Uduma Felix U1, Agwuna Kennedy K2, Emejulu Jude KC3, Sylva Akpan4, Itanyi Ukamaka5, Motah Mathieu6 and Eke Bertha C7
1Department of Radiology, Faculty of Clinical Sciences, College of Health Sciences, University of Uyo, Uyo, Nigeria
2Department of Radiation Medicine, University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu, Nigeria
3Neurosurgical Unit, Department of Surgery, Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital, Nnewi, Nigeria
4Department of Opthalmology, Faculty of Clinical Sciences, College of Health Sciences, University of Uyo, Uyo, Nigeria
5Department of Radiology, University of Abuja Teaching Hospital, Abuja, Nigeria
6Neurosurgical Unit, Department of Surgery, University of Douala, Douala, Cameroon
7Neurology Unit, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Clinical Sciences, College of Health Sciences, University of Uyo, Uyo, Nigeria
- *Corresponding Author:
- Uduma Felix U
Department of Radiology, Faculty of Clinical Sciences
College of Health Sciences, University of Uyo, Uyo, Nigeria
Tel: 2348146129875
E-mail: felixuduma@yahoo.com
Received Date: 09 November 2016; Accepted Date: 14 November 2016; Published Date: 18 November 2016
Citation: Uduma Felix U, Agwuna Kennedy K, Emejulu Jude KC, et al. Neuroradiological Images of Five Selected Intracranial Tumors Encountered in our Practice. Arch Can Res. 2016, 4:4 doi: 10.21767/2254-6081.1000115
Keywords
Chordoma; Medulloblastoma; Acoustic neuroma; Meningioma; Gliomablastoma multiforme; MRI; CT
Image Presentations
Case A
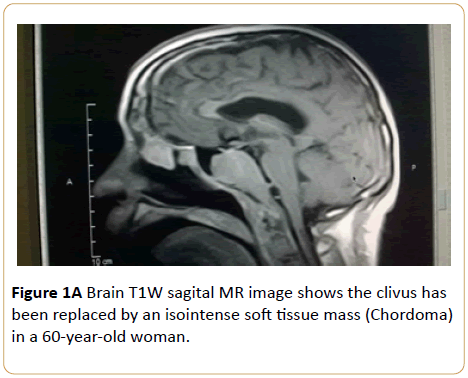
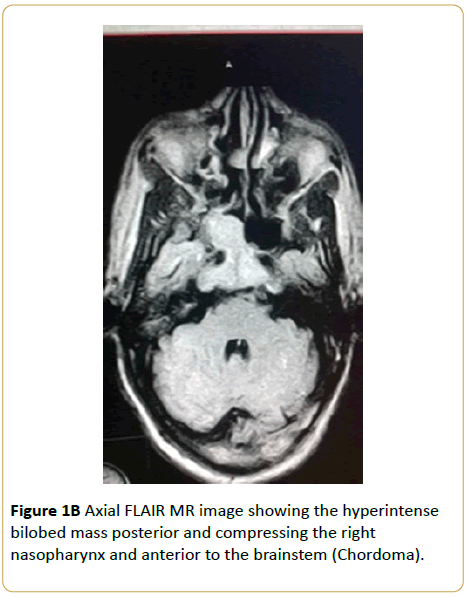
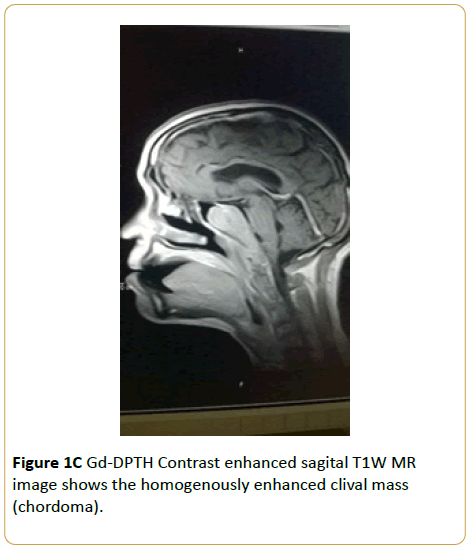
Brain MRI of a 60-year-old woman who presented with headache and tongue weakness showed that the clivus has been replaced by a T1W isointense and T2W hyperintense soft tissue mass with heterogenous enhancement. A diagnosis of chordoma was made (Figures 1A-1C).
Figure 1A: Brain T1W sagital MR image shows the clivus has been replaced by an isointense soft tissue mass (Chordoma) in a 60-year-old woman.
Figure 1B: Axial FLAIR MR image showing the hyperintense bilobed mass posterior and compressing the right nasopharynx and anterior to the brainstem (Chordoma).
Figure 1C: Gd-DPTH Contrast enhanced sagital T1W MR image shows the homogenously enhanced clival mass (chordoma).
Case B
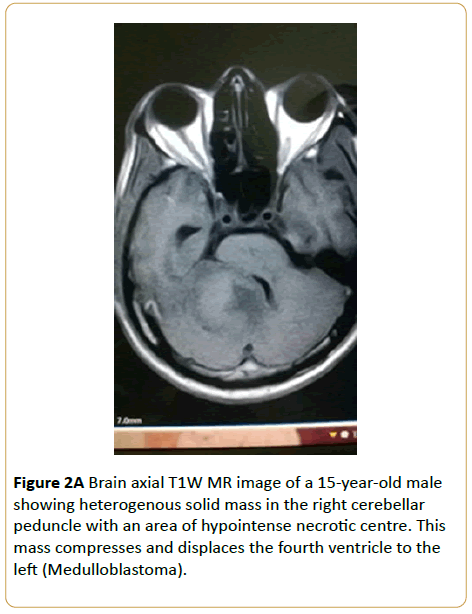
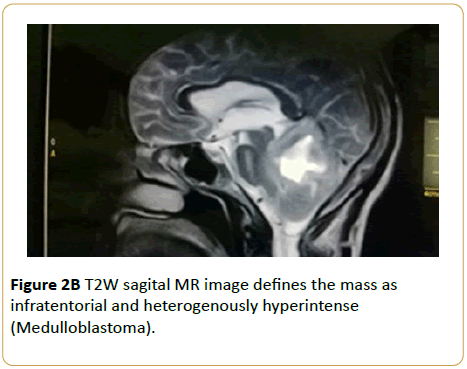
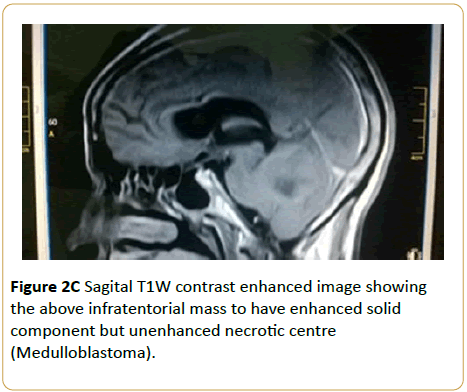
A 15-year-old male presented with headache and abnormal gait. Brain MRI showed T1W isointense solid infratentorial mass in the right cerebellar peduncle with a hypointense necrotic centre. This mass compresses and displaces the fourth ventricle to the left. Only the solid component enhanced (Medulloblastoma) (Figures 2A-2C).
Figure 2A: Brain axial T1W MR image of a 15-year-old male showing heterogenous solid mass in the right cerebellar peduncle with an area of hypointense necrotic centre. This mass compresses and displaces the fourth ventricle to the left (Medulloblastoma).
Figure 2B: T2W sagital MR image defines the mass as infratentorial and heterogenously hyperintense (Medulloblastoma).
Figure 2C: Sagital T1W contrast enhanced image showing the above infratentorial mass to have enhanced solid component but unenhanced necrotic centre (Medulloblastoma).
Case C
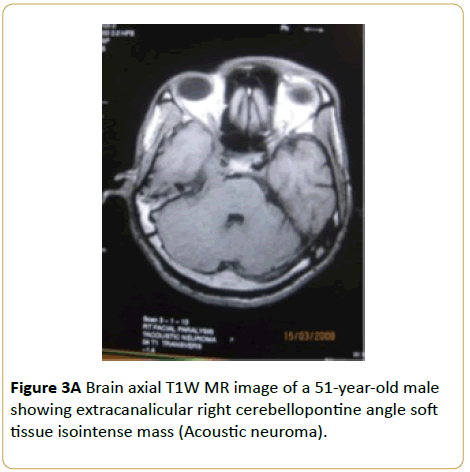
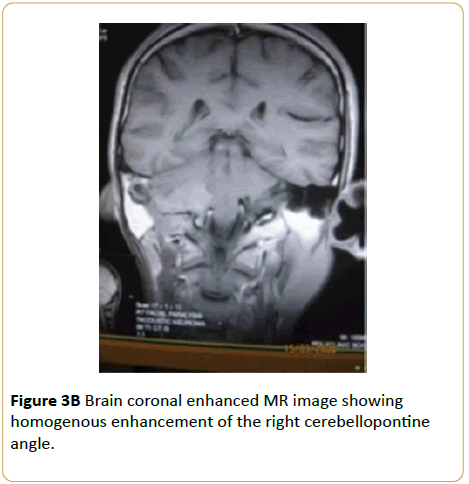
A 51-year-old male presented with right unilateral sensorineural hearing loss and disequilibrium. Brain MRI showed extracanalicular right cerebellopontine angle soft tissue T1W isointense, T2W hyperintense and enhancing mass (Acoustic neuroma) (Figures 3A and 3B).
Figure 3A: Brain axial T1W MR image of a 51-year-old male showing extracanalicular right cerebellopontine angle soft tissue isointense mass (Acoustic neuroma).
Figure 3B: Brain coronal enhanced MR image showing homogenous enhancement of the right cerebellopontine angle.
Case D
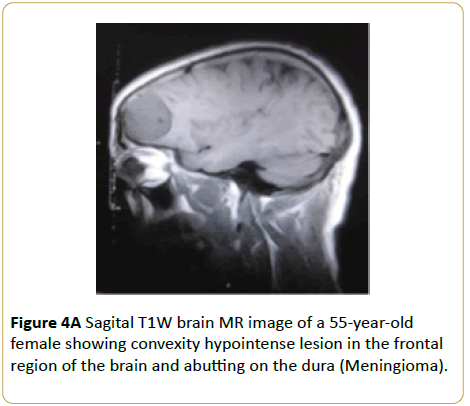
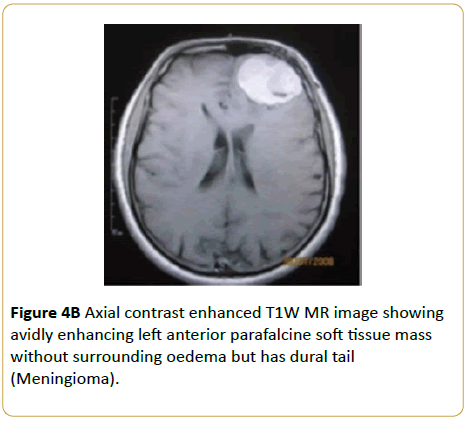
A 55-year-old female presented with persistent headache. Brain MRI showed a convexity T1W hypointense and T2W hyperintense frontal parafalcine soft tissue mass without surrounding oedema (Meningioma) (Figures 4A and 4B).
Figure 4A: HPLC chromatogram of the nine reference compounds in 50% aqueous methanol, measured at 370nm. Retention times for rutin, sutherlandin A, sutherlandin B, kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside, sutherlandin C, sutherlandin D, quercitrin, quercetin and kaempferol were 11.9, 12.7, 13.8, 15.3, 16.2, 17.0, 18.0, 26.2 and 28.1 minutes, respectively.
Figure 4B: HPLC chromatogram of the nine reference compounds in 50% aqueous methanol, measured at 370nm. Retention times for rutin, sutherlandin A, sutherlandin B, kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside, sutherlandin C, sutherlandin D, quercitrin, quercetin and kaempferol were 11.9, 12.7, 13.8, 15.3, 16.2, 17.0, 18.0, 26.2 and 28.1 minutes, respectively.
Case E
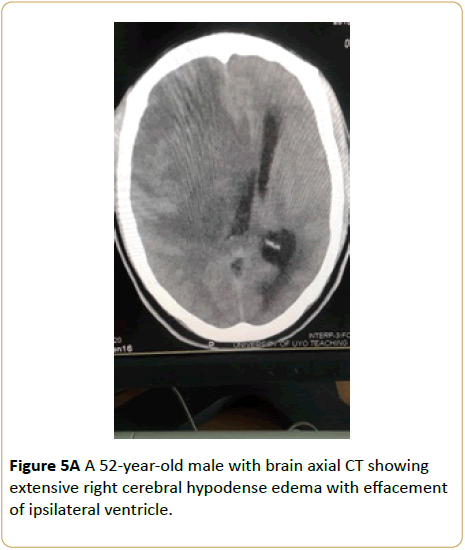
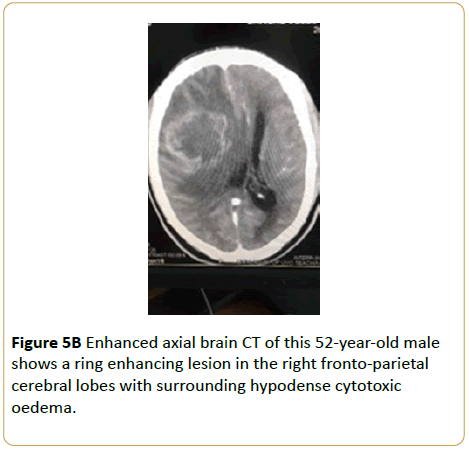
A 52-year-old male presented with occassional loss of consciousness and severe headache. Brain CT showed extensive right cerebral edema with effacement of ipsilateral lateral ventricle. Enhanced CT image revealed a ring enhancing lesion in the right fronto-parietal cerebral lobes with surrounding hypodense cytotoxic oedema. (Glioma multiforme) (Figures 5A and 5B).
Figure 5A: A 52-year-old male with brain axial CT showing extensive right cerebral hypodense edema with effacement of ipsilateral ventricle.
Figure 5B: Enhanced axial brain CT of this 52-year-old male shows a ring enhancing lesion in the right fronto-parietal cerebral lobes with surrounding hypodense cytotoxic oedema.
Conclusion
We have carefully chosen five intracranial tumours of diverse locations to highlight the import of neuroimaging in diagnosis. These tumours are intracranial chordoma (a parasellar tumour), medulloblastoma (infratentorial tumour), acoustic neuroma (cerebello-pontine angle tumour), meningioma (a predominantly convexity tumour) and glioblastoma multiforme (supratentorial tumour). Since this is a pictorial representation, we will only take a cursory look at the neuroimaging features of these tumours.
17593