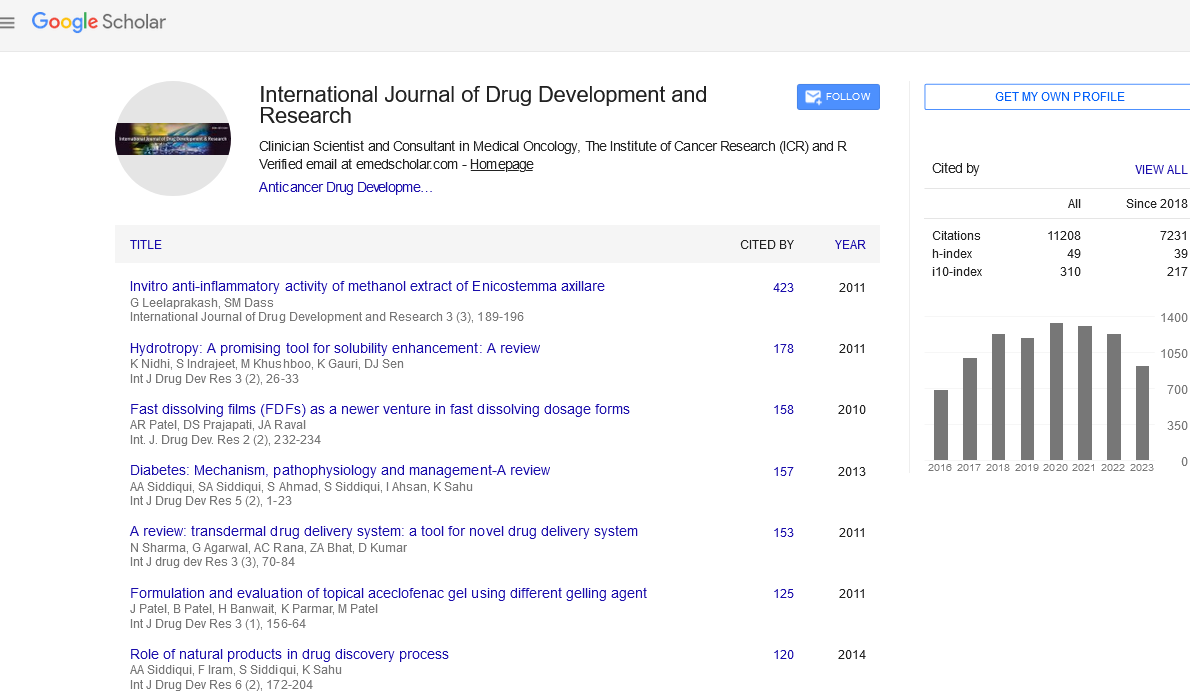
Preliminarily phytochemical and antimicrobial investigation of the crude extract of the leaves of parkinsonia aculeata leaves showed the presence tannin, alkoloids,glycoside,terpenoids flavonoid, terpenes, streriods volatile oil and saponin.The presence of these secondary metabolites indicates the pharmacological property of the plant leaves. The crude ethanolic extract, petroleum ether and chloroform extracts were also found to inhibit pseudomonas aeruginosa, streprococcus faecalis staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, and salmonella typhimurium and klebsiella sp. The tin layer chromatography(TLC) revealed four spots, three spots and two spots for ethanol, petroleum ether and chloroform extract respectively using ethyl acetate: hexane solvent mixture. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of the crude extracts were determined for the various organisms which ranged between 35 and 50 mg/ml while the minimum bactericidal concentration ( MBC) ranged between 45 and 60 mg/ml. parkinsonia aculeata could be a potential source of antimicrobial agents.
5335