Key words
|
| |
| Averrhoa bilimbi, pharmacology, antioxidant, antidiabetic, antimicrobial activi |
| |
Introduction: 1-10
|
| |
| Plants provide wealth of bioactive compounds. They are the main source of drugs that being used from the ancient times as herbal remedies for the health care, prevention and cure of various diseases and ailments .1 Many Indian Plants are used therapeutically for their antidiabetic effect 2 ,antihyperlipidemic activity 3and antibacterial activities. 3 |
| |
| Averrhoa bilimbi (Bilimbi) is medicinally used as a folk remedy for many symptoms. It is used as antibacterial, antiscorbutic, astringent; post–partum protective medicine. It is also used for the treatment of fever, mumps, pimples, inflammation of the rectum and diabetes, itches, boils, rheumatism, syphilis, bilious colic, whooping cough, hypertension, stomach ache, aphthous ulcer and as a cooling drink.5,6 |
| |
| Averrhoa bilimbi fruits have medicinal properties for the effective management of several human ailments7 .Different parts of the plant is used for various conditions. The fruit conserve is administered as a treatment for coughs, beri-beri and biliousness. Syrup prepared from the fruit is taken as a cure for fever and inflammation and to stop rectal bleeding and alleviate internal hemorrhoids. The leaves are applied as a paste or poulticed on itches, swellings of mumps and rheumatism, and on skin eruption. They are applied on bites of poisonous creatures. Malaysians take the leaves fresh or fermented as a treatment for venereal disease. A leaf infusion is a remedy for coughs and is taken after childbirth as a tonic. A leaf decoction is taken to relieve rectal inflammation. A flower infusion is said to be effective against coughs and thrush. In Java, the fruits combined with pepper are eaten to cause sweating when people are feeling "under the weather". A paste of pickled bilimbi is smeared all over the body to hasten recovery after a fever. |
| |
| Very acidic fruits are employed to clean the blade of a kris (dagger), and they serve as mordants in the preparation of an orange dye for silk fabrics. Because of its oxalic acid content, fruit juice is useful for bleaching stains from the hands and rust from white cloth, and also tarnishes from brass. 8 |
| |
| In some villages in India, the fruit of the bilimbi was used in folk medicine to control obesity. This led to further studies on its Antihyperlipidemic properties.9,10 In this review article , we have compiled all possible aspects of A.bilimbi Linn and its potential pharmacological uses as evidenced by the experimental studies conducted by different researchers. |
| |
| Scientific classification: |
| |
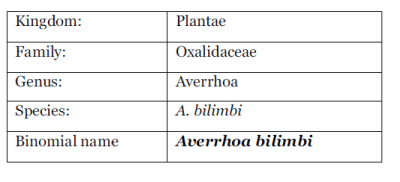 |
| |
|
Other names: 11
|
| |
| Averrhoa obtusangula stokes, Belimbing asam, Belimbing buluh, Belimbing wuluh, Kamias, kalamias, Iba, kolonanas, Ta-ling-pring |
| |
|
Common names:
|
| |
| Creole : bimbling plum, blimblin |
| |
| English : bilimbi, cucumber tree, tree sorrel |
| |
| Filipino : kamias |
| |
| French: blimblim, blinblin, carambolier bilimbi,cornichon des Indes, zibeline, zibeline blonde Indonesian: belimbing asam, belimbing wuluh |
| |
| Khmer : tralong tong |
| |
| Malay : belimbing asam, belimbing buloh, billingbilling, b'ling |
| |
| Spanish: grosella china, mimbro, pepino de Indias, tiriguro, vinagrillo |
| |
| Thai : kaling pring, taling pling |
| |
|
Botanical Description: 5,8,9
|
| |
| Averrhoa bilimbi (Oxalidaceae family) commonly known as bilimbi, is an attractive, long-lived tropical tree, reaching 5-10 m in height; has a short trunk soon dividing into a number of upright branches. The wood is white, soft but tough, even-grained, and is seldom available for carpentry. Leaves mainly clustered at the branch tips, are alternate, imparipinnate;30-60 cm long, with 11-37 alternate or sub opposite leaflets, ovate or oblong, with rounded base and pointed tip; downy; medium-green on the upper surface, pale on the underside; 2-10 cm long, 1.2-1.25 cm wide. Flowers small, fragrant, auxiliary or cauliflorous, 5-petalled, yellowish green or purplish marked with dark-purple, 10-22 mm long, borne in small, hairy panicles emerging directly from the trunk and oldest, thickest branches and some twigs, as do the clusters of curious fruits. Fruit ellipsoid, obovoid or nearly cylindrical, faintly 5-sided, 4-10 cm long; capped by a thin, star-shaped calyx at the stemend and tipped with 5 hair like floral remnants at the apex. Crispy when unripe, the fruit turns from bright green to yellowish-green, ivory or nearly white when ripe and falls to the ground. The outer skin is glossy, very thin, soft and tender, and the flesh green, jellylike, juicy and extremely acid. There may be a few 6-7 flattened, disc-like seeds, 6 mm wide, smooth, brown. |
| |
|
Natural Habitat: 12
|
| |
| A. bilimbi is a tropical tree, more sensitive to cold especially when very young. It prefers direct sunlight and seasonally humid climates, with evenly distributed rainfall throughout most of the year but there should be a 2-3 month dry season. |
| |
|
History of cultivation
|
| |
| Perhaps a native of the Moluccas. In 1793, it was carried from the island of Timor to Jamaica and, after some years, was planted in Cuba and Puerto Rico, Trinidad, the lowlands of Central America, Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Surinam, Guyana and Brazil, and even in northern Argentina and in Hawaii. It is introduced into Queensland around 1896, it was readily adopted and commercially distributed to growers. |
| |
|
Geographic distribution
|
| |
| Native:Indonesia,Malaysia |
| |
| Exotic : Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Colombia, Cuba, Ecuador, Guyana, India, Jamaica, Myanmar, Philippines, Puerto Rico, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Surinam, Tanzania, Thailand, Trinidad and Tobago, United States of America, Venezuela |
| |
|
Biophysical limits
|
| |
| Bilimbi shows optimum growth in rich, moist, slightly acidic and well-drained soil. It also grows and fruits quite well on sand or limestone. |
| |
|
Reproductive Biology
|
| |
| Bilimbi begins to flower around February and then blooms and fruits more or less continuously until December. |
| |
| Parts used: Leaves, Flower, Fruits |
| |
|
Phytochemical constituents: 5,7,9
|
| |
| The fruit extracts contain flavonoids, saponins and triterpenoid. |
| |
| The chemical constituents of A. bilimbi include |
| |
| • Amino acids, |
| |
| • citric acid, |
| |
| • cyanidin–3–O–h–D–glucoside, |
| |
| • phenolics, potassium ion, sugars , |
| |
| • vitamin A. |
| |
|
Nutrition in Bilimbi 13
|
| |
| Bilimbi is a nutrition-packed, starchy fruit that grows mostly on the trunk of tall trees. It is a rich source of Vitamin C. Other than the vitamins and minerals, the fruit also consists of fibre, ash, protein and moisture as well as minerals. |
| |
|
Pharmacological Activity:
|
| |
|
Anti-diabetic activity: 5, 14-18
|
| |
| Benny et al has investigated the hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activity of the semi-purified fractions of an ethanolic leaf extract of Averrhoa bilimbi (ABe) in high fat diet (HFD)-streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. The long term administration of aqueous fraction (AF) at a dose of 125 mg/kg significantly lowered blood glucose and triglyceride concentrations when compared to the vehicle. The hepatic glycogen content was significantly higher in AF-treated rats when compared to diabetic control. They found better amelioration of hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in HFD fed-STZ diabetic rats by the aqueous fraction of leaf extract. Hence they have proposed AF as a potential source for the isolation of active principles for oral anti-diabetic therapy |
| |
| Pushparaj et al has investigated the hypoglycemic activity of an ethanolic extract of Averrhoa bilimbi Linn. leaves in streptozotocin (STZ)-diabetic rats.16 The optimal hypoglycemic dose (125 mg kg-1) was determined by performing the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in both normal and STZ-diabetic rats. |
| |
| They have investigated the effect of repeated administration of ethanolic extract of Averrhoa bilimbi (ABe) leaves, by administering the diabetic rats with vehicle (distilled water), ABe (125 mg kg-1) and metformin (500 mg kg-1) twice a day for 2 weeks and concluded that, like metformin, ABe significantly lowered blood glucose by 50% and thus it has good hypoglycemic activity in STZ-diabetic rats. |
| |
|
Antihyperlipidaemic Activity: 10,15,16
|
| |
| Ambili et al have studied the antihyperlipidaemic properties of Averrhoa bilimbi fruit using Tritoninduced hypercholesterolemia in rats as a model. The fruit and its water extract showed remarkable antihypercholesterolemic activity. An active fraction, which showed activity at a low dose of 0.8 mg/kg, was purified from the water extract. An active component was isolated from the active fraction, which showed optimum activity at a dose of 0.3 mg/kg. The efficacy of the fruit was tested in chronic high-fat diet fed hyperlipidemic rats. The fruit (125 mg/kg) as well as its water extract (50 mg/kg) were found to be effective in lowering lipids in the high-fat diet fed rats. Thus, they have concluded this fruit can be used as a dietary ingredient to prevent as well as treat hyperlipidemia. Puspraj et al also studied the lipid profile in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats and found to be effective .The ethanolic extract of A.bilimbi fruit has significantly increased the antiatherogenic index and HDL-cholesterol/total cholesterol ratio. It also significantly reduced the kidney lipid peroxidation level. Their study showed hypotriglyceridemic, anti-lipid peroxidative and antiatherogenic properties in STZ-diabetic rats.15 |
| |
|
Antimicrobial Activity: 7
|
| |
| A. bilimbi fruits possess potential antibacterial activity. Nurul Huda et al extracted the fruits with hexane, chloroform and methanol. They have subjected all fractions for the the phytochemical screening and antimicrobial activity against grampositive and gram-negative bacteria using discdiffusion method. The chloroform and methanol fruits extract were active on Aeromonas hydrophila, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Saccharimyces cerevisiae, Straphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae and Bacillus subtilis. Their study revealed that the fruit extracts have good inhibitory activity against the tested pathogens compared with the standard antibiotic, streptomycin. |
| |
|
Toxicity studies: 10
|
| |
| Savithri et al has studied the preliminary general toxicity of A. bilimbi fruit in mice. Oral administration of the fruit homogenate daily for 15 days did not result in any toxic symptoms up to a dose of 1 g/kg. |
| |
Conclusion
|
| |
| As the prevalence of obesity and Diabetes mellitus are very common in our society, research on plants with antidiabetic and antihyperlipidaemic action has great value in modern therapeutics. The data compiled shows that, Averrhoa bilimbi is a potent herb for future research since it has antidiabetic and antihyperlipidaemic and antibacterial properties as evidenced by the current research on the various plant parts. For optimum effect in patients, the components responsible should be isolated, purified and further clinical trials has to be conducted. |
| |
Acknowledgment
|
| |
| The authors are grateful to the authors/editors of all those articles, journals and books from where the data for this article has been reviewed and discussed. |
| |
Conflict of Interest
|
| |
| NIL |
| |
Source of Support
|
| |
| NONE |
| |
Tables at a glance
|
 |
 |
| Table 1 |
Table 2 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
|
| |