Key words
|
| |
| Pyrazolo-triazine, Antibacterial, Antifungal, Benzoylation |
| |
EXPERIMENTAL PART
|
| |
|
Synthesis
|
| |
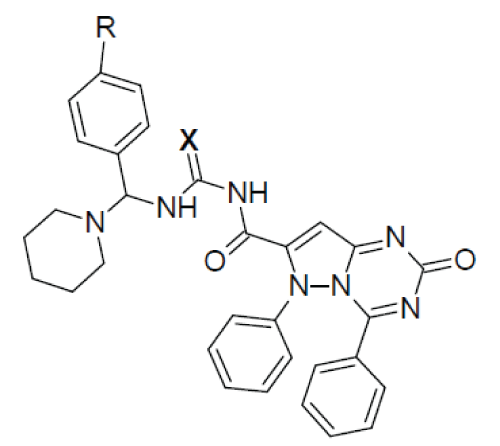
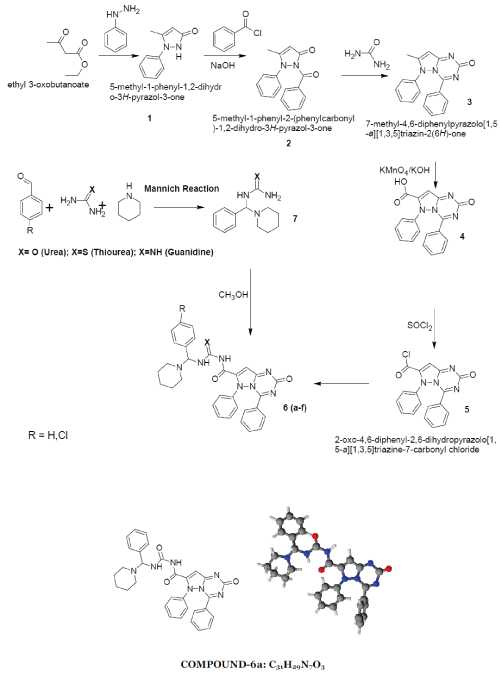
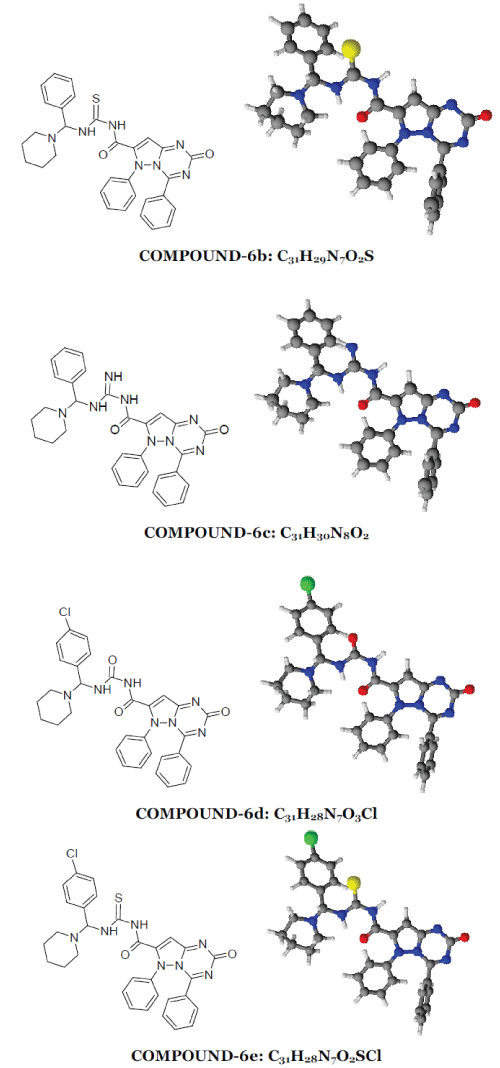
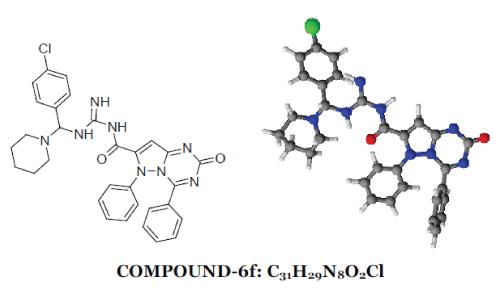
| 2-oxo-4,6-diphenyl-2,6-dihydropyrazolo[1,5- a][1,3,5]triazine-7-carbonyl ring system has been synthesised by the reaction between phenyl hydrazine and ethyl acetoacetate produced pyrazolone moiety (1) which on benzoylation produced benzoyl derivative (2) which on condensation with urea produced 7-methyl-4,6- diphenylpyrazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazin-2(6H)-one ring (3) which on alkaline oxidation with KMnO4/KOH produced carboxylic moiety (4). Treatment with thionyl chloride of (4) produced acid chloride derivative (5). This on condensation with Mannich base produced by benzaldehyde and p-chloro benzaldehyde with urea/thiourea/guanidine (7) produced the desired moiety (6). 1-6 |
| |
| COMPOUND-1 (X=O; R=H, C31H29N7O3): UV: λ (nm): 240, IR [cm-1] (KBr): >C=O (1745), Cyclic >C=O (1710), Mass Spectra [m/z]: M+=546.9, 1HNMR: δ: 1.25 (s, 1H, -CH), 4.2 (s, 1H, -NH), 7.2-7.8 (m, 15H, Ar-H) |
| |
| COMPOUND-2 (X-S; R=H, C31H29N7O2S): UV: λ (nm): 219, IR [cm-1] (KBr): C=S (1292), >C=O (1708), Cyclic >C=O (1691,), Mass Spectra [m/z]: M+=562.7 |
| |
| COMPOUND-3 (X=NH; R=H, C31H30N8O2): UV: λ (nm): 220, IR [cm-1] (KBr): -C=N (1635), -NH (bending) (1550), Cyclic >C=O (1710), Mass Spectra [m/z]: M+=546.9 |
| |
| Compound-4 (X=O, R=Cl, C31H28N7O3Cl): UV: λ (nm): 218, IR [cm-1] (KBr): >C=O (1718), Cyclic >C=O (1641), -C-Cl (880), Mass Spectra [m/z]: M+=582.3, 1H-NMR: δ: 2.5 (s,-CH), 3.2 (d, 1H,- NH), 7.2-7.72 (m, 14H, Ar-H) |
| |
| COMPOUND-5 (X-S; R=Cl, C31H28N7O2SCl): UV: λ (nm): 220, IR [cm-1] (KBr): C=S (1244), >C=O (1679), Cyclic >C=O (1650), -C-Cl (831) Mass Spectra [m/z]: M+=597.6 |
| |
| COMPOUND-6 (X=NH; R=Cl, C31H29N8O2Cl): UV: λ (nm): 217, IR [cm-1] (KBr): -C-Cl (825), -NH (3251), Cyclic >C=O (1647), Mass Spectra [m/z]: M+=581.5 |
| |
|
Molecular Design
|
| |
 |
| |
| X=O (Urea); X=S (Thiourea); X=NH (Guanidine) The synthesised compounds were characterised by N% and spectral datas and antimicrobial and antifungal screening has been performed by zone of inhibition studies and MIC calculation with standard antibiotic/antifungal drug against (gram+ve) and (gram–ve) bacteria and fungal strains on agar media after 24 hours incubation at 37°C for antimicrobial activity and 24°C for antifungal activity. Gram positive: Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 9144, Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633, Gram negative: Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Fungal strain: Candida albicans ATCC 10231 |
| |
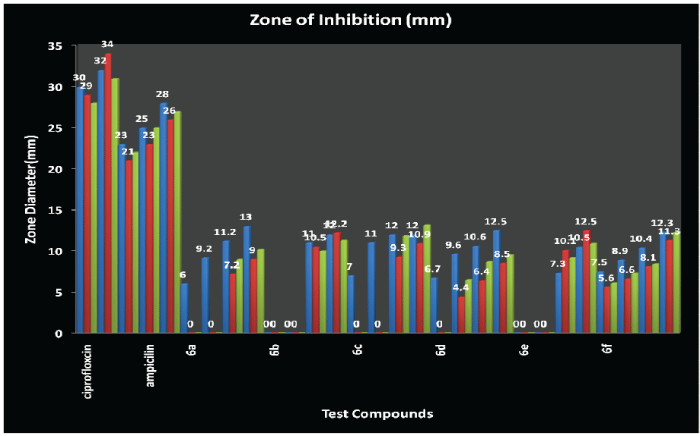
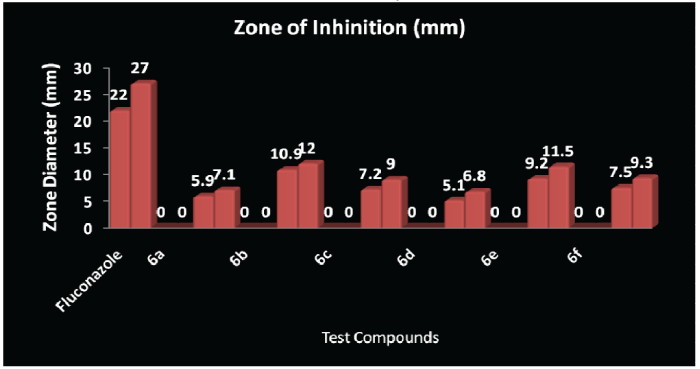
| It has been observed that the Compound-3 (X=NH) showed maximum antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Compound-1 (X=O) against Bacillus subtilis and Compound-5 (X=S) against Staphylococcus aureus. Oxygen and Sulphur has two lone pairs whereas Nitrogen has one lone pair of electrons but the electronegativity of Oxygen (X=O; 3.5), electronegativity of Sulphur (X=S; 2.4) and electronegativity of Nitrogen (X=N+H; 3.1+2.2=5.3). MIC value of all the compounds have been found as 250Hg as Minimum Inhibitory Concentration by serial dilution method and MIC of Ampicillin is 25Hg and for Fluconazole is 5.5Hg. |
| |
|
Scheme
|
| |
 |
| |
 |
| |
 |
| |
ANTIMICROBIAL/ANTIFUNGAL
|
| |
|
SCREENING
|
| |
| The microbiological assay is based upon a comparison of inhibition of growth of microorganisms by measured concentrations of test compounds with that produced by known concentration of a standard antibiotic. Two methods generally employed are turbidometric (tube-dilution) method and filter paper method. In the turbidometric method inhibition of growth of microbial culture in a uniform dilution of antibiotic in a fluid medium is measured. It is compared with the synthesized compounds. Here the presence or absence of growth is measured. The cylinder plate method depends upon diffusion of antibiotic from a vertical cylinder through a solidified agar layer in a Petridis or plate to an extent such that growth of added micro-organisms is prevented entirely in a zone around the cylinder containing solution of the antibiotics.The cup-plate method is simple and measurement of inhibition of microorganisms is also easy. Here we have used this method for antibacterial screening of the test compounds.7-10 |
| |
|
Name of Microorganism
|
| |
| Gram +Ve microorganisms |
| |
| Staphylococcus aureus (MTCC No. 96) |
| |
| Bacillus subtilis (MTCC No. 121) |
| |
| Gram -Ve microorganisms |
| |
| Escherichia coli (MTCC No. 521) |
| |
|
Preparation of medium:-
|
| |
| Nutrient agar 2% |
| |
| Peptone 1% |
| |
| Beef extract 1% |
| |
| Sodium chloride 0.5% |
| |
| Distilled water up to 100ml |
| |
| All the ingredients were weighed and added to water. This solution was heated on water bath for about one and half-hour till it became clear. This nutrient media was sterilized by autoclave. |
| |
|
Apparatus:-
|
| |
| All the apparatus like Petridishes, pipettes, glass rods, test-tubes etc. were properly wrapped with papers and sterilized in hot air oven. |
| |
|
Antimicrobial screening method
|
| |
| • All the Petri dishes were sterilized in oven at 160°C for I hour. |
| |
| • Agar media, borer and test solutions were sterilized in autoclave at 121°C at 15psi. |
| |
| • Molten sterile agar was poured in sterile petri dishes asceptically. |
| |
| • The agar was allowed to cool and the bacterial suspension was poured into the petridishes asceptically. |
| |
| • Placing the sterile filter paper discs in the agar plate and solution of the compounds was added by using pipette (0.1ml) in appropriate four quadrants of petridishes aseptically. |
| |
| Petridishes were incubated at 37°C for antimicrobial and 24ºC for antifungal for 24 hrs and observed the zone of inhibition.11-16 |
| |
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
|
| |
| Structure activity relationship studies of substituted Mannich bases of 2-oxo-4,6-diphenyl-2,6- dihydropyrazolo-[1,5-a] [1,3,5]-triazine-7-carbonyl ring system with variable electronegative atoms (urea/thiourea/guanidine) for antimicrobial and antifungal activity showed that the inhibition of microbial growth is as follows: |
| |
| Antimicrobial activity profile of the synthesised compounds is as follows: Compound-6b(E.coli)>Compound-6a(B.subtilis)> Compound-6d(B.subtilis)=Compound-6e (S.aureus)>Compound-6f(B.subtilis)=Compound- 6f(E.coli)>Compound-6b(S.aureus)>Compound-6b (B.subtilis)=Compound-6c(B.subtilis)>Compound- 6c(E.coli)>Compound-6b(E.coli)=Compound- 6f(S.aureus)>Compound-6a(B.subtilis)>Compound- 6b(B.subtilis)=Compound-6c(B.subtilis)> Compound-6c(S.aureus)=Compound-6e(E.coli) >Compound-6d(B.subtilis)>Compound-6b (S.aureus)=Compound-6e(B.subtilis)>Compound-6f (B.subtilis)>Compound-6a(E.coli)>Compound-6e (S.aureus)>Compound-6d(B.subtilis)>Compound- 6d(E.coli)>Compound-6c(S.aureus)>Compound-6a (B.subtilis)>=Compound-6a(E.coli)>Compound-6f (B.subtilis)>Compound-6d(E.coli)>Compound-6d (S.aureus)>Compound-6f(E.coli)>Compound-6f (S.aureus)>Compound-6f(B.subtilis)>Compound-6e (B.subtilis)=Compound-6f(E.coli)>Compound-6a (S.aureus)>Compound-6c(B.subtilis)>Compound-6d (B.subtilis)>Compound-6f(S.aureus)>Compound-6d (E.coli)>Compound-6d(S.aureus)>Compound-6f (E.coli)>Compound-6a(B.subtilis)>Compound-6f (S.aureus)>Compound-6d(S.aureus). |
| |
| Antifungal activity profile of the synthesised compounds is as follows: Compound-6b(C.albicans)>Compound-6e (C.albicans)>Compound-6b(C.albicans)> Compound-6f(C.albicans)>Compound-6e (C.albicans)>Compound-6c(C.albicans)> Compound-6f(C.albicans)>Compound-6c (C.albicans)>Compound-6d(C.albicans)> Compound-6a(C.albicans)>Compound-6a (C.albicans)> Compound-6d(C.albicans). |
| |
| CONCLUSION: It has been observed that the Compound-3 (X=NH) showed maximum antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Compound-1 (X=O) against Bacillus subtilis and Compound-5 (X=S) against Staphylococcus aureus. Oxygen and Sulphur has two lone pairs whereas Nitrogen has one lone pair of electrons but the electronegativity of Oxygen (X=O; 3.5), electronegativity of Sulphur (X=S; 2.4) and electronegativity of Nitrogen (X=N+H; 3.1+2.2=5.3). MIC value of all the compounds have been found as 250Hg as Minimum Inhibitory Concentration by serial dilution method and MIC of Ampicillin is 250Hg and for Fluconazole is 5.5Hg. |
| |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
|
| |
| The author Kaumil Navnitbhai Modi is thankful to the project guide Prof. Dr. Dhrubo Jyoti Sen and the staff members of Shri Sarvajanik Pharmacy College, Mehsana, Gujarat to fulfil the project successfully. All the authors are thankful to the Quality Assurance Department of Shri Sarvajanik Pharmacy College, Mehsana for UV and IR spectral data, Oxygen Healthcare, Ahmedabad for Mass spectral data and Punjab University for NMR spectral datas. |
| |
Tables at a glance
|
|
|
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
| HISTOGRAM 1 |
HISTOGRAM 2 |
|
| |