Floros N, Schelzig H and Oberhuber A*
Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, University of Duesseldorf, Germany
*Corresponding Author:
Alexander Oberhuber
Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
University of Duesseldorf, Moorenstraße 5
40225 Duesseldorf, Germany.
Tel: 0211/81-19679
Fax: 0211/81-19091
E-mail: Alexander.Oberhuber@med.uniduesseldorf. de
Received Date: October 14, 2016; Accepted Date: October 17, 2016; Published Date: October 19, 2016
Citation: Floros N, Schelzig H, Oberhuber A. Collapsed Thoracic Stent Graft After Traumatic Aortic Rupture. Ann Clin Lab Res. 2016, 4:4 doi: 10.21767/2386-5180.1000127
The number of endovascular interventions of the thoracic aorta is rapidly increasing, due to reduced morbidity and mortality. In the majority of cases the interventions can be carried out safely. Major endovascular related complications are retrograde aortic dissections, stroke and paraplegia, vascular injuries and stent graft collapse as well.
Case Blog
The number of endovascular interventions of the thoracic aorta is rapidly increasing, due to reduced morbidity and mortality. In the majority of cases the interventions can be carried out safely. Major endovascular related complications are retrograde aortic dissections, stroke and paraplegia, vascular injuries and stent graft collapse as well [1].
An aortic stent graft collapse can affect the whole diameter of the graft at a high anatomical level of the aorta or only partly, followed by hypoperfusion of the visceral and renal arteries. The incidence of stent graft collapse in TEVAR varies from 1% to 19% [2,3]. In most cases the collapsing stent graft can be repaired endovascularly.
We describe the endovascular repair of an aortic rupture with a 28 × 150 mm Gore TAG endoprosthesis (W.L. Gore and Associates, Flagstaff, Ariz, USA) in a 24 mm aorta of a 57-yearold man. On postoperative day 43 a complete aortic obstruction, caused by the collapse of the stent grafts lumen, was diagnosed. Restoration of blood flow was attempted by balloon moulding. After the initially successful balloon dilatation a recollapse of the stent graft was seen in the transesophageal echocardiography (Figures 1-3 and videos 1-3). The recollapse was then managed with a second stent graft. No further adverse event was seen in the postoperative course.
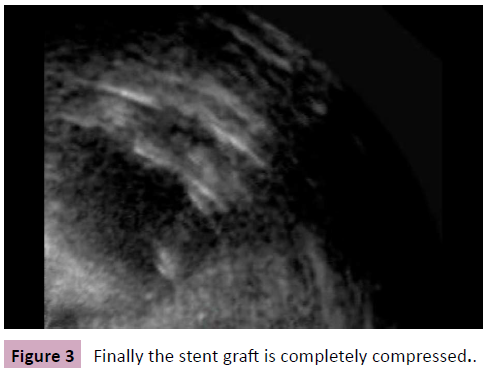
Figure 1: The transesophageal echocardiography shows the complete expansion of the stent graft, but a slight compression during the systole.
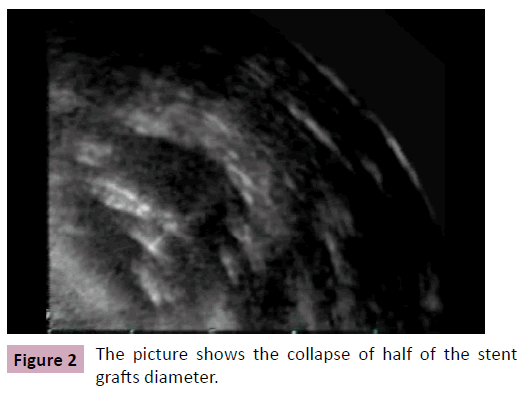
Figure 2: The picture shows the collapse of half of the stent grafts diameter.
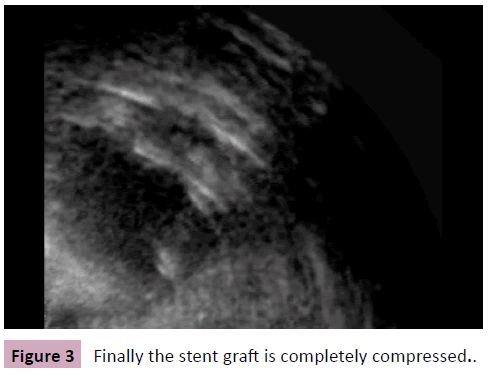
Figure 3: Finally the stent graft is completely compressed.

Video 1: After balloon moulding the stent graft is re-expanded, but shows a pulse synchronic compression of the lumen.

Video 2: Only a few seconds later the stent graft undergoes a re-collapse with the compression of nearly half of the diameter.

Video 3: Finally the stent grafts lumen is completely collapsed with the following occlusion of the aorta.
17262
References
- Bischoff G, Orend KH (2015) Traumatic vascular injuries. Vascular Surgery 20: 225-242.
- Oberhuber A, Erhard L, Orend KH, Sunder-Plassmann L (2010) Ten years of endovascular treatment of traumatic aortic transection: a single centre experience. ThoracCardiovasc Surg 58: 143-147.
- Tadros RO, Lipsitz EC, Chaer RA, Faries PL, Marin ML, et al. (2011) A multicenter experience of the management of collapsed thoracic endografts. J Vasc Surg 53:1217-1222.