Keywords
|
| Oxidative stress, Carbon tetrachloride, Hybanthus enneaspermus, Na+/K+ATPase, Ca2+ATPase |
Introduction
|
| ATPases play an important role in the maintenance of molecular mechanisms of membrane proteins [1]. ATP itself, as a neurotransmitter, neuromodulator , and participate in the synthesis and release of nitric oxide by shear stress in endothelial cells [ 2,3,4 and 5 ]. The inactivation of Na+/K+ATPase leads to oxidative stress is the condition of unbalanced state between oxidants and antioxidants. The rabid metabolic nature of Ccl4 is highly inactivate the membrane bound enzymes when it is administrated into living things [ 6,7 and 8] .Ccl4 is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 is a isoenzyme which convert the Ccl4 into CCl3 ? and it reacts with oxygen of cellular proteins and lipids to produce a trichloromethyl peroxyl radical which attacks rabidly lipid membrane of endoplasmic reticulam than trichloromethyl free radical. It has been leads to liver cirrhosis, aging, ca2+ and Na2+ influx and finally cell swelling in mitochondria which allows the mitochondrial membrane damage, reduced carbonylation of protein, loss of enzyme activity and cell death. The medicinal value of the chosen plant Hybanthus enneaspermus has not been extensively worked out. Previously reported that the chosen plant having alkaloids, flavanoids, tannins, cardio glycosides, saponins, and terpenoids like compounds in Hybanthus enneaspermus [ 9, 10 and 11]. Hence in the present study, an attempt has been made to create an animal model with oxidative stress using CCl4 and the ethanolic extract of Hybanthus enneaspermus on mitochondrial Na+/K+ATPase, Ca2+ATPase and Mg2+ATPase activities were evaluated. |
Materials and methods
|
|
Plant material and preparation of extract
|
| Whole plants of H. enneaspermus were collected in the month of November and December from PRIST University Campus, Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India. The collected plants were identified and authenticated by a Botanist Prof. Dr. K. Singaravadivel, Department of Microbiology, Indian Institute of Crop Processing Technology, Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India. The collected plants were openair- dried under the shade, pulverized in to a moderately coarse powder (using pestle and mortar). Three-hundred grams (300 g) of the powered plants were extracted with ethanol (70%) using soxhlet apparatus for 48 h. A semi-solid extract was obtained after complete elimination of alcohol under reduced pressure. The extract was stored in refrigerator until used. The extract contains both polar and non-polar phytocomponents |
| Animals: Wistar strain male albino rats, weighing 180-200 g were selected for the study. The animals were housed individually in polypropylene cages under hygienic and standard environmental conditions (28±2ºC, humidity 60-70%, 12 h light/dark cycle). The animals were allowed a standard feed and water ad libitum. They were acclimatized to the environment for 1 week prior to experimental use. All the animal experiments were duly approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (743/03/abc/CPCSEA dt 3.3.03) Guidelines. (IAEC) |
| Induction of oxidative stress: Oxidative stress through hepatic injury was created by intraperitoneal injection of CCl4 in corn oil (1:1 v/v, 3ml/kg) [12]. The control animals received vehicle alone through intraperitoneal injection. |
| Experimental protocol: Rats were divided into four groups with six animals in each group. Group I animals were served as normal control. Group II was administered with corn oil (3ml/kg, i.p.) as vehicle control. Group III was given single dose (29th day) of CCl4 in corn oil (1:1 v/v, 3ml/kg, i.p.). Groups IV was treated with ethanolic extract of Hybanthus enneaspermus (500 mg/kg body weight) for 28 days and given single dose of (29th day) CCl4 in corn oil (1:1 v/v, 3 ml/kg, i.p.). Six hours after CCl4 intoxication, the experimental animals were sacrificed. The blood was collected with EDTA as anticoagulant. Serum was separated by centrifugation. Kidney and heart were excised immediately and immersed in physiological saline. It was suspended in 10% (w/v) ice-cold 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) and cut into small pieces. The required amount was weighed and homogenized using a Teflon homogenizer. Tissue homogenate and serum were used for the estimation of various biochemical parameters. |
|
Biochemical analysis:
|
| The mitochondrial homogenate was used for assaying membrane bound enzymes like Na+/K+ATPase,[13] Ca2+ATPase,[14] and Mg2+ATPases[15], activities. The amount of inorganic phosphorus was determined by the method of Fiske and Subbarow[16]. Protein was estimated by the method of Lowry et al.[17] |
|
Statistical analysis
|
| Statistical analysis values were expressed as mean ± SD for six rats in the each group and statistical significant differences between mean values were determined by one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons [18]. Statistical analysis carried out by Ms-Windows based graph pad Instat software (Graph Pad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) 3 version was used. A value of p < 0.001 was considered statistically significant. |
Results and Discussion
|
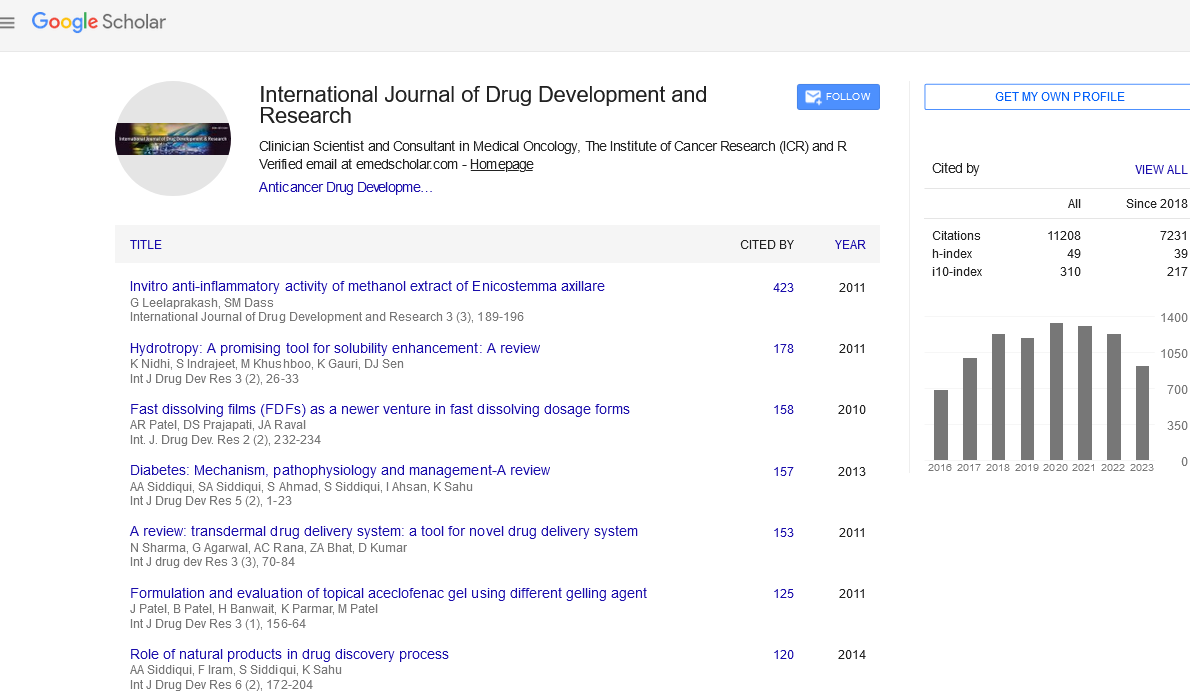
| The actions of mitochondrial Na+/K+ATPase, Ca2+ATPase and Mg2+ATPase in kidney and heart were studied after inducing oxidative stress by using Ccl4 as a toxic inducer. All three ATPases showed apparent inhibition in Ccl4 induced oxidative stress rats. In Hybanthus enneaspermus treated rats restored the levels of Na+/K+ATPase, Ca2+ATPase and Mg2+ATPase in kidney and heart ( Table 1 and 2). Oxidative stress is mainly caused by the mitochondrial dysfunction and energy depletion. Oxidative stress can be defined as a disturbance in the prooxidant/antioxidant balance and it is associated with more than hundred diseases such as arthritis, carcinogenesis, and aging and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome[ 19]. In conclusion, the restored activities of kidney and heart mitochondrial Na+/K+ATPase, Ca2+ATPase and Mg2+ATPase were observed after treatment with CCl4 and Hybanthus enneaspermus rats and thus, the Hybanthus enneaspermus extracts were proved as a potent membrane bound enzyme stabilizer. |
Acknowledgement
|
| The authors are thankful to PRIST University, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu, India for their financial and excellent technical support. |
Tables at a glance
|
 |
 |
| Table 1 |
Table 2 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance
|
|
|
| |