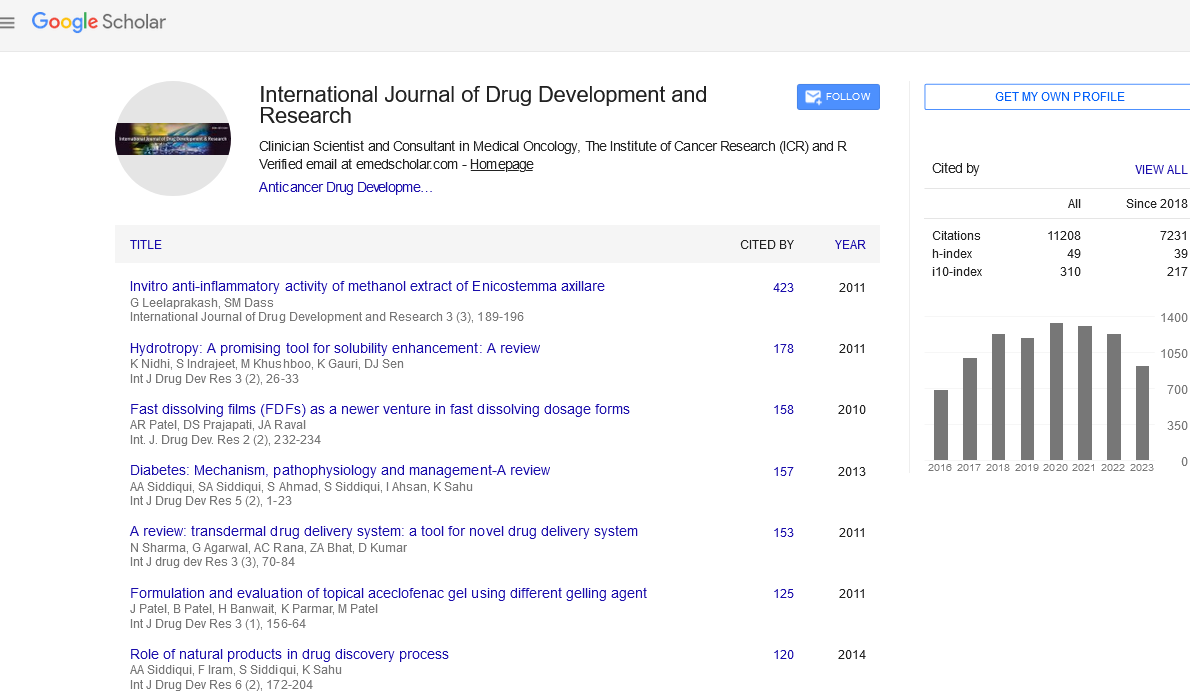
Prostaglandins are formed from arachidonic acid by the action of cyclooxygenase and subsequent downstream synthetases. Two closely related forms of the cyclooxygenase have been identified which are now known as COX-1 and COX-2. Both isoenzymes transform arachidonic acid to prostaglandins, but differ in their distribution and their physiological roles. Meanwhile, the responsible genes and their regulation have been clarified. COX-1, the pre-dominantly constitutive form of the enzyme, is expressed throughout the body and performs a number of homeostatic functions such as maintaining normal gastric mucosa and influencing renal blood flow and platelet aggregation. In contrast, the inducible form is expressed in response to inflammatory and other physiological stimuli and growth factors, and is involved in the production of the prostaglandins that mediate pain and support the inflammatory process. All the classic NSAIDs inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 at standard anti-inflammatory doses. Simmons also recently co-discovered COX-3 in 2002 and analyzed this new isozyme's relation to acetaminophen (paracetamol), arguably the most widely used analgesic drug in the world. The clinical ramifications and knowledge of COX isozymes are therefore rapidly expanding and could perhaps offer significant hope for future treatments of pain, inflammation and fever.
5331