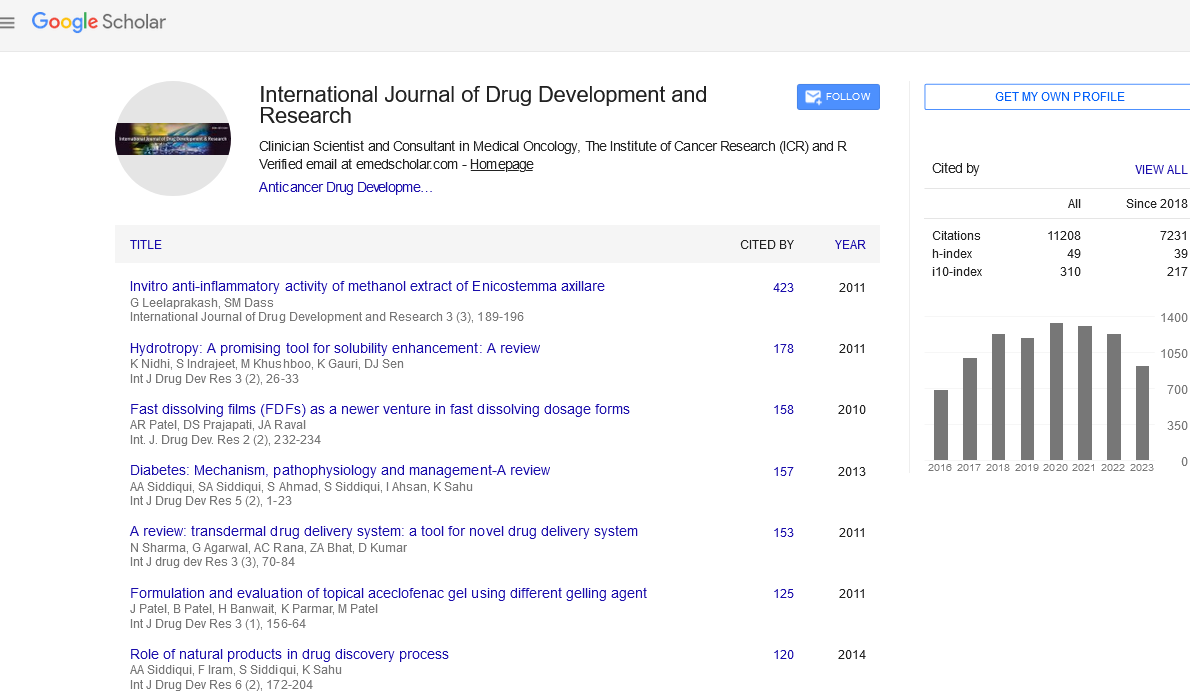
Approximately 40 per cent of new drug candidates have poor water solubility and the oral delivery of such drugs is frequently associated with implications of low bioavailability, high intra and inter-subject variability, and lack of dose proportionality. Bioavailability problem of lipophillic drugs can be solved by formation of Self-Micro Emulsifying Drug Delivery System (SMEDDS). SMEDDS appears to be a unique and industrially feasible approach to overcome the problem of low oral bioavailability associated with the lipophillic drugs. Self-micro emulsifying formulations are mixtures of oils and surfactants, ideally isotropic, and sometimes containing co-solvents, which emulsify spontaneously to produce fine oil-in-water emulsion when introduced into aqueous phase under conditions of gentle agitation. The digestive motility of the stomach and intestine provide the agitation necessary for self-emulsification in vivo. This review describes SMEDDS as one of the important approaches to overcome the formulation difficulties of potent lipophillic drugs.
5317