Keywords
Escherichia coli, β-lactamases, TEM genes.
Introduction
Diarrhea is a condition that has a major impact on global health. Extensive efforts to control diarrhea as one of the biggest killers of children under the school age are exerted [1]. Among those effort is the determination of causative agents and their characterization. People in developing countries suffer most from infectious forms of diarrhea. Escherichia coli are the most common etiologic pathogens of diarrhea in human and are common inhabitant of the human and animal gut [2]. Treatment in severe cases is typically consists of a broadspectrum antimicrobial, although resistance to such drugs has greatly increased over the last several years. The widespread use of antibiotics could be associated with the selection of antibiotic resistance mechanisms in pathogenic and nonpathogenic isolates of E. coli [3,4].
Increasing antimicrobial resistant E.coli in particular among immunocompromised patients to traditional and recent agents had been documented in several areas and became an emerging problem [4-6]. Resistance of bacteria to different antimicrobials is a multifactor process [5]. Resistance to β-lactam antibiotics in Gram-negative bacteria can be due to three mechanisms; decreased accumulation of the drugs by the cell, hydrolysis of the antibiotics by β-lactamases or alteration in the penicillin binding proteins that reduce their affinity to the drugs [7]. These mechanisms may be determined by genes that reside in the chromosome, on plasmids or transposons [8].
Over 200 β-lactamases have been classified into four main groups and eight subgroups according to their functional and structural characteristics. The classical TEM and SHV enzymes are the predominant plasmid-mediated β-lactamases of gram-negative rods which have been reported [9]. The classical TEM enzyme is the predominant plasmid-mediated β-lactamases of Enterobacteriaceae [10]. The phenomenon of multi-resistance to commonly prescribed drugs has been repeatedly reported in E.coli strains of different serogroups [11]. Therefore this study was carried out to Study the spread of resistant E. coli recovered from diarrheic children and study the suggested major mechanism of such resistance by studying the antibiotics resistance pattern of isolated E. coli. Also PCR assay for detection of blaTEM genes which is very helpful in determining genes responsible for resistance and in getting better and broader view on the most potent methods of management.
Material and Methods
A total of 250 stool specimens collected from Egyptian children under the age of six and suffered from diarrhea. They were collected from pediatric clinic of Egyptian public hospital.
The recovered isolates of E.coli were identified and confirmed using API 20E test strips (bioMérieux Vitek, Hazelwood, Mo.). E. coli ATCC 25922 was used as a reference strain.
Antimicrobial susceptibility test
Antimicrobial susceptibility test was performed according CLSI [12]. The used antimicrobials were obtained from Oxoid (England) and included: amikacin, ampicillin, cefepime, cephalexin, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, imipenem, aztreonam, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, kanamycin and ofloxacin.
Detection of β-Iactamase producing E.coli
The isolates were screened for β-Iactamase production by Spot Iodometric Overlay Method (IOM) [13] with some modifications.
Multiplex PCR assay for Detection of TEM, encoding genes (blaTEM):
PCR amplifications of the blaTEM genes were carried out [14,15]. The following primers sequences were used in these reactions; Tem-1-F: 5′-TTCTTGAAGACGAAAGGGC-3′. Tem-1-R; 5′-ACGCTCAGTGGAACGAAAAC-3′.Tem-2-F;5′- CTCACAAGATG AAACGGC-3′. Tem-2-R; 5′-ACGCGCACTCGAACGAGAAC- 3′. Total genomic DNA was extracted in order to perform the test.
Results
In the present study, among 250 stool specimens isolated from children under school age suffering from diarrhea, there were 214 positive E. coli specimens represent a percentage of 85.6% of total specimens.
Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of the isolated of E.coli strains:
The recovered E.coli isolates were tested for their antimicrobial susceptibility against twelve different antimicrobials. Antimicrobials of different classes were used to estimate the incidence of resistance to each agent, table 1. The presence of multiple drug resistance to three different antimicrobial agents was very clear in more than 88 % of tested isolates. The most predominant resistance was recorded to Beta-lactam antibiotics.
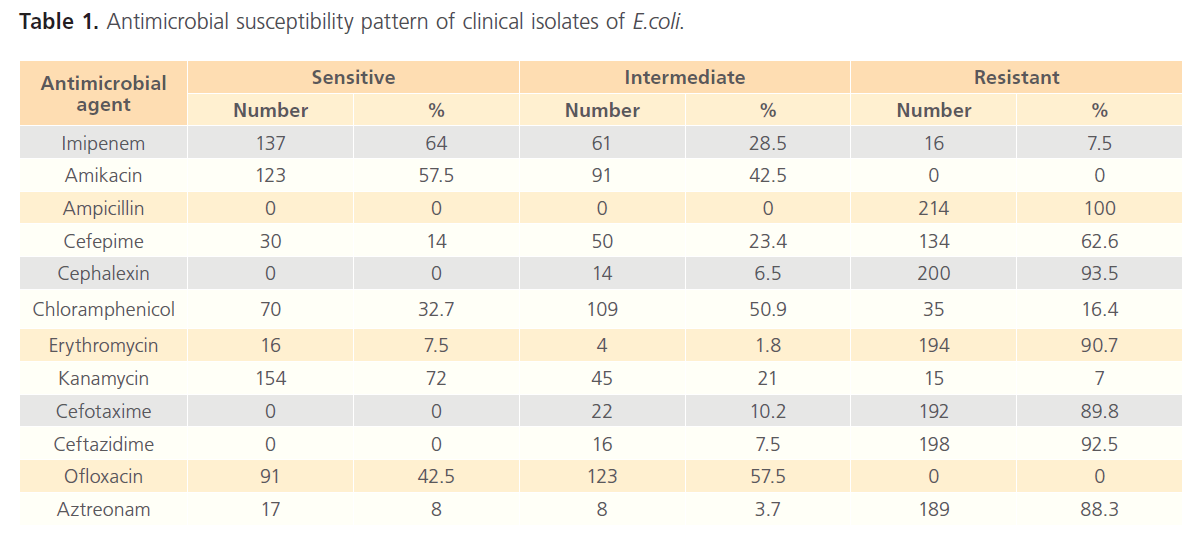
Table 1: Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of clinical isolates of E.coli.
Detection of β-lactamase production by the IOM:
A total of 214 E.coli isolates were tested for β-lactamase production using the IOM. A total of 199 (93 %) isolates were found β-lactamase producers.
PCR detection of blaTEM genes in isolated E.coli:
Multiplex PCR showed that blaTEM genes responsible for the production of β-lactamases were detected in 193 E.coli isolates (90%) of the examined E.coli isolates. TEM-1 encoding gene was detected in 112 isolates which represent 52.3% of total E.coli isolates. Both blaTEM-1 and blaTEM-2 genes were detected in 83 (37.7%) of isolated E.coli. Results of this step are illustrated in figure 1. No isolate indicated the presence of blaTEM-2 gene alone.
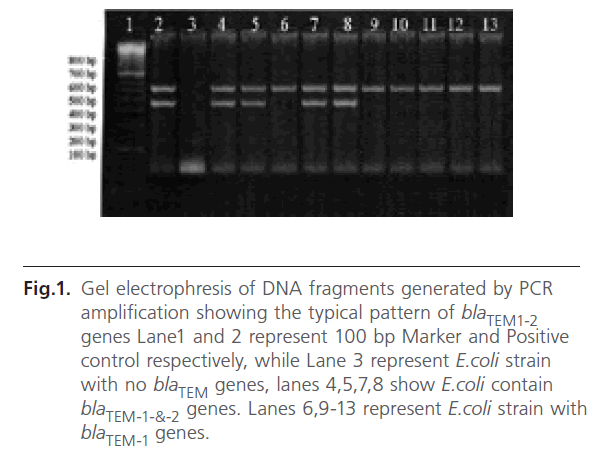
Figure 1: Gel electrophresis of DNA fragments generated by PCR amplification showing the typical pattern of blaTEM1-2 genes Lane1 and 2 represent 100 bp Marker and Positive control respectively, while Lane 3 represent E.coli strain with no blaTEM genes, lanes 4,5,7,8 show E.coli contain blaTEM-1-&-2 genes. Lanes 6,9-13 represent E.coli strain with blaTEM-1 genes.
Discussion
In our study, 93% of screened Escherichia coli were found β-lactamases producers. This finding was in compatible with the results of antimicrobial susceptibility test.
Results for the antimicrobial susceptibility testing of the different isolated E. coli strains in this study revealed higher yield of beta-lactamases producing E. coli than some previous studies [2,16]. It is reasonable to attribute the emergence of higher rate of resistance to the extensive use of antibiotics without control in developing countries [5,15].
In the present study, most of isolated E.coli (88%) were resistant to at least three different antimicrobials. This is in agreement with another study in South India [17], where all the isolated E.coli from general population were multi-resistant to at least three antimicrobials.
According to the antibiograms, different resistance patterns were defined. Moreover, it should be taken into consideration that due to the declining use of old antibiotics, minimal resistance pattern were detected to old antibiotics rather than β-lactam group as amikacin, chloramphenicol and kanamycin. This can be attributed to limitation of exposure and selective pressure to old antibiotics. The same was noticed also to the relatively new antimicrobial imipenem which may be due to its availability only in injection form which limits its misuse.
Resistance of the examined E.coli to different Beta-lactam antibiotics revealed that several resistance mechanisms were involved as previously reported [18-21]. In the present study attention was paid especially to the most frequent reported mechanism of hyper-production beta-lactamases mediated by blaTEM genes [15]. PCR detection of TEM genes in the present study revealed that about 90 % of the examined E.coli isolates contain blaTEM genes either TEM-1 or TEM-1 and TEM-2 together which are responsible for the production of β-lactamases. Positive PCR results for the blaTEM-1 gene were found in 52.3 % of the studied multidrug resistant E.coli isolates. Both blaTEM-1&2 genes were found in 37.7 % of resistant E.coli isolates. Results of PCR revealed that the majority of isolated E. coli from diarrheic Egyptian children contained blaTEM enzymes encoding genes.
The wide spread of antimicrobial resistance detected in this study reflects the overuse of antimicrobial drugs. There is no doubt that the widespread dissemination of organisms producing potent β-lactamases will severely limit the therapeutic options of physicians facing these organisms.
Molecular characterization of E. coli strains from stools samples differ in different studies among different geographical regions [2,22]. Inactivation of these drugs by plasmid mediated β-lactamases was apparently the major mechanism of resistance in our study in Egypt. This indicates the importance of the characterization of diarrhea etiological agents according to the affected region in order to establish the relevant treatment policy and infection control measures.
The high rate of resistant phenotypes detected in this study strongly recommends the judicious use of antibiotics which in turn would be useful in limiting the rapidity of spread of this resistance. Finally, attention must be paid for fecal contamination, environmental sanitation, and personal hygiene as important control measures of spread of multiresistant bacterial infections.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
138
References
- Vila, J., M. Vargas, C. Casals, H. Urassa, H. Mshinda, et al.,(1999) Antimicrobial resistance of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli isolated from children under the age of 5 years from Ifakara, Tanzania. AntimicrobAgents Chemother.43 (12): p. 3022-4.
- Al-Gallas, N., O. Bahri, A. Bouratbeen, A. Ben Haasen, and R. Ben Aissa,(2007) Etiology of acute diarrhea in children and adults in Tunis, Tunisia, with emphasis on diarrheagenic Escherichia coli: prevalence, phenotyping, and molecular epidemiology. Am J Trop Med Hyg.77 (3):p. 571-82.
- Saenz, Y., L. Brinas, E. Dominguez, J. Ruiz, M. Zarazaga, et al.,(2004) Mechanisms of resistance in multiple-antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli strains of human, animal, and food origins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.48 (10): p. 3996-4001.
- Jafari, F., M. Hamidian, M. Rezadehbashi, M. Doyle, S. Salmanzadeh- Ahrabi, et al.,(2009) Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli and Shigella species associated with acute diarrhea in Tehran, Iran. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol.20 (3): p. e56-62.
- Gad, G.F., H.A. Mohamed, and H.M. Ashour,(2011) Aminoglycoside resistance rates, phenotypes, and mechanisms of Gram-negative bacteria from infected patients in upper Egypt. PLoS One.6 (2): p. e17224.
- Ashour, H.M. and A. El-Sharif,(2009) Species distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of gram-negative aerobic bacteria in hospitalized cancer patients. J Transl Med.7: p. 14.
- Okeke, I.N.,(2009) DiarrheagenicEscherichia coli in sub-Saharan Africa: status, uncertainties and necessities. J Infect Dev Ctries.3 (11): p. 817-42.
- Davison, H.C., J.C. Low, and M.E. Woolhouse,(2000) What is antibiotic resistance and how can we measure it? Trends Microbiol.8 (12): p.554-9.
- Kaye, K.S., H.S. Gold, M.J. Schwaber, L. Venkataraman, Y. Qi, etal.,(2004) Variety of beta-lactamases produced by amoxicillinclavulanate-resistant Escherichia coli isolated in the northeastern United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.48 (5): p. 1520-5.
- Robin, F., J. Delmas, E. Machado, B. Bouchon, L. Peixe, et al.,(2011)Characterization of the Novel CMT Enzyme TEM-154. AntimicrobAgents Chemother.55 (3): p. 1262-5.
- Malik, Y.S., Y. Chander, K. Olsen, and S.M. Goyal,(2011) Antimicrobial resistance in enteric pathogens isolated from Minnesota pigs from1995 to 2004. Can J Vet Res.75 (2): p. 117-21.
- CLSI, (2008) Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute,PerformanceStandards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Infobase;.
- Lee, W.S. and L. Komarmy,(1981) Iodometric spot test for detectionof beta-lactamase in Haemophilusinfluenzae. Journal of clinicalmicrobiology.13 (1): p. 224-5.
- Brinas, L., M. Zarazaga, Y. Saenz, F. Ruiz-Larrea, and C. Torres,(2002)Beta-lactamases in ampicillin-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from foods, humans, and healthy animals. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy.46 (10): p. 3156-63.
- Speldooren, V., B. Heym, R. Labia, and M.H. Nicolas-Chanoine,(1998)Discriminatory detection of inhibitor-resistant beta-lactamases inEscherichia coli by single-strand conformation polymorphism-PCR.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.42 (4): p. 879-84.
- Carattoli, A., A. Garcia-Fernandez, P. Varesi, D. Fortini, S. Gerardi,et al.,(2008) Molecular epidemiology of Escherichia coli producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases isolated in Rome, Italy. J ClinMicrobiol.46 (1): p. 103-8.
- Amyes, S.G., S. Tait, C.J. Thomson, D.J. Payne, L.S. Nandivada, et al.,(1992) The incidence of antibiotic resistance in aerobic faecal florain south India. J Antimicrob Chemother.29 (4): p. 415-25.
- Brinas, L., M. Zarazaga, Y. Saenz, F. Ruiz-Larrea, and C. Torres,(2002) Beta-lactamases in ampicillin-resistant Escherichia coli isolatesbfrom foods, humans, and healthy animals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.46 (10): p. 3156-63.
- Tenover, F.C.,(2006) Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Am J Infect Control.34 (5 Suppl 1): p. S3-10; discussion S64- 73.
- Sharma, J., M. Sharma, and P. Ray,(2010) Detection of TEM & SHV genes in Escherichia coli &Klebsiellapneumoniae isolates in a tertiary care hospital from India. Indian J Med Res.132: p. 332-6.
- Lim, K.T., R. Yasin, C.C. Yeo, S. Puthucheary, and K.L. Thong,(2009) Characterization of multidrug resistant ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolates from hospitals in Malaysia. J Biomed Biotechnol.2009: p. 165637.
- Rugeles, L.C., J. Bai, A.J. Martinez, M.C. Vanegas, and O.G. Gomez- Duarte,(2010) Molecular characterization of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains from stools samples and food products in Colombia. Int J Food Microbiol.138 (3): p. 282-6