963, 21,157