Research Article - (2022) Volume 14, Issue 5
Reference values of left ventricular mechanical dispersion assessed by two-dimensional longitudinal speckle-tracking strain in normal subjects
Cardiologist/Radiologist, Aversi Clinic, Tbilisi, Georgia, USA
Department of Internal Medicine, Aversi Clinic, Tbilisi, Georgia, USA
*Correspondence:
David Maisuradze, Cardiologist/Radiologist, Aversi Clinic, Tbilisi, Georgia,
USA,
Email:
Received: 25-Apr-2022, Manuscript No. ipaom-22-12771;
Editor assigned: 28-Apr-2022, Pre QC No. P-12771;
Reviewed: 17-May-2022, QC No. Q-12771;
Revised: 22-May-2022, Manuscript No. R-12771;
Published:
30-May-2022
Abstract
Left ventricular mechanical dispersion measured by two dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography (MD) is a novel strain derived parameter that reflects temporal cardiac contraction heterogeneity and has consequently gained attention as a predictor of increased arrhythmic risk in selected cardiac diseases.
Keywords
Left ventricular; LVEF; Mechanical
Abbreviations
MD: Mechanical Dispersion; LV: Left Ventricle; GLS: Global Longitudinal Strain; VA: Ventricular Arrhythmia; SCD: Sudden Cardiac Death; VT: Ventricular Tachycardia; TAVI: Trans Aortic Valvular Intervention
Introduction
LV mechanical dispersion along with LV GLS may provide additional valuable risk markers of VA and SCD in pre dialysis and dialysis patients [1,2]. Mechanical dispersion by strain echocardiography may be a marker of ventricular arrhythmias beyond EF. Mechanical dispersion was increased in those with any arrhythmic events (nsVT or sustained VT) vs. patients free of arrhythmic events [3,4]. Mechanical dispersion was pronounced in patients after TAVI. Mechanical dispersion was independently associated with mortality and could confer additional risk requiring closer post procedural follow-up [5]. LV mechanical dispersion assessed by speckle tracking echocardiography increases significantly with severity of AS and is significantly associated with all-cause mortality. However, LVEF may not recover after AVR and patients may remain symptomatic. Speckle tracking echocardiographic parameters of LV shortening and mechanical dispersion have been proposed to detect LV systolic dysfunction at an earlier stage than LVEF and are related to the presence of myocardial fibrosis on cardiac magnetic resonance [6]. There is increasing interest in assessment of left ventricular mechanical dispersion but normal data are limited [3].
Methods
We prospectively studied 50 adult outpatients with normal diastolic function and normal LVEF. A complete two dimensional echocardiography examinations was performed, including speckle tracking with measurements of LV systolic global longitudinal strain and Mechanical Dispersion on a commercially available system Epiq7. Time intervals from start Q/R on electrocardiogram to peak negative strain during the study were assessed. Mechanical dispersion was defined as the standard deviation of this time interval from 16 left ventricular segments, reflecting myocardial contraction heterogeneity. p-value is significant at <0.05
Results
The values of GLS among the studies varied from/-16.7/to/-24.2%/(Mean GLS = -19 ± 1.59%), p.0.0001, (T.N1) the values of MD varied from 1.4 to 33.6 (mean MD-14. 4 ± 8.5), p.0.0002 (Fig. 1.)
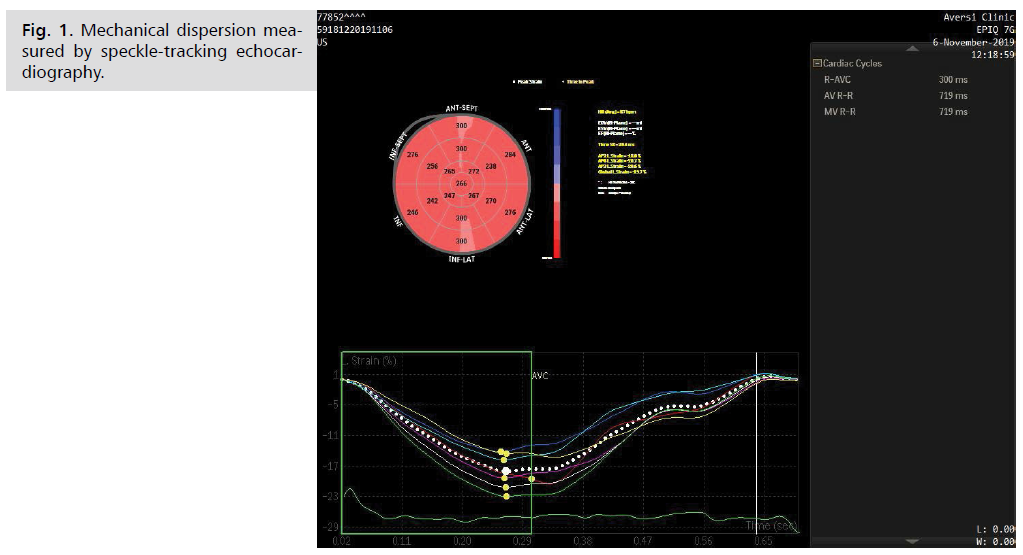
Fig 1: Mechanical dispersion measured by speckle-tracking echocardiography.
The values of EF varied from 55% to 63% (mean EF-58 ± 2.5), p.0.0004 Age of patients varied from 16 to 52, (mean age-60.8), n=52%, 26 were male, n=48%, 24 were female (Tab. 1.).
| Factors |
Mean ± SD |
P- value |
| Age |
60.8 ± 14 |
0.25 |
| GLD |
19 ± 1.59 |
<0.0001 |
| MD |
14.4 ± 8.5 |
<0.00001 |
| EF |
58 ± 2.5 |
0.008 |
*SD=Standard Deviation, P value is signification at <0.05, EF: Ejection Fraction
Tab. 1. N1 Mechanical Dispersion data (N=50) in Normal subject.
Conclusion
This study determined values of mechanical dispersion in subjects with a normal EF and normal GLS. Further studies are needed to clarify the relation between mechanical dispersion and different cardiac disease
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
All authors declare that the material has not been published elsewhere, or has not been submitted to another publisher.
Data Availability
Authors declare that all related data are available concerning researchers by the corresponding author's email.
Acknowledgments
None.
REFERENCES
- Rodriguez-Zanella H, F Boccalini, E Secco, et al. Left ventricular mechanical dispersion measured with two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography predicts severe arrhythmic events in patients with ischemic and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy." Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017:iii80-1.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
- Hensen Liselotte CR, Kathleen Goossens, Tomaz Podlesnikar, et al. Left ventricular mechanical dispersion and global longitudinal strain and ventricular arrhythmias in predialysis and dialysis patients. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2018;31:777-783.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
- Aagaard EN, Kvisvik B, Pervez MO. Left ventricular mechanical dispersion in a general population: data from the Akershus Cardiac Examination 1950 study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020; 21:183-190.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
- Haugaa, Kristina H, Nina E Hasselberg. Mechanical dispersion by strain echocardiography: A predictor of ventricular arrhythmias in subjects with lamin A/C mutations. JACC Cardiovascular Imaging .2015: 104-106.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
- Klaeboe LG, Brekke PH, Aaberge L, et al. Impact of transcatheter aortic valve implantation on mechanical dispersion. Open Heart. 2019 ;7:e001199.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at
- Prihadi EA, Vollema EM, Ajmone Marsan N , et al. Determinants and prognostic implications of left ventricular mechanical dispersion in aortic stenosis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019; 20:740-748.
Google Scholar, Crossref, Indexed at