Keywords
Aslantas Dam Lake, Rotifera, Chlorophyll a
Introduction
It is a well-established fact that phytoplankton is the base of food chain pyramid in the aquatic environments such as lakes. Zooplankton, following phytoplankton, is the second most important ring of the pyramid of aquatic ecosystems for energy conversion and as food resources. Therefore the importance of zooplankton for fish production and fisheries is obvious. At the same time, many scientists indicated that certain species of rotifers are indicators showing water quality, pollution and eutrophication. (Berzins, 1987; Mikschi, 1993; Saksena, 1987; Sharma, 1983).
This paper presents an analysis of rotifer abundance in Aslantas Dam Lake which is one of the most important freshwater resources of south eastern Mediterranean region of Turkey. There have been no previous rotifer studies undertaken for this lake. The dam was established over the River Ceyhan at 45 km up from Mediterranean Sea for flood prevention, irrigation and hydro electric energy production in 1985. The dam is situated 146 m above the sea level and covers an area of 6.050 ha. Maximum measurements of width and length are 6 km and 16 km, respectively, and the deepest place in the lake measures 93 m (DS?, 1966).
Besides agriculture, fish such as Cyprinus carpio, Silurus glanis, Capoeta sp., Barbus sp., Leiciscus cephalus and Alburnus orentis are providing an important economical benefit for the local people although the dam was built for irrigation purposes DS?, 2000).
Materials and Methods
The abundance of rotifer fauna in Aslantas Dam Lake was observed between March 2001 and April 2002 using 5 stations for sampling (Figure 1). Sampling was made in monthly intervals except December due to bad weather conditions. Besides, dissolved oxygen analyses of water in April and May were not recorded caused by oxygen meter malfunction.
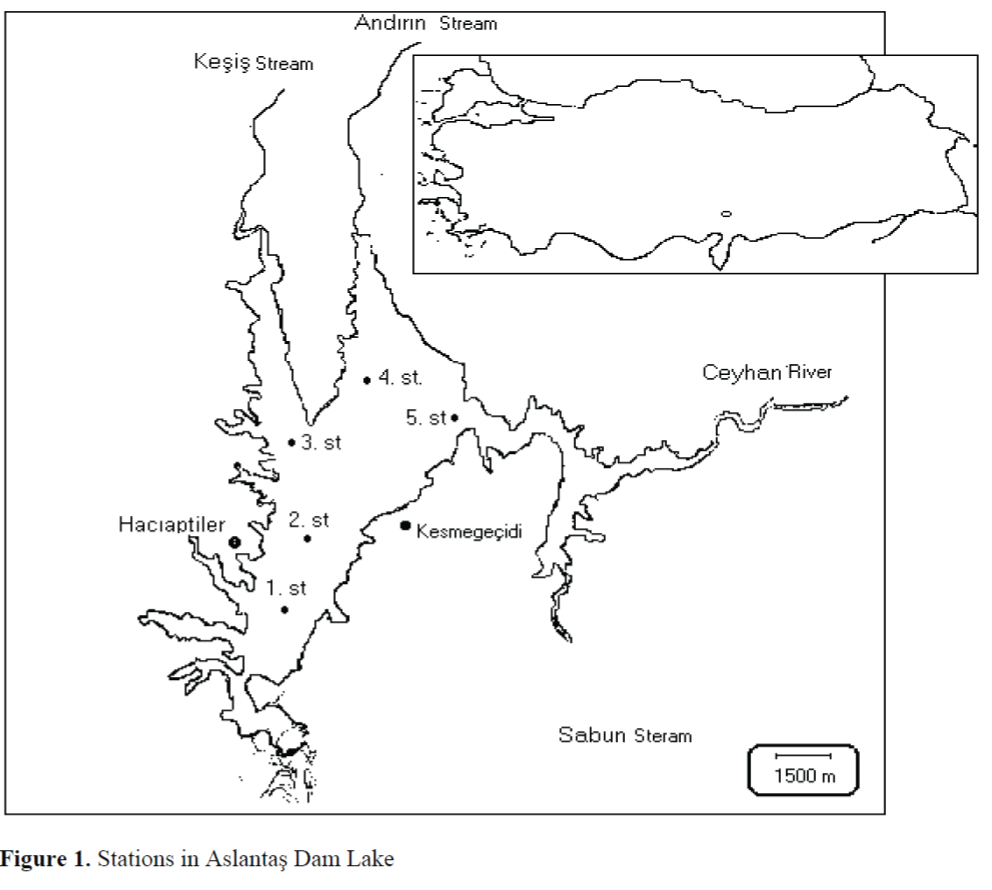
Figure 1. Stations in Aslantas Dam Lake
Rotifer samples were collected using horizontal plankton net with 60 μm mesh, 1 m length and 30 cm in diameter, and standard Hydrobiyos brand vertical plankton net with 60 μm mesh, and the samples were collected from the surface and different depths in all stations. Water sampling was made using Nansen bottle and the samples were taken from the surface in all stations except Station 1 and Station 2, where sampling was extended to 50 m depth by taking samples from 0.0- 1.0-2.5-5.0-7.5-10.0-15.0-20.0-30.0-40.0-50.0 m depths.
Parameters such as dissolved oxygen (DO), temperature, pH, light penetration measurements were recorded during sampling time at study area. Additionally, the depth of photic zone (light penetration zone) at stations 1 and 2 was determinedby multiplying the depth of Secchi disk with 2.7 (Cole, 1983; Moss, 1988). Chlorophyll-a was analyzed using the method described by APHA, (1995).
The samples, collected with nets and preserved in 4% formaldehyde, were used for qualitative analyses (classification) of rotifer (Dussart, 1969; Voigt and Koste, 1978; Stemberger, 1979; Tsalolikhin, 1994; Tsalolikhin, 1995). Quantitative analyses was carried out following filtration of 5 L water trough 60 μm meshes and preserving the results in 4% formaldehyde.
Results and Discussion
The analyses and observations revealed the following results for physico-chemical parameters shown in Table 1.
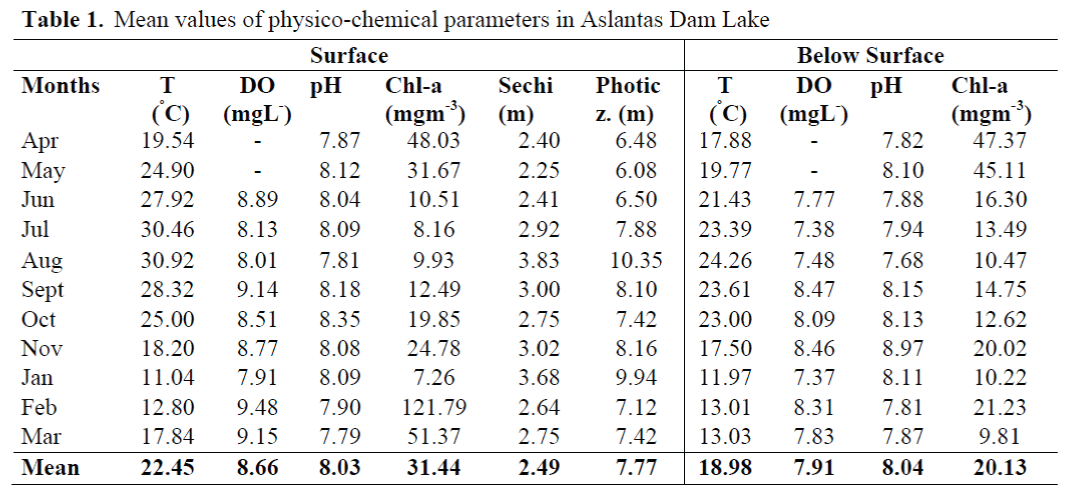
Table 1. Mean values of physico-chemical parameters in Aslantas Dam Lake
Maximum temperatures were measured in August as 30.92ºC, whereas minimum temperatures were reached in January as 11.04ºC.
The level of DO was maximum (9.48 mgL-1) in February and minimum (7.37 mgL-1) in January. The highest pH was 8.97 in November while it was the lowest with 7.68 in August.
Chlorophyll a at surface reached the highest level with 121,79 mgm-3 in February, and the level found out to be the lowest in January with 7.26 mgm-3.
The last parameter, light penetration found to be maximum in August (3.83 m) and minimum in May (2.25 m). Consequently, the range of photic zone was determined to be the largest in August it was determined that the range of photic zone extended to maximum 10.35 m in August and minimum 6.08m in May. Additionally, vertical average values physico-chemical parameters was presented.
The maximum values of the parameters were observed in different depth i.e. temperature (22.40°C) at 1 m, DO (8.58 mgL-1) at surface, pH (8.07) at 5 m, and chlorophyll a (34.51 mgm-3) at 7.5 m. However the minimum values were observed at the depths below 30 m, It was 12.10°C at 35 m, 6.01 mgL-1 at 32 m, 7.59 at 50 m and 2.22 mgm-3 at 32 m, respectively (Table 2).
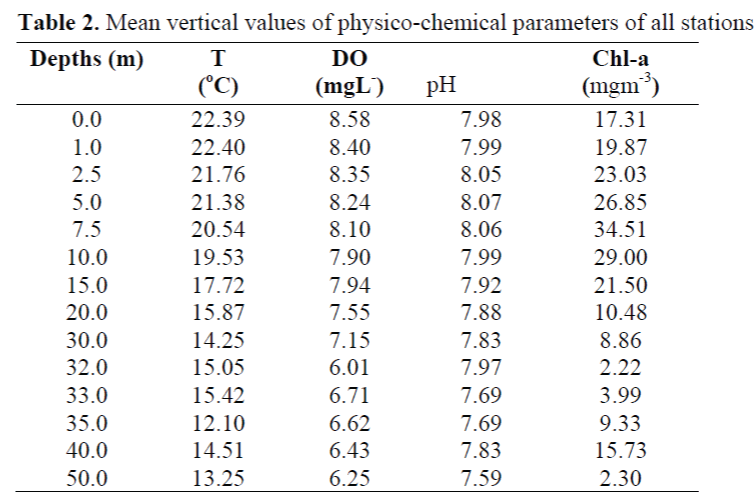
Table 2. Mean vertical values of physico-chemical parameters of all stations
Taxonomy
As result of this study, it was determined that rotifers in Aslantas Dam Lake are represented with 33 species and 2 subspecies (Table 3). They belong to 15 families in which the number of genus is 21. Determined fauna is listed below according to classification by Wallace and Snell (1991).
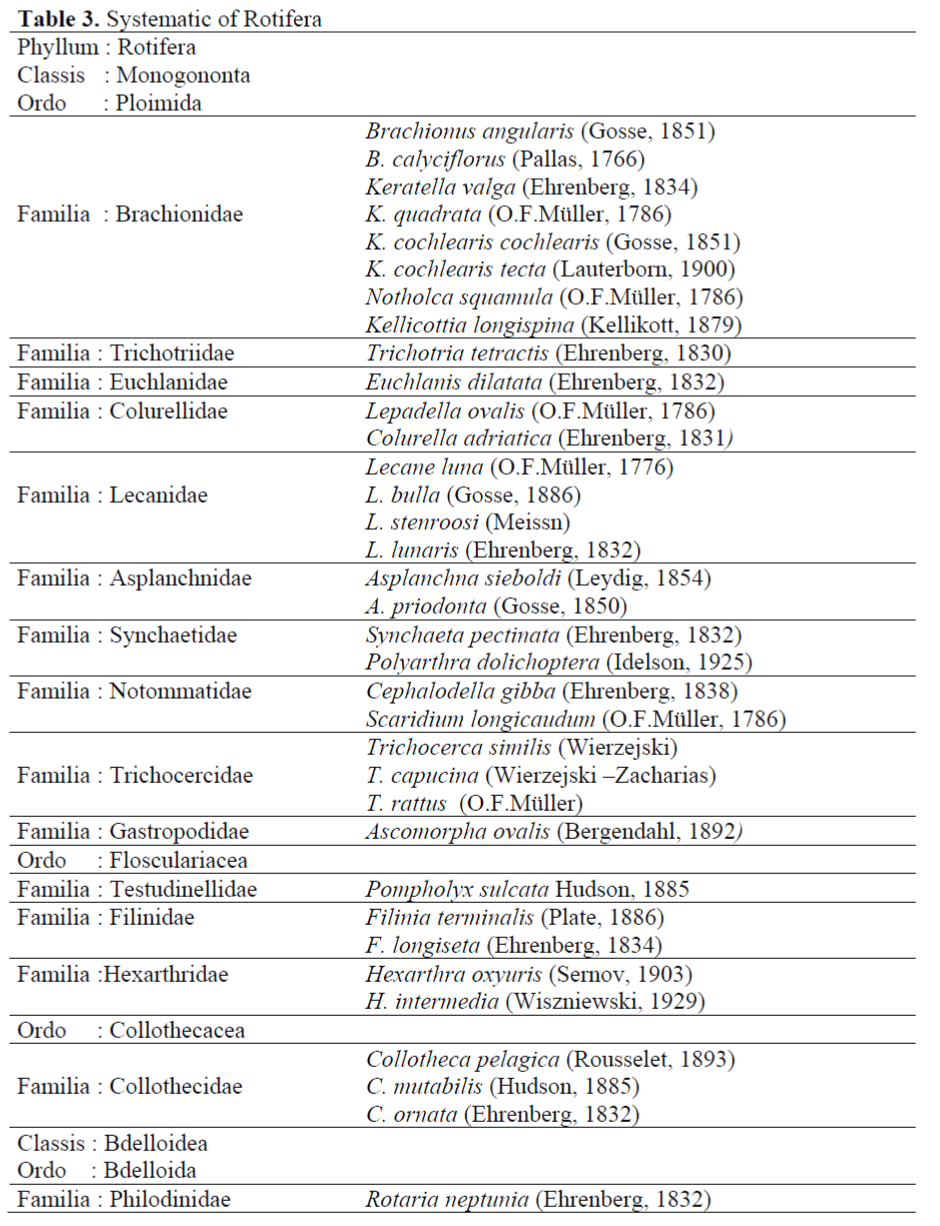
Table 3. Systematic of Rotifera
Monthly distribution
The monthly presence of determined rotifers at surface and below surface was tabulated in Table 4.
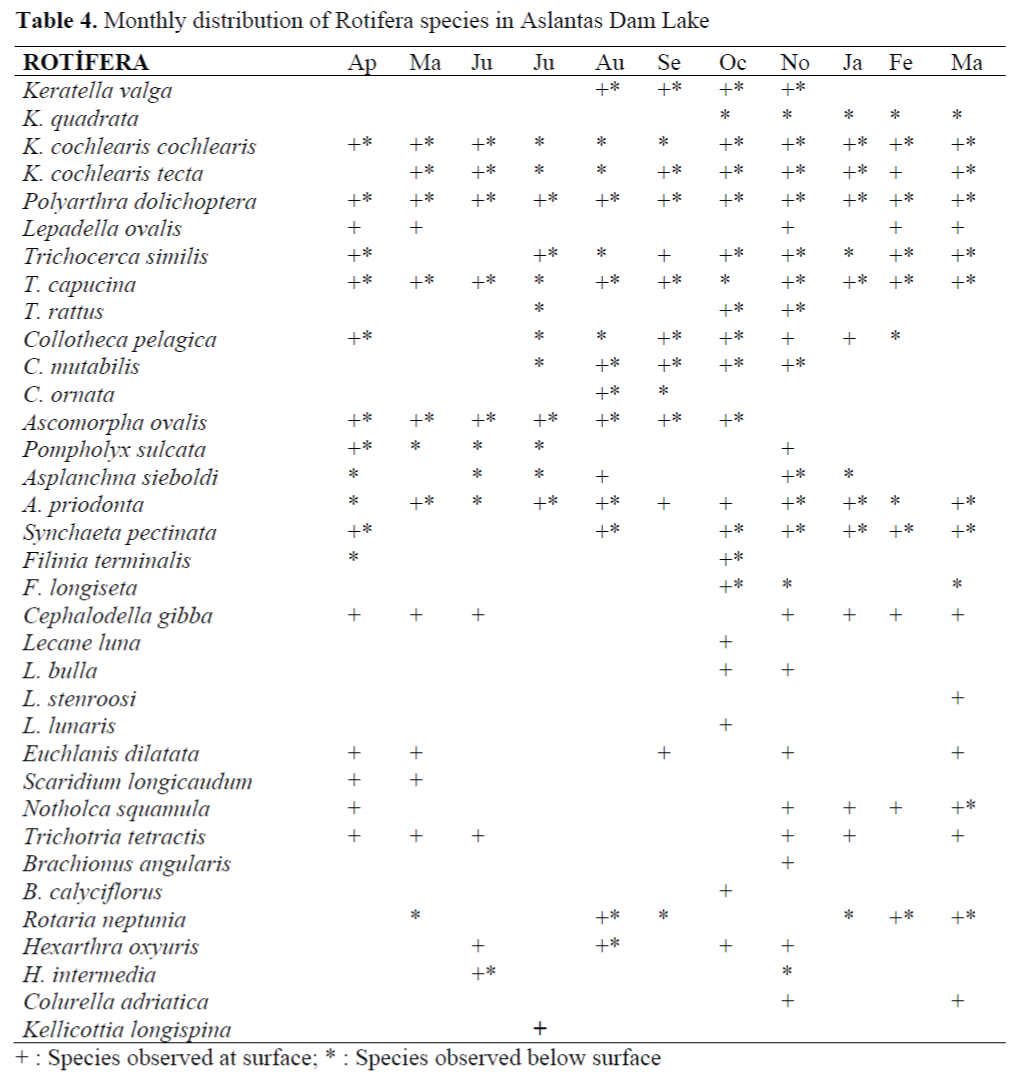
Table 4. Monthly distribution of Rotifera species in Aslantas Dam Lake
Some species such as K. cochlearis cochlearis, Polyarthra dolichoptera, Asplanchna priodonta and Trichocerca capucina were present in the lake throughout the year. Some others such as K. cochlearis tecta, Trichocerca similis, Collotheca pelagica, Synchaeta pectinata, C. gibba were observed most of the year. The rest of the representatives of Rotifera were observed for a period of 6 month or less. It was also determined that some species showed tendency to live at surface, for example, Lepadella ovalis, Lecane luna, L. stenroosi, L. lunaris, L. Bulla, Cephalodella gibba, Euchlanis dilatata, Scaridium longicaudum, Trichotria tetractis, Brachionus angularis, B. calyciflorus, Colurella adriatica and Kellicottia longispina. The species living below the surface only was Keratella quadrata.
The monthly distribution of total Rotifera has been shown in Figure 2. The figure shows that rotifer abundance was the most at surface in August whereas it was March below surface. Rotifers were at the least abundant level in May both surface and below surface.
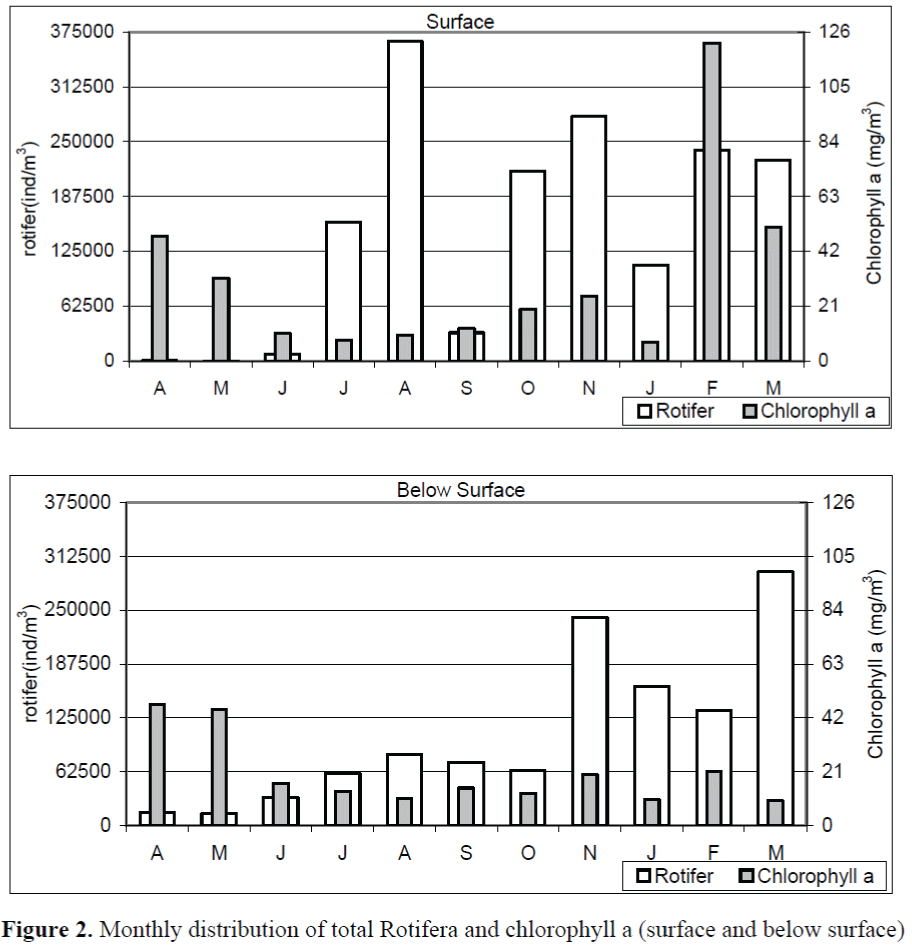
Figure 2. Monthly distribution of total Rotifera and chlorophyll a (surface and below surface)
Vertical distribution
Vertical distribution of total Rotifera has shown in Figure 3. Rotifera were mainly distributed between 2.5 and 10 m. It was found out that the number of total Rotifera increased up to 5 m. There was a constant decrease up to 33 m from 5 m onwards. The number of total Rotifera was the least at 50 m.
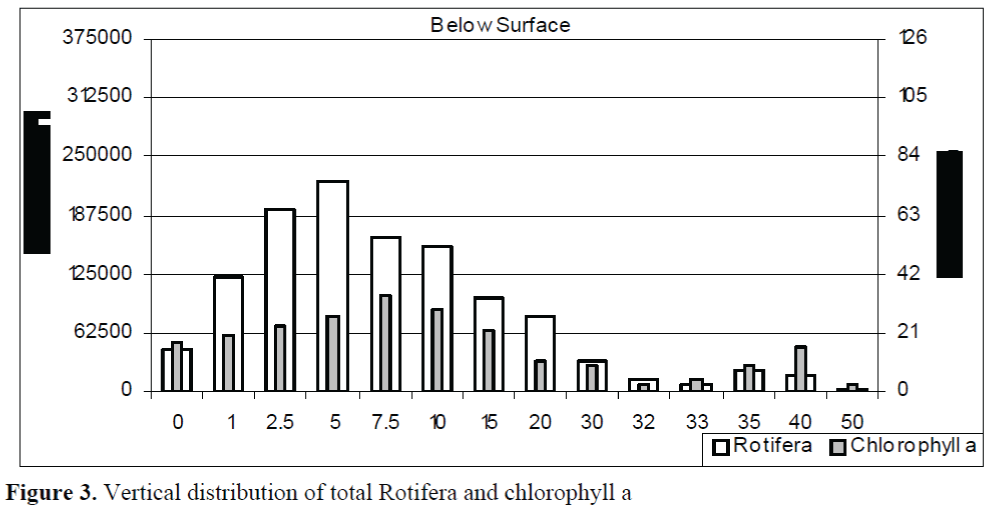
Figure 3. Vertical distribution of total Rotifera and chlorophyll a
Vertical distribution of species is such; the most abundant depth (5 m) occupied mostly by K. cochlearis cochlearis (102458 ind.m-3) and P. dolichoptera (62706 ind.m-3). Main species of the least abundant depth (50 m) were K. cochlearis tecta, T. capucina and Ascomorpha ovalis with a represantation number of 1901 ind m-3, 1098 ind m-3 and 394 ind m-3, respectively.
Light dependent distribution showed that 63.58% of Rotifera prefered to live in photic zone and remaining 36.42% was collected from aphotic zone (Figure 4).
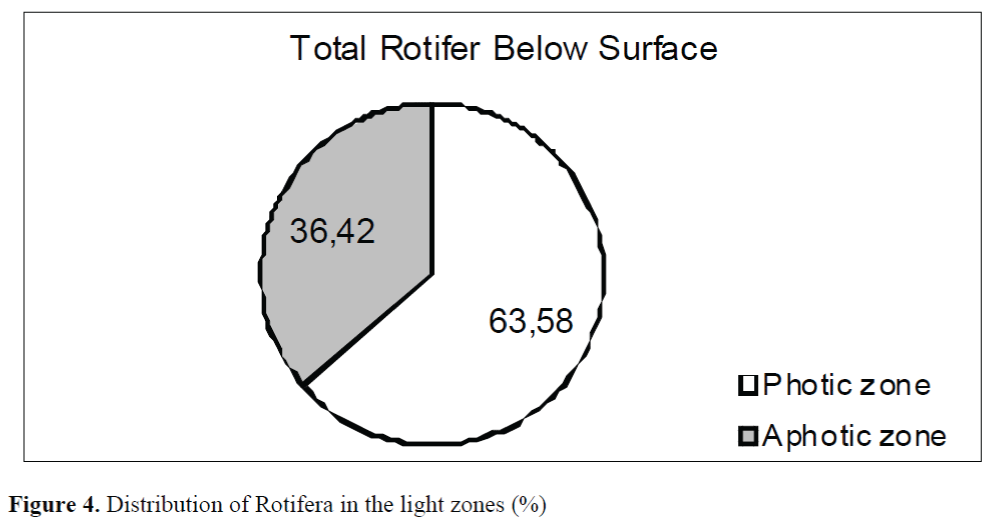
Figure 4. Distribution of Rotifera in the light zones (%)
Vertical Distribution of rotifer Species has shown in Table 5. The most abundant species, K. cochlearis cochlearis (102458 ind m-3) and P. dolichoptera (62706 ind m-3), were commonly found at 5 m depth.
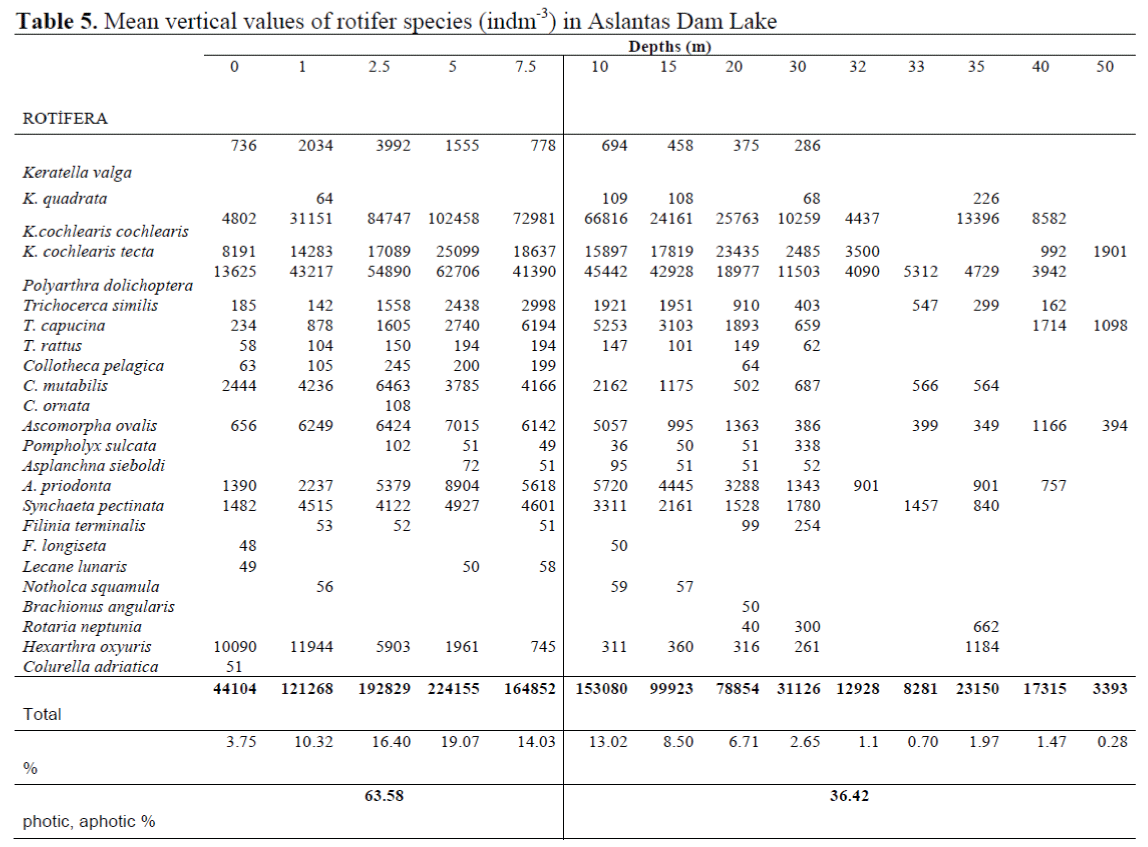
Table 5. Mean vertical values of rotifer species (indm-3) in Aslantas Dam Lake
Analyses revealed that 34.59% of rotifers at surface was P. dolichoptera (603107 ind m-3) and 29.29% of rotifers below surface was K. cochlearis cochlearis (449553 ind m-3). On the other hand the least abundant species at surface was Hexarthra intermedia which represented 0.01% of total Rotifera while there were two species namely B. angularis and C. adriatica, each of which representing only 0.003% of Rotifera below surface.
Rotifer-chlorophyll a interaction
Analyses between rotifer and chlorophyll a interaction monthly and vertically given in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively.
While the level of chlorophyll a decreased gradually from April to July at surface and from April to August below surface, a gradual increase at the number of rotifer was observed. Both the number of rotifer and the level of chlorophyll a has fluctuated independently from August onwards (Figure 1).
In consideration of vertical relation between the number of rotifers and the chlorophyll a level, both showed a gradual increase up 5 m. The number of rotifer reached to the highest number at 5 m whereas the level of chlorophyll a was the highest at 7.5 m. Both values reached to the lowest level at 50 m (Figure 2).
As a result of this study a total of 35 species of rotifer has been determined a first record for Aslantas Dam Lake. 33 of them are species and 2 of them are subspecies. Species of Hexarthridae two which determined in Aslantas Dam Lake, is reported to be likely inhabitants of freshwater (Demirhindi, 1972) and they are observed previously, 13 different resoirvuar in Turkey (Demirsoy, 1996). However Hexarthra oxyuris is reported to live in brackish and saline water (Dumont and Ridder, 1987; Ustao?lu and Akyürek, 1994; Brock and Sheel, 1983; Dumont, 1981). These reports show that species of Hexarthridae are mostly euryhaline.
Some of the species i.e., K. longispina, Lecane luna and Notholca squamula inhabits both freshwater and saline habitats. Lepadella ovalis prefers brackish waters and marshlands. Some species occur only a period of year. For example, Rotaria neptunia and B. angularis can be observed only in winter and spring. However, some others, e.g. C. gibba and A. priodonta can be found all year around (Saler and ?en, 2000). It is reported that B. calyciflorus can be found frequently in warm waters; Keratella quadrata lives in all waters as well as oligothrophic and eutrophic lakes (Emir, 1990); Mathew (1979) reports that Pompholyx sulcata is a winter species while Hexarthra intermedia is a hypertermic species. K. longispina is reported to be a hypothermic species (Primicerio and Klemetsen, 1999). This is also supported with the presence of the species in considerably cold water of Turkey such as Abant Lake, Yedigöller and Cip Dam Lake.
The presence of afore mentioned species in Aslantas Dam Lake are related with ecological requirements of these species. However, the presence of L. ovalis, a brackish water and marshland species, all year around and the presence of hypothermic K. longispina in July when Aslantas Dam Lake is not cold at all, is very interesting.
Analyses reveal that the rotifers are distributed abundantly near surface and the total number is the highest at 5 m (Figure 3). Previous reports on the depth dependent distribution of zooplankton claims that rotifers does not show orderly vertical taxis. Instead, most of them prefer proximities close to the surface although they are not likely to be at the surface. However, the number of rotifers decreases as the depth increases (Kolisko, 1974). Nevertheless there are examples of species i.e. Rotaria neptunia, found in depths (Ventela et. al., 1997). Dumont and Ridder (1987) reports that Hexarthra oxyuris shows distribution between 5-20 m we have obtained similar results with R. neptunia which was observed between 20-35 m. H. oxyuris was distributed up to 30 m and they were mostly abundant at 1 m as it is in line with the report of Kolisko (1974).
Kolisko (1974) claims that zooplankton such as rotifers densely, inhabit photic zone where there is an abundance of food as well. Therefore rotifers often do not migrate vertically. Similar findings were obtained as a result of this study. Most of the total Rotifera (63,58%) was collected from photic zone. The remaining 36,42% of Rotifera was obtained from aphotic zone.
Reporters agree that there is a close relation between phytoplankton and zooplankton as far as food chain is concerned. An increase in the number of zooplankton results in a consequential decrease in the number of phytoplankton. The number of zooplankton, usually, increases following the period of phytoplanktonic renewal and development (Cirik and Cirik, 1991; Kolisko, 1974; Horn and Goldman, 1994; Wu and Culver, 1991; Noges, 1997). We have similarly, shown that relatively low number of rotifer was observed while chlorophyll a were increasing gradually. In contrast, a low level of chlorophyll a was determined when the rotifer reached to their peaks. However, a deviation from the reports was observed when the relation between rotifers and chlorophyll a in depths is examined. We found that the number of rotifer decreased when the level of chlorophyll a decreased in depths and vice verse.
Brachionus calyciflorus, B. angularis, K. quadrata, K. cochlearis tecta, Euchlanis dilatata, L. luna, Pompholyx sulcata, Filinia longiseta are reported to be eutrophic species (Rylov, 1963; Borutski, 1963; Brooks, 1971; Voigt and Koste, 1978). However, Kolisko (1974) claims that most of these species inhabits oligotrophic lakes of temperate climates even though they are few in number (200-500 ind L-1). The value of chlorophyll a (31.44 mgm-3) confirms that Aslantas Dam Lake is characteristically not eutrophic.
Conclusions
In conclusion, rotifers in Aslantas Dam Lake are represented with 33 species and 2 subspecies. Some of rotifer species showed tendency to live at surface, for example, Lepadella ovalis, Lecane luna, L. stenroosi, L. lunaris, L. Bulla, Cephalodella gibba, Euchlanis dilatata, Scaridium longicaudum, Trichotria tetractis, Brachionus angularis, B. calyciflorus, Colurella adriatica and Kellicottia longispina. On the other hand, the species living below the surface only was Keratella quadrata. Rotifer species were mainly distributed between 2.5 and 10 m. It was found out that the number of total Rotifera increased up to 5 m. There was a constant decrease up to 33 m from 5 m onwards. The number of total Rotifera was the least at 50 m. Thus, it was found that more rotifer species preferred to live in photic zone (63.58%) and less of them preferred (36.42%) in aphotic zone.
1141
References
- APHA, (1995). Standart Methods for the Examinationnof Water and Waste Water, 19th Ed.nAmerican Public Health Association, Washington,nD.C. 1325
- nBerzins, B., (1987). Rotifer Occurrence in Relationnto pH, Hydrobiologia, 147: 107-116.ndoi: 10.1007/BF00025733
- nBorutski, E.V., (1963). Fauna of the USSR CrustaceanVol. III, No. 4 freshwater Harpacticoida.nJorusalem, 314
- nBrock, M.A., Shiel, R.J.,(1983). The compositionnof aquatic communities in saline wetlands innAvustralia. Hydrobiologia 105(1): 77-84.ndoi: 10.1007/BF00025178
- nBrooks, J.L., (1971). Eutrophication and changesnin the composition of the zooplankton. In eutrophication,ncauses, consequences, correctives.nNational Academic Science WashingtonnD.C. 236-255
- nCirik, S., Cirik, S., (1991). Limnoloji (Ders Kitabi).nEge Üniversitesi Su Ürünleri YüksekokulunYayinlari No: 21, Bornova-Izmir,n135
- nCole, G.A., (1983). Textbook of Limnology. ThenC.V. Mosby Company, London, 399
- nDemirhindi, Ü.,(1972). Türkiye’nin bazi lagün venacisu gölleri üzerinde ilk planktonik arastirmalar.nIstanbul Üniversitesi Fen FakültesinMecmuasi Seri B., 37(3-4): 205-232
- nDemirsoy, A., (1996). Genel ve Türkiye zoocografyasi,nhayvan cografyasi. Ankara, 630
- nDSI, (1966). Ceyhan Aslantas Projesi, AsaginCeyhan Gelistirilmesi Teknik ve EkonomiknFizibilite Raporu, Adana
- nDSI, (2000). Baliklandirma Çalisma Raporlari.nDSI Seyhan Su Ürünleri Arastirma ve ÜretimnIstasyonu (Basilmamis), Adana
- nDumont, H.J., (1981) , Kratergöl a Deep HypersalinenCrater –Lake in the Steppic Zone ofnWestern Anatolia (Türkey) ,Subject tonOccasional Limno-meterological Perturbations,nHydrobiologia, 82: 271-279. doi:n10.1007/BF00048721
- nDumont, H.J., Ridder, D. M., (1987). Rotifersnfrom Turkey. Hydrobiologia, 147: 65-73.ndoi : 10.1007/BF00025727
- nDussart, B., (1969). Les Copepodes des EauxnContinentales d’Europe Occidentale Tale II.nCyclopoides et Biologie. N.Boubee et Cie,nParis, 292
- nEmir, N., (1990). Samsun Bafra Gölü RotatorianFaunasinin Taksonomik Yönden Incelenmesi.nTurkish Journal of Zoology, 14(1): 89-n106
- nHorn, A.J., Goldman, C. R., (1994). Limnoloji.nMcGraw-Hill, inc. New York 576
- nKolisko, R.A., (1974). Plankton Rotifers Biologynand Taxonomy. Biological Station Lunz ofnthe Austrian Academy of Science, Stutgart,n146
- nMathev, P.M., (1979). Studies on the Zooplanktonnof a Tropical Lake Central Inland FisheriesnFauna. India
- nMikschi, E., (1973). Rotifer Distribution in Relationnto Temperature and Oxygen Content,nHydrobiologia, 186/187: 209-214
- nMoss, B., (1988). Ecology of fresh waters. Mannand medium. London: Blackwell Science,n417
- nNoges, T., (1997). Zooplankton-PhytoplanktonnInteractions in Lakes Vortsjarv, Peipsi (Estonia)nand Yaskhan (Turkmenia). Hydrobiologia,nBelgium, 342/343: 175-184
- nPrimicerio, R., Klemetsen, A., (1999). ZooplanktonnSeasonal Dynamics in the NeighbouringnLakes Takvatn and Lombola (NorthernnNorway). Hydrobiologia, Netherlands, 411:n19-29. doi: 10.1023/A:1003823200449
- nRylov, V.M., (1963). Fauna of USSR CrustaceanVol. III, No. 3, Freshwater Cyclopoida.nJorusalem 314
- nSaksena, N. D., (1987).Rotifera as indicators ofnwater quality. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica,n15: 481-485. doin:10.1002/aheh.19870150507
- nSaler, S., Sen, D., (2000). Cip Baraj Gölün(Elazig) Rotifera Faunasinin TaksonomiknYönden Incelenmesi. Firat Üniversitesi Fennve Mühendislik Bilimleri Dergisi, 12(1):n329-337
- nSharma, B. K., (1983).The Indian Species of ThenGenus Brachionus (Eurotatoria:nMonogononta: Brachionida) Hydrobiologia,n104: 31-39
- nStemberger, R.S., (1979). A Guide to Rotifers ofnthe Laurentian Great Lakes, EnvironmentalnMonitoring and Support Laboratory Officenof Research and Development, U.S. EnvironmentalnProtection Agency, EPA-600/4,n185
- nTsalolikhin, S.J., (1994). Key to Freshwater Invertebratesnof Russia and adjacent Lands. StnPetersburg, 395
- nTsalolikhin, S.J., (1995). Key to Freshwater Invertebratesnof Russia and adjacent Lands. StnPetersburg, 627
- nUstaoglu,M.R., Akyürek, M., (1994). AksehirnGölü Zooplanktonu. XII. Ulusal BiyolojinKongresi, Edirne
- nVentela, A. M., Saarikari, V., Vuorio, K., (1997).nVertical and Seasonal Distribution of Micro-nOrganisms, Zooplankton and Phytoplanktonnin a Eutrophic Lake. Laboratory of Ecologynand Animal Systematics, Hydrobiologia,n363: 229-240. doi:n10.1023/A:1003181923569
- nVoigt, M., Koste, W., (1978). Rotatoria. ÜberordnungnMonogononta. Berlin I. Textband,n650, II. Tafelband 234
- nWu, L., Culver, D.A., (1991). Zooplankton Grazingnand Phytoplankton Abundance. Journalnof Great Lakes Research, 17(4): 425-436.