Clinical Images - (2016) Volume 7, Issue 2
Images in Pediatric Dermatology: Mimicking Molluscum Contagiosum
Ebtisam Elghblawi*
Specialist Dermatologist, AOA Hospital, Tripoli, Libya
- Corresponding Author:
- Ebtisam Elghblawi
Specialist Dermatologist, AOA Hospital, Tripoli, Libya
Tel: +218 926111310
E-mail: ebtisamya@yahoo.com
Received date: Jun 16, 2016; Accepted date: Jun 20, 2016; Published date: Jun 24, 2016
Citation: Elghblawi E. Images in Pediatric Dermatology: Mimicking Molluscum Contagiosum. Transl Biomed. 2016, 7:2.
Abstract
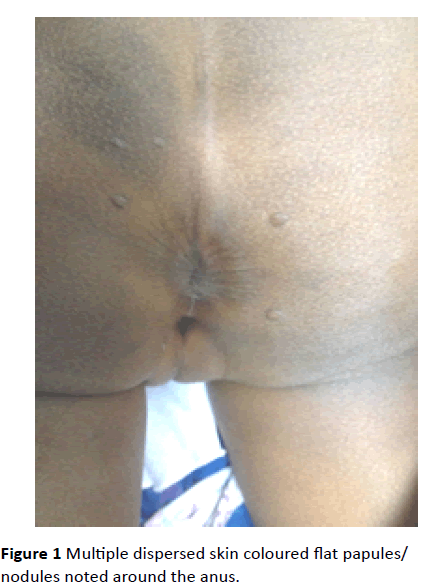
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is common in childhood; in this 4-year-old black girl, her mother notes the peri-anal nodular lesions since a year and claimed it has increased recently. The mother had a history of common warts. On examination, multiple dispersed skin coloured flat papules/ nodules noted around the anus. They were firm and hard. Differentials can be molluscum contagiosum, HPV induced lesions and perianal warts. I excised one and sent for biopsy which revealed a hyperkeratosis of epidermis only with no evidence of MC at all. This case warrants a careful examination and consideration for childhood abuse which was not the case here. Electrocautery removal was employed and the patient came for a follow up and so far content about the outcome.
Introduction
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is common in childhood; in this 4-year-old black girl, her mother notes the peri-anal nodular lesions since a year and claimed it has increased recently. The mother had a history of common warts. On examination, multiple dispersed skin coloured flat papules/ nodules noted around the anus (Figure 1). They were firm and hard. Differentials can be molluscum contagiosum, HPV induced lesions and perianal warts. I excised one and sent for biopsy which revealed a hyperkeratosis of epidermis only with no evidence of MC at all. This case warrants a careful examination and consideration for childhood abuse which was not the case here. Electrocautery removal was employed and the patient came for a follow up and so far content about the outcome.
Figure 1: Multiple dispersed skin coloured flat papules/ nodules noted around the anus.
This case shows that it is not always easily to differentiate the clinical manifestations presented from other skin lesions.
9833