| Sage (Salvia) species are the largest members of Lamiaceae or mint family [1,2]. Many species of salvia are native to Mediterranean region [3]. Sage family members especially common sage (Salvia officinalis) have been used traditionally throughout the world as a remedy for the treatment of many common ailments such as, cough, asthma, bronchitis, angina, mouth and throat inflammations, depression, digestive and circulation disorders, excessive sweating, skin and many other diseases [4-6]. |
| There are some chemical compounds like flavonoids, terpenoids and essential oils present in different species of Salvia [3]. Essential oils are the important sources for the screening of antimicrobial, antioxidant, free radical scavenging and anti-cancer activities [7]. Common sage (Salvia officinalis) is considered to have highest amount of essential oil compared to the other salvia species [4,8] and sage essential oil have shown to have carminative, antispasmodic, antiseptic and astringent properties [9,10]. New studies have shown that Salvia essential oils are effective in the treatment of large range of diseases like, nervous system, heart and blood circulation, respiratory, digestive, metabolic and endocrine diseases [9,10]. |
| • Salvia officinalis has been used as a traditional remedy against diabetes in many countries and its glucose-lowering affects have been demonstrated in animal studies [11]. Teainfusions of Salvia officinalis have shown to be as effective as metformin, which is an oral anti-diabetic drug used for the treatment of type II diabetes and act by reducing liver glucose production as well as rising the action of insulin [11]. |
| • Over the course of several studies on anti-obese components from natural medicine, the extract of Salvia officinalis leaves showed inhibitory effect against the pancreatic lipase activity and eventually was effective to reduce body weight and obesity [12]. Chinese sage (Salvia miltiorrhiza (SM)) which is similar to common sage, was recently shown to lower plasma cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides as well as increase HDL levels in lipidemic rats [11]. Cholesterol lowering effect of sage could be responsible partly at least, in prevention of cardiovascular diseases [13]. |
| • Salvia species, among many herbal extracts are known for the beneficial effects on memory disorders, depression and cerebral ischemia [14,15]. Studies have shown that essential oil of Salvia officinalis has inhibitory effect on acetylcholinesterase activity of the brain in certain concentration [16]. Also rosemarinic acid present in sage, in addition to anti-oxidant activity has shown to have anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective activity against Aβ (amyloid beta plaques) toxicity in neuronal cells and therefore, could be used as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease [17]. |
| • It has been demonstrated that flavonoids and polyphenolic compounds of sage species are responsible for strong antioxidant and radical-scavenging and antimicrobial properties of the herbs [18,19]. Carnosic acid, rosemarinic acid and caffeic acid which are present in sage play a very important role to protect the body against the oxidative stress [20,21]. |
| • Sage is effective in inhibiting the growth of some tumor cells in clinical trials. In a study, it was found that Ursolic acid found in sage has strong anti-inflammatory effect [22]. In addition Ursolic acid effectively inhibits angiogenesis, invasion of tumor cells and metastasis and suppresses the lung colonization of B16 melanoma cells in vivo [23]. Salvia officinalis water extract also showed a significant decrease in the induced oxidative damaged cells in rats and seems to have the ability to prevent colorectal cancer cell growth [24]. Another study on Salvia officinalis also demonstrated a strong cytotoxic activity of the extract on human prostate carcinoma cells [9]. |
| • In a study done on the antibacterial effect of sage against selected food spoiling bacteria in vitro, indicates that sage essential oil is a good alternative to the traditional antibiotics for some infections as well as food preservatives [4]. |
| • Sage has been used traditionally in treating abdominal spasms and diarrhea. Studies suggest that the extract of Salvia officinalis can have relaxing effects on gut motility and eventually posses anti spasmodic and anti-diarrheal activities [6]. |
| • The use of sage has been proven to be effective in reducing menopausal symptoms such as sweating and hot flashes. In clinical study, the use of once-daily fresh extract of Salvia officinalis was effective in treatment of hot flashes and climacteric symptoms [25]. |
| In recent decades, with more extensive researches on herbal medicines, the role of many of them as a source of natural therapeutic agent to treat a variety of diseases, with benefits of the lower cost and easy accessibility have been recognized. Sage (Salvia) species have been traditionally used for the relief and treatment of a number of minor and common diseases. With the increased knowledge of chemical compositions and pharmacological properties of sage through many studies and clinical trials, it has been discovered that sage species could be used as a natural effective Phytotherapy treatment for minor health problems as well as chronic or serious diseases such as Diabetes, Obesity, Cancer, and Alzheimer’s. |
Common Names
|
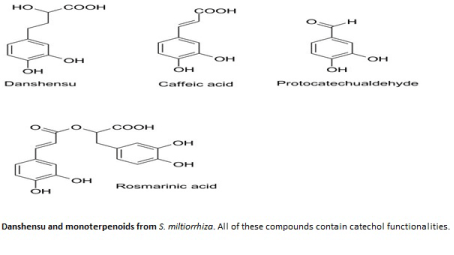
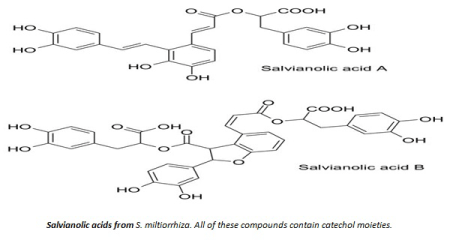
| Salvia officinalis has numerous common names. Some of the best known include sage, common sage, garden sage, golden sage, kitchen sage, true sage, culinary sage, Dalmatian sage, and broadleaf sage. Cultivated forms include purple sage and red sage. In Turkey, Salvia officinalis is widely known as adaçay±, meaning "island tea". In the Levant it’s called maramia (Figures 1 and 2). |
Chemical Composition
|
| The commonly known from sage Salvia Officinalis a total of 28 components were identified (Table 1). The principal components in the sage oils were 1, 8-cineole, camphor, alpha-thujone, betathujone, borneol, and viridiflorol. The chemo types of sage were not determined in investigated samples. The concentration of the main compounds in the drugs cultivated in different type of sage and different location varied in about the same range as the concentrations of these compounds in the oils of drugs obtained from other countries. The comparatively high concentration of toxic thujones seems to be characteristic to sage leaves cultivated in different location as well. |
Schematic Pathway and Extraction/ Purification
|
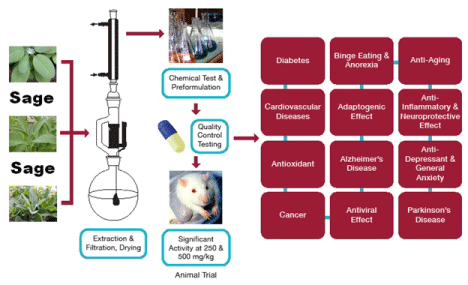
| The aim of our future research is to extract Sage in to the filtration equipment then by purification and extended quality control produce tablets for the animal trials (Figure 3). |
Tables at a glance
|
 |
| Table 1 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
|
| |
| |
| |