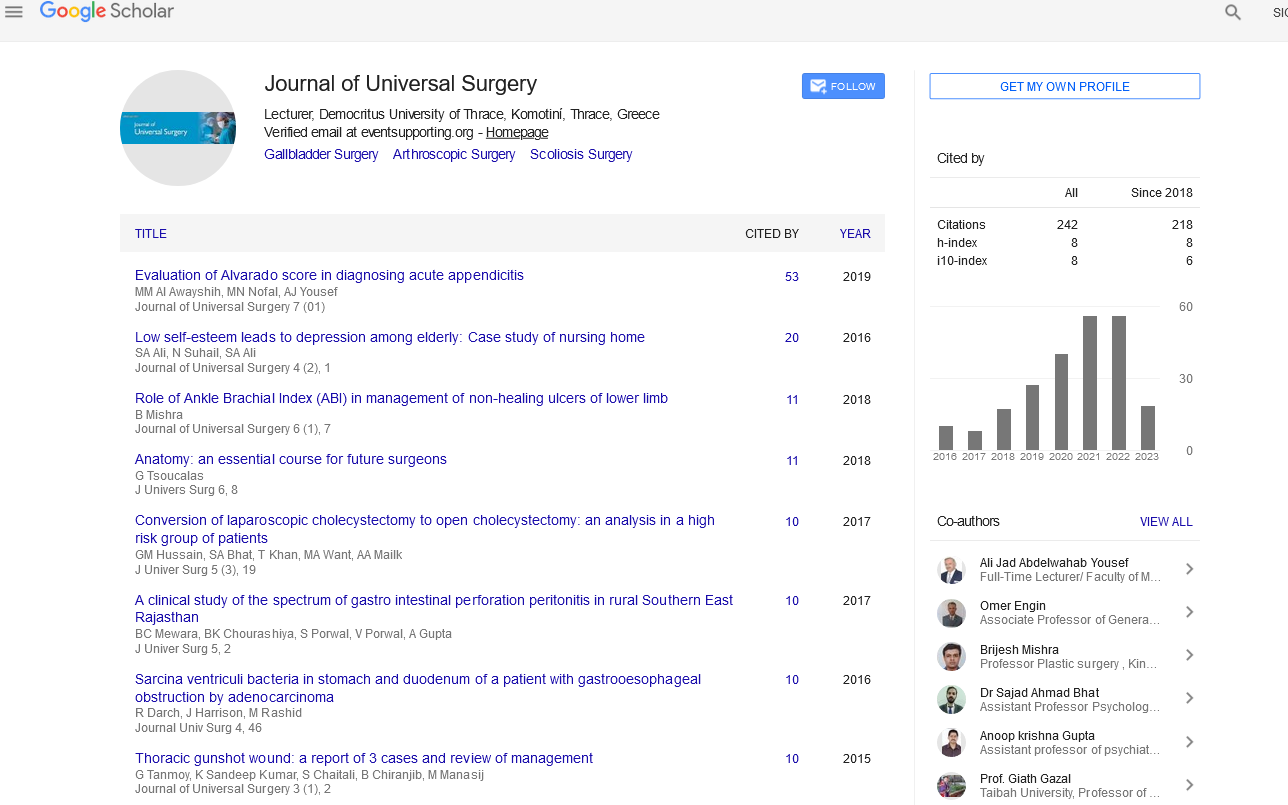
Introduction
The cataract remains the leading cause of avoidable blindness in the world. According to the latest assessment, cataract is responsible for 51% of world blindness, which represents about 20 million people (2010). Although cataracts can be surgically removed, in many countries barriers exist that prevent patients to access surgery. Manual small incision cataract surgery (MSICS) and phacoemulsification are the most popular methods of cataract extraction today. MSICS is significantly faster, less expensive and less technology-dependent than phacoemulsification. MSICS has been extensively practiced in developing countries like India. Intratunnel phaco fracture is a new nucleus management technique, where the lens nucleus is broken inside the sub 6 mm sclerocorneal tunnel and removed in contrast to other contemporary techniques. This is our original technique.
Intratunnel Phacofracture Technique
Intratunnel phaco fracture nucleus management technique was first described by author [1]. It’s a simple, inexpensive reproducible technique. Per case consumable expenditure of cataract extraction using this technique is given in Table 1.
First postoperative day visual outcome of 6 mm intratunnel phacofracture is given in Tables 2 and 3.
(Source: US Ophthalmic Review, 2014; 7(1):26–30)
(Source: US Ophthalmic Review, 2014; 7(1):26–30)
The mean uncorrected visual acuity and mean best corrected visual acuity at first post operative day were 0.367 (Snellen equivalent 20/46) and 0.226(Snellen equivalent 20/33) log MAR units respectively. No serious per and post-operative complication encountered [1].
Anesthesia
Manual small incision can be done performed under peribulbar or topical anesthesia.
Site of Incision
Site of incision is chosen according keratometry values (K1and K2). The superotemporal quadrant for right eye and the superonasal quadrant for left eye should be chosen if K1 and K2 difference is equal or less than 1.0 diopter (Figure 1). If K1 and K2 difference is more than 1.0 diopter then incision should be on steeper axis made. If K1 is steeper than K2 then superior incision (Figure 2) and If K2 is steeper than K1 then temporal incision (Figure 3).
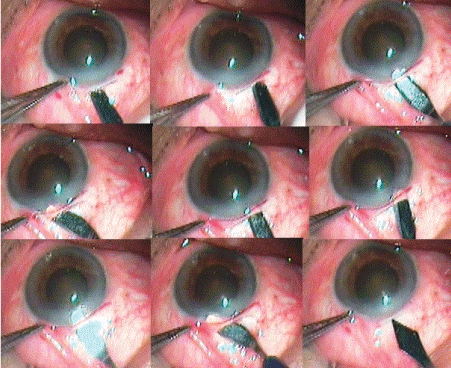
Figure 1: If K1 and K2 difference is less than 1 diopter then superotemporal incision for right eye and superonasal for left eye.
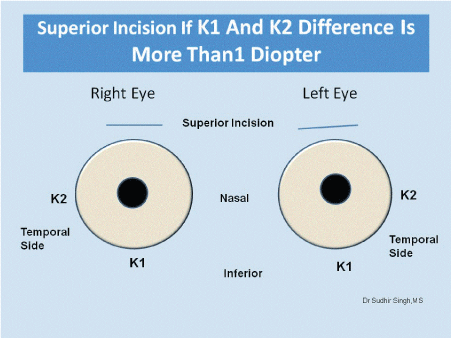
Figure 2: If K1 is more than 1.0 diopter from K2 then superior incision for both the eyes.
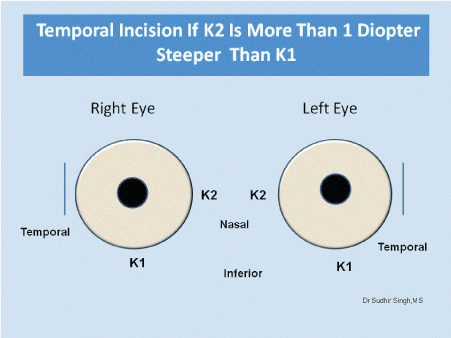
Figure 3: If K2 is more than 1.0 diopter from K1 then temporal incision for both the eyes.
Surgical Steps
Cleaning and draping
The skin of the eyelids, lid margins and around the eye is cleaned with 10 percent solution of povidone-iodine solution. Drape is applied. Wire speculum is placed. Cul de sac is thoroughly washed with Ringer’s lactate solution or balanced salt solution.
Superior Rectus Bridle Suture
A 4/0 silk superior rectus bridle suture is placed beneath the tendon of the superior rectus muscle. It is helpful to positioning eye after local anesthesia. Superior rectus bridle suture is not used when surgery is planned under topical anesthesia.
Conjunctival Flap
A fornix based conjunctival flap at the limbus with a chord length of approximately 6.5 mm was made. After careful dissection of the Tenon’s capsule, light cautary was applied (Figure 4).

Figure 4: Fornix-based Conjuctival Flap, Cautary and Partial Scleral Groove Demonstration.
Sclera-corneal Tunnel
A 6 mm scleral frown incision, 1.5 mm from the limbus is made with a 15 number Bard Parker blade (Figure 5). A funnel shaped sclerocorneal tunnel incision is created with a steel crescent knife. One side port is made 90 degrees apart on either side of the scleral tunnel with a 15 degree knife temporally in right eye and nasally in left eye. With a 2.8 mm keratome, the anterior chamber was entered 1.5 mm into the clear cornea. Anterior chamber is entered with 1.5 mm in clear cornea with help of 3.2 mm keratome (Figure 6). The hydroxyl propyl methyl cellulose 2 % (HPMC) viscoelsatics is injected into anterior chamber.

Figure 5: Corneoscleral Tunnel Making Demonstration.
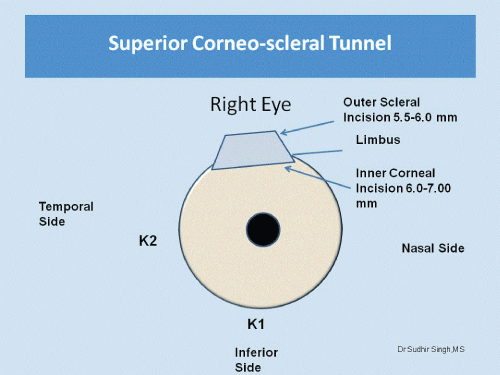
Figure 6: Sclerocorneal tunnel dimensions in superior quadrant.
Central Circular Capsulorhexis
The central circular capsulorhexis is made with help of 26 gauze needle capsulotome. If glow is poor then capsule was stained with trypan blue dye under the air bubble. Then viscoelsatics is injected and capsulorhexis is made. The size of capsulorhexis is depends on the size of the nucleus .It may vary from 5.5 mm to 7.5 mm (Figure 7). If nucleus size was anticipated large then two relaxing incisions are made at the margins of the capsulorhexis. Capsulorhexis can also be made by capsulorhexis forceps.
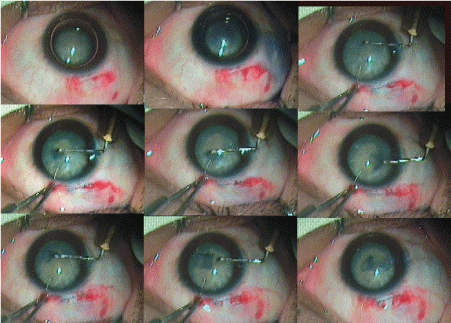
Figure 7: Capsular Staining and Capsulorhexis Creation with Needle Capsulotome.
Hydrodissection Procedure
The Hydrodissection is made with 26 gauze cannula place on 2 CC syringe filled irrigating fluid.
Nucleus Prolapse in the Anterior Chamber
The internal incision of the tunnel was enlarged sideways to 7 mm the 5.1 mm keratome (Figure 8) .Anterior chamber is formed again with viscoelsatics and the nucleus is rotated within the capsule using a Sinskey hook. The nucleus was prolapsed into anterior chamber using a Sinsky hook. A Sinskey hook was used to retract the capsulorhexis to engage the equator and lever out one pole of the nucleus outside the capsular bag and the rest of the nucleus was rotated into the anterior chamber. If the nucleus was too large then two or three relaxing incision were made at the capsulorhexis margins at equidistance (Figure 9).
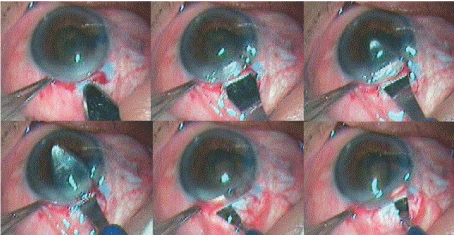
Figure 8: Tunnel Enlargement with 5 mm Keratotome and Enlargement of the Internal Incision with 2.8 mm Keratome.
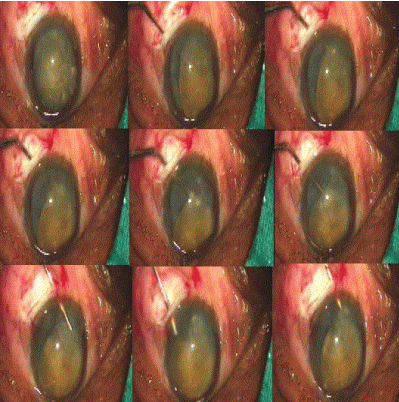
Figure 9: Nucleus Rotation and Prolapse in Anterior Chamber.
Nucleus Management
Up to this step all above mentioned steps are same as in other manual small incision techniques. Intratunnel phacofracture technique is different than other phacofracture techniques of anterior chamber. Enough viscoelsatics is placed between cornea and superior surface of the nucleus to protect endothelium; between nucleus and iris to keep away iris from nucleus. The nucleus is rotated within the capsule using a Sinskey hook. The globe was stabilized with tooth forceps and the small Lewis lens loop (AA 1915 from Appasamy Associate, India) is introduced through the tunnel and positioned between the iris and the nucleus. The nucleus is engaged in the lens loop and slowly withdrawn from the anterior chamber while the posterior lip of the tunnel is depressed. Once the nucleus got engaged in the tunnel, then the Lewis loop is pulled posteriorly and upwards. This causes breaking and removal of a part of the nucleus and other part remains engaged in the tunnel. By viscoelsatics the engaged part of the nucleus is pushed back into the anterior chamber and rotated so its longitudinal axis was coincided with longitudinal axis of the tunnel. Again viscoelsatics is placed between the cornea and superior surface of the nucleus and between the nucleus and iris. The lens loop is introduced through the tunnel and positioned between the iris and the remaining part of the nucleus. The remaining part of the nucleus is engaged in the lens loop and slowly withdrawn from the anterior chamber while the posterior lip of the tunnel was depressed. Most of the times remaining part of the nucleus comes out. If it still break down then remaining part again pushed in the anterior chamber with help of viscoelsatics and previous steps were repeated till it comes out (Figure 10).
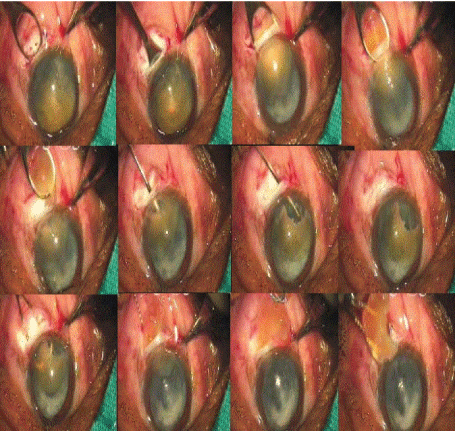
Figure 10: Demonstration of Intratunnel Phacofracture Using Levis Lens Loop.
Cortical Matter Clean Up
The remaining cortical matter clean up is done with direct 23 gauge Simcoe irrigating aspirating cannula. The anterior chamber is formed with Viscoelsatics (Figure 11).
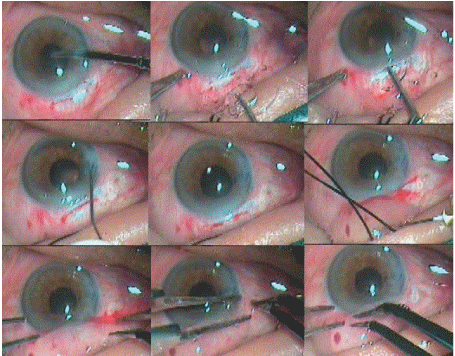
Figure 11: Irrigation Aspiration, Intraocular Lens Implantation, Wound Sealing and Conjunctival Flap Repositioning.
Intraocular Lens Implantation
A single piece PMMA intraocular lens of 5.5-6.00 mm optic size and 12.5 mm total size is implanted into the capsular bag. The anterior chamber is washed out thoroughly by Simcoe irrigation aspiration cannula using Ringer’s lactate solution (Figure 11).
Conjunctival Flap Reposition
The conjunctival flap is reposited back and cauterized at the edges.
Main Ports and Side ports Sealing
Main port and side ports are sealed with stromal hydration using a 26 gauze cannula.
Subconjuctival Injection
A 0.5 cc subconjuctival gentamycin with dexamethasone injection is given. Eye is pad patched
Discussion
The most commonly practiced MSICS techniques are Blumenthal, visco-expression, irrigating wire vectis and fish hook needle. These techniques require a 7 to 9 mm large incision, which leads to more astigmatism. So if nucleus is managed to remove though a sub 6 mm incision at appropriate site would result approximately same astigmatism as 3.2 mm phacoemulsification [2-5]. Intratunnel phaco fracture is a new technique innovated by Sudhir Singh, where the lens nucleus is broken inside the sub 6 mm sclerocorneal tunnel and removed. As nucleotomy maneuvering taken place inside the corneo-scleral in contrast to other nucleotomy techniques where maneuverings take place inside the anterior chamber. By Intratunnel phacofracture technique all types of the cataracts were successfully taken out through sub 6 mm wide tunnel. The mean uncorrected visual acuity and mean best corrected visual acuity at first post operative day were 0.367 (Snellen equivalent 20/46) and 0.226(Snellen equivalent 20/33) log MAR units respectively. No serious per and post operative complication encountered [2-8].
Financial Disclosure
The author has no financial interest in any product mentioned.
8300
References
- Sudhir Singh (2014) First Postoperative Day Visual Outcome Following 6 mm Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery Using IntratunnelPhacofracture Technique. US Ophthalmic Review, 7:26–30.
- Oshika T, Nagahara K, Yaguchi S, Emi K, TakenakaH,et al. (1998) Three year prospective randomized evaluation of intraocular lens implantation through 3.2 and 5.5 mm incisions. J Cataract Refract Surg,24:509-514.
- Gokhale NS, Sawhney S (2005) Reduction in astigmatism in manual MSICS through change in astigmatism site. Indian J Ophthalmol, 53:201-203.
- George R, Rapauliha P, Sripriya AV, Rajesh PS, Vahan PV, et al. (2005) Comparision of endothelial cell loss and surgically induced astigmatism following conventional extracapsular cataract surgery, manual small incision surgery and phacoemulsification. Ophthal Epidemiol,12:293-297.
- Gogate PM, Kulkarni SR, Krishnaiah S, Deshpande RD, Joshi SA, et al. (2005) Safety and efficacy of phacoemulsification compared with manual small incision cataract surgery by a randomized controlled clinical trial: Six weeks results. Ophthalmology, 112:869-7411.
- Gogate P, Deshpande M, Nirmalan PK (2007) Why do phacoemulsification? Manual small-incision cataract surgery is almost as effective, but less expensive. Ophthalmology,114:965–968.
- Gogate PM, Kulkarni SR, Krishnaiah S (2005) Safety and efficacy of phacoemulsification compared with manual small-incision cataractsurgery by a randomized controlled clinical trial: six-week results. Ophthalmology, 112:869–874.
- Ruit S, Tabin G, Chang D (2007) A prospective randomized clinical trial of phacoemulsification vs manual sutureless small-incision extracapsular cataract surgery in Nepal. Am J Ophthalmol,143:32–38.