Keywords
|
| Thiazole derivatives, biological activities |
INTRODUCTION
|
| Thiazoles are a class of organic compounds related to azoles with a common thiazole functional group. Thiazole is aromatic, heterocyclic organic compound that has a five-membered molecular ring structure, C3H3NS. |
| The thiazole moiety is a crucial part of vitamin B1 (thiamine) and epothilone, benzothiazoles are important thiazoles example eluciferin. Thiazoles have been used to give N-S free carbenes and transition metal carbene complexes. The amino atom can be alkylated to create a thiazolium cation; thiazolium salts are catalysts in the Stetter reaction and the Benzoin condensation. Thiazole dyes are used for dying cotton. Thiazoles are well represented in bisomolecules. |
 |
BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES
|
| Anticonvulsant activity |
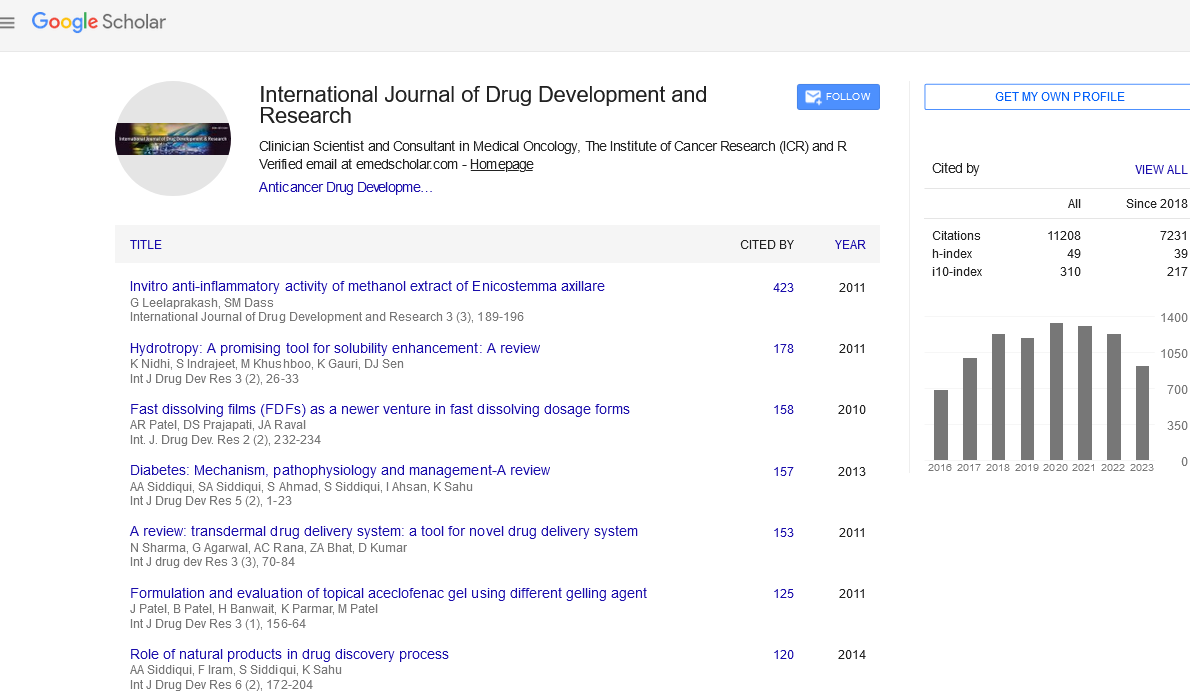
| Satoh et al[1] identified 4-fluoro-N-[4-[6- (isopropylamino)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]- N-methyl benzamide (1) as a potent mGluR1 antagonist as PET tracer, it would have great potential for elucidation of mGluR1 functions in human. |
| Agarwal et al[2] synthesized a series of 5-[(Nsubstituted benzylidenylimino)amino]-2-oxo/thiobarbituric acids and screened, in vivo for anticonvulsant and acute toxicity studies. The compounds (2a) and (2b) found to be more potent. |
 |
| Siddiqui et al[3] synthesized a series of thiazolesubstituted thiadiazole derivatives and screen for anticonvulsant activity in vivo by models such as MES and scPTZ. Three compounds (3a-c) were found to be potent. |
| Siddiqui et al[4] synthesized a series of 3-[4- (substituted phenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-ylamino]-4- (substituted phenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5- thiones and screened for in vivo anticonvulsant activity via MES and scPTZ. Compounds (4a and 4b) showed significant anticonvulsant activity with ED50 values 23.9 mg/kg and 13.4 mg/kg respectively in MES screen and 178.6 mg/kg and 81.6 mg/kg respectively in scPTZ test. |
 |
 |
| Banerjee et al[5] studied the SAR of over 250 compounds.1-acetyl-4-benzyl-2-(thiazol-2- yl)semicarbazide (5), displayed moderate-excellent activity in mice (MES ip ED50 =22 mg/kg, PI = 5.4) and rat (MES po ED50 = 6.2 mg/kg, Tox TD50> 250) which exceed that of phenytoin. |
| Siddiqui et al[6] prepared several heteroaryl semicarbazones and evaluated for anticonvulsant activity utilizing scPTZ and MES tests at 30, 100 and 300 mg/kg dose levels. Compounds (6a-c) exhibited significant anticonvulsant activity at 30 mg/kg dose level comparable to the standard drug phenytoin. |
 |
 |
Antimicrobial activity
|
| Abdel-Wahab et al[7] synthesized various pyrazoline incorporated thiazole derivatives (7a-d) and screened for antibacterial and antifungal activity against Escherichia coli and Aspergillus niger. |
| A series of arylidene-2-(4-(4-methoxy/bromophenyl) thiazol-2-yl)hydrazines and 1-(4-(4-methoxy/bromo phenyl)-thiazol-2-yl)-2- cyclohexylidene/cyclopentylidene hydrazines were synthesized, and screened for antimicrobial and antifungal activities by Bharti et al[8]. Among the tested compounds (8a-c, 9a-b, 10a and 10b) were more potent. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| A novel series of 7�-[2-(2-amino-5-chlorothiazol-4- yl)-2(Z)-((S)-1-carboxy ethoxyimino)acetamido] cephalosporins bearing various pyridinium groups at the C-3′ position were synthesized by Yamawaki et al[9] . Among these cephalosporins, 2-amino-1-(3- methylamino-propyl)-1H-imidazo-[4,5-b]- pyridinium group at the C-3’ position (11) showed potent and well-balanced antibacterial activities against P. aeruginosa and other Gram-negative pathogens. |
| Khalil et al[10] synthesized some 3-oxopropiononitrile and thioamide derivatives for new thiazole, out of these compound (12) showed potent antibacterial activity. |
 |
 |
| A stereospecific synthesis of some thiazolidinones and thiazoles was achieved conveniently by Aridoss et al[11] and Antimycobacterial activity were tested against Mycobacterium tuberculosis indicated that some compounds (13a-c) and (14a-c) exhibited two fold enhanced potency than Rifampicin. |
 |
 |
| Karegoudar et al[12] reported a series of novel 4- aryl/chloroalkyl-2-(2,3,5-trichlorophenyl)-1,3- thiazoles and by condensing 2,3,5- trichlorobenzenecarbothioamide with phenacyl bromide afforded 4-aryl-2(2,3,5- trichlorophenylidene hydrazino) -1,3-thiazoles in good yield. Among these compounds (15a-d), (16ab) and (17a-b) possessed potent activity. |
 |
 |
 |
| Mallikarjuna et al[13] synthesized a series of 4- isopropylthiazole-2-carbohydrazide analogs, derived clubbed oxadiazole-thiazole and triazole-thiazole derivatives and evaluated them for in vitro antibacterial, antifungal and antitubercular activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv strain by broth dilution assay method. The synthesized compounds (18a-c) showed potent antitubercular efficacy. |
| Several 1-(4-(4’-chlorophenyl)-2-thiazolyl)-3-aryl-5- (2-butyl-4-chloro-1H-imidazol-5yl)-2-pyrazoline derivatives were prepared by Dawane et al[14] and tested for antibacterial and antifungal activity. Among these compounds, (19a-e) exhibited stronger antifungal and antibacterial activities. |
 |
 |
| Adibpour et al[15] reported the synthesis and antibacterial activity of several new 5-((3- oxoisothiazol-2(3H)-yl)methyl)-3-phenyloxazolidin- 2-ones and analogous 2-(4-substituted phenyl)- 3(2H)-isothiazolones substituted at 4 and/or 3- positions of the phenyl moiety with different groups of which some have shown to increase the antibacterial activity of both 3-aryl-2-oxazolidinones and 3(2H)-isothiazolones was described. The compounds (20a-c) showed potent activity. |
| Arshad et al[16] synthesized two novel series of thiazolylcoumarin derivatives and screened in vitro for antibacterial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Candida albicans. The three compounds (21a, 21b and 22) exhibited very good activity. |
 |
 |
 |
| Patel et al[17] synthesized 2-substituted phenyl-3-{1- cyclopropyl-6-fluoro- 7-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl piperazin-1-yl]-4-oxo-1,4- |
| dihydroquinoline}carboxamido-1,3-thiazolidin-4- ones and screened for antifungal and antibacterial activities. Compounds (23a-c) showed excellent activity against fungi, whereas compounds (23d-f) displayed against bacteria. |
| Sindhu et al[18] synthesized oxovanadium (IV) complexes of Schiff’s bases (24). These complexes were monomeric possessing a 1:2 (metal: ligand) stoichiometry and screened compounds evaluated for antibacterial activity. |
 |
 |
| Anti-inflammatory activity |
| Sondhi et al[19] reported variety of N-(4-phenyl-3- (2′,3′,4′-(un)substituted phenyl)thiazol-2(3H)- ylidene)-2,4-(un)substituted acridin-9-amine and 1- [(2,4-(un)substituted acridin-9-yl)-3-(4-phenyl-3- (2′,3′,4′-(un)substituted phenyl)thiazol-2(3H)- ylidene)]isothiourea derivatives and screened for anti-inflammatory, analgesic and kinase (CDK1, CDK5 and GSK3) inhibition activities. Out of these compounds, (25) and (26) showed potent activity. |
 |
| A series of 3-(2’-substituted indolidene aminothiazol- 4’-yl)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)indoles were synthesized by Singh et al[20] and them evaluated for their antiinflammatory activity against carrageenan induced edema in albino rats at a dose of 50 mg/kg p.o. The most active compound of this series (27) was found to show higher percent of inhibition of edema, lower ulcerogenic liability and acute toxicity than phenyl butazone. |
 |
| Kalkhambkar et al[21] prepared tri heterocyclic thiazoles containing coumarin and carbostyril (1-aza coumarin) by the reaction of the in situ generated 4- thioureidomethyl carbostyril and 3-bromoacetyl coumarins and tested for in vivo analgesic and antiinflammatory activities. Hence the compounds (28af) seem to be more effective as slow acting antiinflammatory agents. |
 |
 |
| A series of 2-(2,4-disubstituted-thiazole-5-yl)-3-aryl- 3H-quinazoline-4-one derivatives were designed and synthesized by Giri et al[22] and evaluated for antiinflammatory activity in vivo for acute inflammation. Two of the compounds (29a) and (29b) turned out to be the most promising dual inhibitors of NF-kB and AP-1 mediated transcriptional activation with an IC50 of 3.3 mM for both. |
| A series of adamantane derivatives of thiazolyl-Nsubstituted amides were synthesized by Koualty et al[23] and tested for anti-inflammatory activity as well as lipoxygenase and cycloxygenase inhibitory actions. Among the tested compounds, (30) showed potent activity. |
| Substituted thiazoles with different structural features were synthesized and screened for their antiinflammatory activity by Franklin et al[24] in acute carrageen in induced rat paw edema model and chronic formalin induced rat paw edema model. The compound (31) showed potent anti-inflammatory activity. |
 |
 |
 |
| Anticancer activity |
| A number of N-bis(trifluoromethyl)alkyl-N′-thiazolyl and benzothiazolylureas have been synthesized and evaluated by Luzina et al[25] against the human cancer cell lines. The most sensitive cell lines relative to the tested compound was: (32) PC-3 (prostate cancer, log GI50 −7.10), and SR (leukemia, log GI50 −5.44) human cancer cells. |
| Synthesis and activity of a series of 4-thiazolyl substituted analogs of novel pyrrolocarbazole as poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-(PARP-1) inhibitors have been disclosed by Dunn et al[26]. Among these compounds, (33) found to be more potent. |
 |
 |
| A series of 3,4-diarylthiazol-2(3H)-ones and three 3,4-diarylthiazol-2(3H)-imines were synthesized and evaluated by Liu et al[27] for their cytotoxicity in a panel of human cancer cell lines. Two compounds (34) and (35) showed potential anticancer activity against human CEM cells with IC50 values of 0.12 and 0.24 μM, respectively. |
 |
| 34, R1 = 3-NH2, 4-OMe, R2 = 3',4',5'-(OMe)3, R3 = H |
 |
| 35, R1 = 3-NH2, 4-OMe, R2 = 3',4',5'-(OMe)3, R3 = Cl |
| Havrylyuk et al[28] synthesized a series of 5-arylidene derivatives and evaluated them for antitumor activity. Among the tested compounds, 2-{2-[3- (benzothiazol-2-ylamino)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin- 5-ylidene methyl]-4-chlorophenoxy}-N-(4- methoxyphenyl)acetamide (36) were found to be the most active with log GI50 and log TGI values 5.38 and 4.45 respectively. |
| Shao et al[29] synthesized novel ferrocenyl containing thiazole derivatives from 2-amino-4-ferrocenyl-5- (1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-yl)- 1,3-thiazole and substituted benzoyl chloride and evaluated of anticancer activities. Thiazole (37a) and (37b) showed good inhibition percentages against human cancer cell lines. |
| Marini et al[30] studied that incorporation of planar heterocyclic thiazole nucleus in place of one of the amine like clinically ineffective trans-[PtCl2(NH3)2] (transplatin) to obtained compound (38). On the basis of results they concluded that such compounds significantly enhanced anticancer activity. |
 |
 |
 |
| Antidiabetic activity |
| The optimization of the led GK activator to 3-[(1S)-2- hydroxy-1-methylethoxy]-5-[4-(methylsulfonyl) phenoxy]-N-1,3-thiazol-2-ylbenzamide (39), a potent GK activator was described by Iino et al[31]. Following oral administration, this compound exhibited robust glucose lowering in diabetic model rodents. |
| Identification and synthesis of novel 3-alkoxy-5- phenoxy-N-thiazolyl benzamides as glucokinase activators were described by Iino et al[32]. Removal of an aniline structure of the prototype led and incorporation of an alkoxy or phenoxy substituent led to the identification of 3-isopropoxy-5-[4- (methylsulfonyl)phenoxy]-N-(4-methyl-1,3-thiazol- 2-yl)benzamide (40) as a novel, potent, and orally bioavailable GK activator. |
 |
 |
| Anti-HIV activity |
| Rawal et al[33] synthesized a series of 2-(2,6- dibromophenyl)-3-heteroaryl-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one and evaluated as selective human immunodeficiency virus type-1 reverse transcriptase (HIV-1, RT) enzyme inhibitors. In vitro cell assay showed that eight compounds (41a-h) effectively inhibited HIV-1 replication at 20-320 nM concentrations with minimal cytotoxicity in MT-4 as well as in CEM cells. Rawal et al[34] synthesized a series of 2-aryl-3- heteroaryl-1,3-thiazolidin-4-ones. Compounds having isothiourea or thiourea functional group showed high anti-HIV-1 activity. In vitro tests showed that the compound (42) exhibited EC50 at 0.26 lM with minimal toxicity in MT-4 cells as compared to 0.35 μM for thiazobenzimidazole (TBZ). |
 |
 |
| Masuda et al[35] synthesized various N-3-alkylated thiazolidene sulfonamide. The effects of different bases and solvents were investigated, and the NaH– THF combination was found to be the most effective at conferring high yields and endo-selectivity. Among the tested compounds an endo-alkylated compound (43) found to be showed more potent antiretroviral activity |
| Barreca et al[36] synthesized a series of 2,3-diaryl- 1,3-thiazolidin-4-ones. They revealed that some potent compounds (44a and 44b) are effective for inhibiting HIV-1 replication at nanomolar concentrations so considered as non-nucleoside HIV- 1 RT inhibitors (NNRTIs). |
| Turan-Zitouni et al[37] synthesized 3,4-diaryl-3Hthiazol- 2-ylidene)pyrimidin-2-yl amine derivatives and evaluated them for anti-HIV activity. Among the tested compounds the compound (45) showed excellent activity. |
 |
 |
 |
| Anti-Alzheimer activity |
| A novel clubbed triazolylthiazole series of cdk5/p25 inhibitors, potentially useful for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, was disclosed by Shiradkar et al[38] . Evaluation of the SAR of substitution within these series had allowed the identification of compounds (46a) and (46b) which significantly reduce brain cdk5/p25 and thus have potential as possible treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. |
| Helal et al[39] used high-throughput screening with cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5)/p25 that led to the discovery of N-(5-isopropyl-thiazol-2- yl)isobutyramide (47). This compound was an equipotent inhibitor of cdk5 and cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (cdk2)/cyclin E (IC50 = ca. 320 nM). |
 |
| Antihypertensive activity |
| Some 1-(4-arylthiazol-2-yl)-3,5-diaryl-2-pyrazoline derivatives were synthesized by Zitouni et al[40] by reacting 1-thiocarbamoyl-3,5-diaryl-2-pyrazoline derivatives with phenacetylbromide. The hypotensive activities were evaluated by using the tail-cuff method. An increase in the hypotensive activity of the compounds (48a-d) has been observed. |
| Abdel-Wahab et al[41] synthesized potent derivative of thiazolylmalonamide, tetrachloroisoindolylimide, and triazole and evaluated for antihypertensive "- blocking activity and low toxicity. Among these compounds, (49) found to be more potent. Dash et al[42] synthesized two potent compounds, WS75624 A (50) and WS75624 B (51) as endothelin converting enzyme (ECE) inhibitors and reported as potential antihypertensive agents |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Antioxidant activity |
| Shih et al[43] synthesized 3-aryl-4-heterocyclic sydnones derivatives. The antioxidant activity of synthesized compounds was evaluated, Among these compounds, 4-methyl-2-[(3-arylsydnon-4-ylmethylene) hydrazono]-2,3-dihydro-thiazole-5- carboxylic acid ethyl ester (52a-d) and 4-phenyl-2- [(3-arylsydnon-4-yl-methylene)hydrazono]-2,3- dihydro-thiazoles (53a-d) exhibited the potent DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) radical scavenging activity, comparable to that of vitamin E. Bozdag?-Du¨ndar et al[44] studied a series of 2,4- dichlorothiazolyl thiazolidine-2,4-dione and 4- chloro-2-benzylsulfanylthiazolyl-thiazolidine-2,4- dione derivatives and they were tested for their antioxidant properties by determining their effects on superoxide anion formation, and the 2,2- diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) stable free radical Compound (54) showed the best superoxide anion scavenging activity. |
| The antioxidant activity of the synthesized compounds (2-amino thiazole derivatives) was evaluated by Gouda et al[45] they reported that the three compounds (55a-c) showed potent antioxidant activity, after postulating the structure-activity relationship (SAR) of them. |
 |
 |
 |
Conclusion
|
| Thiazoles can be easily synthesized and offer countless modifications by numerous reaction modes in various positions due to their high reactivity. This has been comprehensively documented. Apart from the synthetic interest, the known and expected biological or medicinal activities of the numerous derivatives deserve particular mentions. Thus the quest to explore many more modifications on thiazole moiety needs to be continued. |