Hisashi Ito1*, Tetsumasa Kamei1, Raymond P Onders2, Shigeru Fukutake1, Sanae Odake1,3, Shunsaku Kohriki4 and Jun Kawachi5
1Department of Neurology, Shonan Fujisawa Tokushukai Hospital, Fujisawa, Japan
2Department of Surgery, University Hospitals of Cleveland and Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, USA
3Department of Internal Medicine, Sodegaura Satsuki-dai Hospital, Sodegaura, Japan
4Department of Surgery, Shonan Fujisawa Tokushukai Hospital, Fujisawa, Japan
5Department of Surgery, Shonan Kamakura General Hospital, Kamakura, Japan
*Corresponding Author:
Dr. Hisashi Ito
Department of Neurology, Shonan Fujisawa
Tokushukai Hospital, 251-0041, Fujisawa, Japan
Tel: +81-466-35-1177
Fax: +81-466-35-1300
E-mail: hisashi.ito@tokushukai.jp
Received Date: April 19, 2018 Accepted Date: April 25, 2018 Published Date: April 28, 2018
Citation: Ito H, Kamei T, Onders RP, Fukutake S, Odake S, et al. (2018) Diaphragm Pacing Could Have Efficacy for Sleep Condition in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosci Vol.9 No.3:256. doi: 10.21767/2171-6625.1000256
Keywords
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Respiratory insufficiency; Diaphragm pacing
Introduction
Respiratory insufficiency is a critical problem in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Earlier administration of non-invasive ventilation (NIV) prolongs the survival in ALS patients and is regarded as the standard care [1,2]; however, its effect on quality of life remains to be elucidated. Diaphragm pacing (DP) is used to augment respiration when patients have intact diaphragm motor units and has been applied to patients with spinal cord injury and ALS [3,4]. We have reported the efficacy and safety of DP for Japanese ALS patients and pathological findings of the autopsied case [5-7]. In this article, we focused on the ancillary impact of DP on sleep condition in ALS patients.
Patients and Methods
This study was ancillary to a prospective, open-labeled, nonrandomized trial for 5 Japanese ALS patients without positive pressure mechanical ventilation (3 men and 2 women, aged 59.6 ± 9.6 years). Eligibility criteria were as for the main study, namely that patients had to be 21 years or older, familial or sporadic ALS diagnosed with laboratory-supported probable, probable, or definite according to the World Federation of Neurology El-Escorial criteria; with bilateral phrenic nerve function clinically acceptable as demonstrated by bilateral diaphragm movement with fluoroscopic sniff test or electrophysiological study; chronic hypoventilation was documented by at least one of the following: FVC less than 50% predicted, or MIP (maximal inspiratory pressure) less than 60 cm H2O, or PaCO2 greater than or equal to 45 mmHg or nocturnal SaO2 less than or equal to 88% for at least 5 continuous minutes; suitable surgical candidate, and negative pregnancy test in female participants of childbearing potential. Patients were excluded if they had cardiac or pulmonary disease that would increase the risk of general anesthesia, or diaphragm abnormality such as a hiatal hernia or paraoesophageal hernia. Additionally, we excluded those who were implanted electrical device such as cardiac pacemaker or defibrillator, and had severe psychological problem including dementia [5,6].
We started DP with NeuRx RA/4 Diaphragm Pacing System R (NeuRx, Synapse Biomedical, Ohio, USA). We did not restrict the concomitant use of other NIV and 2 patients had already been administered NIV at inclusion (Table 1). We implanted DP electrodes into the diaphragm close to the phrenic motor point laparoscopically under general anesthesia according to previous reports [3,8]. In brief, the diaphragm was exposed, the phrenic nerve motor point was mapped, pacing electrodes were implanted, and finally the wires were routed to the external pulse generator. Two pacing electrodes were placed on the motor points of the diaphragm on each side and intraperitoneal electrode. We continued DP for 24 hours a day. Diaphragm contractions were induced by delivering trains of stimuli with the conditions of: frequency, < 20 Hz; pulse width, < 200 μsec; and intensity, < 25 mA, as tolerated.
| No. |
Age/
Gender |
Criteria |
Initial sympton |
Duration *** (months) |
ALSFRS-R |
Bulbar score *** |
Use of NIV |
| 1 |
70/F |
probable |
LMNs* in lower limb |
20 |
33 |
12 |
(-) |
| 2 |
63/M |
definite |
LMNs* in upper limb |
32 |
42 |
9 |
(-) |
| 3 |
60/M |
probable |
LMNs* in lower limb |
26 |
28 |
11 |
nasal CPAP Cough Assist |
| 4 |
44/F |
probable |
UMNs* in lower limb |
28 |
14 |
6 |
(-) |
| 5 |
61/M |
definite |
LMNs* in lower limb |
14 |
43 |
12 |
BiPaP |
*Lower motor neuron sign; **Upper motor neuron sign; ***Disease duration from the onset to inclusion; ****Mild: 9~12, Moderate: 5~8, Severe: 0~4
Table 1: Demographics and disease characteristics of patients at inclusion.
The primary study data was collected within one month before implantation. Repeat evaluations were performed 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24 months post implant in the main study [6]. Collected data comprised ALS functional rating scale (ALS-FRSr); spirometric variables including predicted vital capacity (%, sitting); blood gas; fluoroscopic diaphragm evaluation; tolerance and safety information. These assessments were performed with NIV other than DP turned off. The study design is summarized in Figure 1.
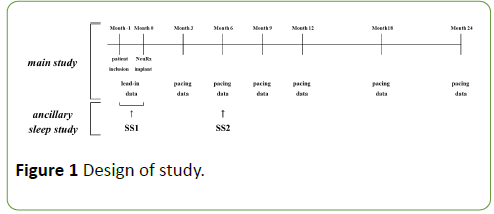
Figure 1: Design of study.
For the ancillary sleep study, reported here, one-night laboratory polysomnographic recordings (PSG, Philips Respironics GK, Japan) within 1 month before (SS1) and 6 months of DP (SS2) were performed. At SS1 the sleep study was performed with NIV for those patients using NIV. As SS2 the sleep study was again performed with NIV for those patients using NIV (there was no change in the patients using NIV at SS1 to SS2). Additionally, DP was used during the PSG for all patients at SS2. Statistical analysis was performed using paired t-test and significance was set up p<0.05. This study was approved by the Review Board of Tokushukai Medical Alliance, and the patients provided written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki before implantation.
Results
4 patients (2 men and 2 women, aged 59.5 ± 11.0 years) completed to evaluate sleep condition because one patient (No. 3) withdrew because he was introduced mechanical ventilation with tracheostomy triggered by an accidental aspiration. All patients met the inclusion criteria for chronic hypoventilation and demonstrated bilateral phrenic nerve function as demonstrated by electrophysiological studies.
The use of DP after 6 months was as follows; frequency 12Hzpulse width 63.1 ± 26.3 μsec (20 to 80 μsec), intensity 10 ± 1.6 mA (6 to 11 mA). Neither modification of already administered NIV nor new administration of NIV were observed in a follow up period. Riluzole, a tetrodotoxinsensitive sodium channels blocker, had been administered for at least three months before the implantation in all patients.
According to the progression of ALS, motor function and vital capacity deteriorated with significance, however, PaCO2 did not elevate significantly. Regarding sleep condition, total sleep time (TST, min), sleep latency (min), Stages 1-2 duration (% TST), REM sleep duration (% TST), and time spent with SpO2 under 90% (min) showed no significant difference between the couple of polysomnographic studies, which indicated that the first-night effect was negative. On the other hand, arousal index (AI, per hour) declined in all patients. In addition, apneahypopnea index (AHI, per hour) and wake after sleep onset (WASO, min) declined in 2 patients and was similar in other 2 patients (Table 2 and Figure 2).
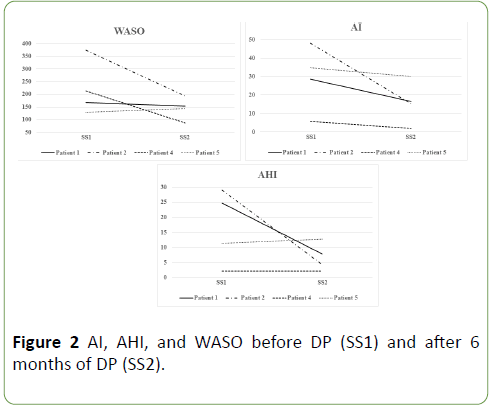
Figure 2: AI, AHI, and WASO before DP (SS1) and after 6 months of DP (SS2).
| Variables |
SS1 (within 1
month before DP) |
SS2 (6 months
after DP) |
p-value |
| ALSFRS-r |
34.0 ± 11.6 |
22.3 ± 0.7 |
0.0353 < 0.05 |
| (18 ~ 43) |
(14 ~ 31) |
| VC (% pred) |
68 ± 11.4 |
29.9 ± 16.2 |
0.0314 < 0.05 |
| (57.7 ~ 83.4) |
(7.3 ~ 42.1) |
| PaCO2 (mmHg) |
37.9 ± 0.7) |
41.7 ± 3.3 |
0.0667 |
| (37.3 ~ 38.9) |
(38.0 ~ 45.9) |
| Total sleep time (TST), min |
344.6 ± 75.9 |
371.5 ± 40.5 |
0.2549 |
| (231.5 ~ 393.5) |
(343.5 ~ 431.0) |
| Wake after sleep onset, min |
220.6 ± 108.0 |
144.5 ± 44.0 |
0.1006 |
| (128.5 ~ 374.0) |
(86.5 ~ 193.0) |
| Sleep latency, min |
36.1 ± 10.2 |
33.4 ± 43.0 |
0.4603 |
| (26.0 ~ 49.5) |
(0.0 ~ 96.0) |
| Stages 1-2 duration, % TST |
77.7 ± 4.6 |
74.2 ± 8.3 |
0.2201 |
| (72.0 ~ 83.2) |
(64.0 ~ 81.3) |
| REM sleep duration, % TST |
21.6 ± 5.1 |
25.0 ± 7.9 |
0.2337 |
| (16.5 ~ 28.0) |
(18.2 ~ 34.0) |
| Arousal index, per hour |
29.4 ± 17.7 |
16.0 ± 11.6 |
0.0717 |
| (5.8 ~ 48.2) |
(1.9 ~ 30.2) |
| Apnea-hypopnea index, per hour |
16.8 ± 12.4 |
6.8 ± 4.6 |
0.1083 |
| (2.1 ~ 29.0) |
(2.1 ~ 12.8) |
| Time spent with SpO2 <90%, min |
1.6 ± 3.1 |
3.9 ± 6.0 |
0.1119 |
| (0.0 ~ 6.2) |
(0.0 ~ 12.6) |
| *paired t-test |
Table 2: ALSFRS-r, respiratory variables, and sleep condition in before DP (SS1) and after 6 months of DP(SS2).
Discussion
This is the first study of the efficacy of DP with NeuRx on sleep condition in ALS patients from Japan. Our study was small; however, our results confirmed the previous research with a longer period of evaluation [9]. Additionally, this is the first study, worldwide, to beneficial effect of active DP for sleep. The previous research compared sleep before and after diaphragm conditioning, but without DP active during the PSG.
This study showed a trend toward improvement in sleep with active DP, despite continued progression of ALS. As CO2 expiration depends mainly on internal intercostal muscles, DP has little relation with CO2 level and the compensation with respiratory rates might prevent CO2 accumulation. Therefore, the combination uses of BiPaP and DP may be optimum to prolong the survival.
Based on the results of a multicenter study compared with published historical data for NIV as the control [1], the US food and Drug Administration approved NeuRx for humanitarian device exemption in 2011 [10]. To the contrary, the combination of NIV and DP with NeuRx was less effective than NIV alone for survival in randomized-controlled trial in the UK [11]. Another trial in France showed that DP with NeuRx had no benefit on quality of life and improvement of survival [12].
The heterogeneity of clinical features and course of ALS might influence the different results observed in these clinical trials. In addition, the difference of the percentage of bulbar palsy or definite ALS patients, and the average age between groups could attribute to this discrepancy [11,12]. We have to identify the suitable clinical form of ALS, appropriate timing of introduction, and proper condition of stimulation for DP with NeuRx in future.
Conclusion
DP with NeuRx could prevent worsening of sleep condition at least 6 months from DP. Further investigation should be necessary to identify the optimal target patient of ALS and way of pacing with NeuRx.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts.
22810
References
- Lechtzin N, Scott Y, Busse AM, Clawson LL, Kimball R, et al. (2007) Early use of non-invasive ventilation prolongs survival in subjects with ALS. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 8: 185-188.
- Andersen PM, Abrahams S, Borasio GD, De Carvalho M, Chio A, et al. (2012) EFNS Task Force on Diagnosis and Management of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: EFNS guidelines on the clinical management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (MALS) - Revised report of an EFNS task force. Eur J Neurol 19: 360-375.
- Onders RP, Elmo M, Khansarinia S, Bowman B, Yee J, et al. (2009) Complete worldwide operative experience in laparoscopic diaphragm pacing: results and differences in spinal cord injured patients and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Surg Endosc 23: 1433-1440.
- Onders RP, Elmo M, Kaplan C, Katirji B, Schilz R (2014) Final analysis of the pilot trial of diaphragm pacing in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with long-term follow-up: diaphragm pacing positively affects diaphragm respiration. Am J Surg 207: 393-397.
- Ito H, Odake S, Kohriki S, Kawachi J, Kamei T (2015) Diaphragm pacing in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis – A short-term analysis of safety and effectiveness. Neurological Therapeutics 32: 501-505.
- Ito H, Odake S, Fukutake S, Kohriki S, Kawachi J, et al. (2017) Diaphragm pacing in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis – A long-term analysis of safety and effectiveness. Neurological Therapeutics 34: 121-124.
- Ito H, Kamei T, Odake S, Nakano M, Okeda R, et al. (2016) An autopsy case of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with diaphragm pacing. Intern Med 55: 3511-3513.
- Onders RP, Carlin AM, Elmo M, Sivashankaran S, Katirji B, et al. (2009) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: the Midwestern surgical experience with the diaphragm pacing stimulation system shows that general anesthesia can be safely performed. Am J Surg 197: 386-390.
- Gonzalez-Bermejo J, Morelot-Panzini C, Salachas F, Redolfi S, Straus C, et al. (2012) Diaphragm pacing improves sleep in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 13: 44-54.
- Humanitarian device exemption post-approval study of NeuRx diaphragm pacing system for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (NCT01605006): https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01605006
- DiPALS Writing Committee, on behalf of the DiPALS Study Group Collaborators (2015) Safety and efficacy of diaphragm pacing in patients with respiratory insufficiency due to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (DiPALS): A multicentre, open-label, randomized controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 14: 883–892.
- Gonzalez-Bermejo J, Morélot-Panzini C, Tanguy ML, Meininger V, Pradat PF, et al. (2016) Early diaphragm pacing in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (RespiStimALS): A randomized controlled triple-blind trial. Lancet Neurol 15: 1217-1227.