Keywords
Chronic kidney disease; creatinine; Diabetes mellitus; estimated glomerular filtration rate; MDRD equation
Introduction
In 1999, the World Health Organization (WHO) [1] defined diabetes mellitus as “a metabolic disorder of multiple etiologies, characterized by chronic hyperglycemia with disturbances of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both.
The effects of diabetes mellitus (DM) include long-term damage, dysfunction and failure of various organs [1]. Thus, the metabolic abnormalities of diabetes result from inadequate insulin action on target tissues, due to deficient insulin secretion or insensitivity to insulin action, or a combination of both [2,3].
Diabetes is an important cause of death, illness, and disability across the world. By 2010 it is estimated that 250 million people worldwide will suffer from diabetes [4]. Diabetes substantially increases the risk of blindness, renal diseases, coronary arterial disease, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral vascular disease [5,6]. As Diabetic nephropathy is a major cause of death among people with diabetes and an important cause of morbidity and increased health care costs due to diabetes.
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by absolute (type 1) or relative (type 2) insulin insufficiency. Patients with diabetes can develop kidney disease and about one-third develop diabetic nephropathy, which accounts for almost half of new ESRD cases [7].
Diabetes mellitus is becoming a major health problem in Saudi Arabia. Changes in the lifestyle of the population are thought to be important factors in the increase of its prevalence [8,9], which exceeded 23% [10,11].
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus in the Saudi population is high and 90% of diabetics suffer from Type II DM. An epidemiological study of Saudi subjects aged 15 years or older, from different regions of the kingdom found that the ageadjusted prevalence of DM (using WHO criteria) was higher in urban areas (males 12%, females 14%) than rural areas (males 7%, females 7.7%) [12].
The highest prevalence was in urban females aged 51–60 years (49%). In rural females of similar age the prevalence was 29%. Some 56% of those found to be diabetic in this survey had no prior knowledge that they had DM. In another survey, it was found that 17% of those aged 30 years or older had DM [13].
Diabetes is the most common cause of kidney failure, accounting for more than 40 percent of new cases. Even when drugs and diet are able to control diabetes, the disease can lead to nephropathy and kidney failure [14].
Nor can they explain fully the interplay of factors leading to diabetic nephropathy-factors including heredity, diet, and other medical conditions, such as high blood pressure. They have found that high blood pressure and high levels of blood sugar increase the risk that a person with diabetes will progress to kidney failure [14].
The incidence of diabetes has reached epidemic proportions throughout the world, with an expected doubling in the number of patients with type II diabetes in the next 25 years [15]. This, in turn, will lead to an increased incidence of diabetic nephropathy, with approximately 30% progressing to stage 5 CKD.
CKD prevalence increases with age, and men with CKD have a more rapid decline in renal function and progression of their renal disease than women [16,17].
There is no data available on the incidence of diabetic renal disease in Saudi diabetics. What is known is that the vast majority of Saudi diabetics entering dialysis (96%) are of Type II. In a study of a diabetic outpatient clinic, 12.8% of patients had dipstick proteinuria and of the remaining patients 41.3% had microalbuminuria [12].
Al-Khader (2001) has followed 28 patients with Type II DM complicated by diabetic nephropathy (indicated by presence of normal size kidney, presence of diabetic retinopathy and proteinuria, and confirmed by renal biopsy). He has found that the mean plasma creatinine in these patients at the start of observation was 180±64.7 μmol/l. Mean age was 61.2 years (±7.4). There were 16 males and 12 females. Twenty-four (85.9%) had progression of their renal disease over 19.7±9.4 months of follow-up. Of these 24, 12 required dialysis (50%) after a mean follow-up period of 18 months. The remaining patients doubled their creatinine (from a mean of 180.2 to a mean of 349.1±149) over a 19.7-month period. Thus, of the 28 patients who began the study, 42.8% became dialysis dependent and 42.8% doubled their creatinine; only 15% had a stable.
The aim of the present work is to assess the renal function using the estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) in the case of Diabetes Mellitus patients.
Patients and Methods
Patients
The study was conducted throughout the Northern Province of Saudi Arabia, Skaka, Al-Jouf. DM Saudis patient from Prince ABDULLRAHMAN AL SODAIRY HOSPITAL-SKAKA were chosen randomly.
Data was collected under the following headings: age, sex, serum Glucose, urea, and creatinine level, from 98 case notes in the month of Rabi-II (April 2009). They were divided into different age groups and also separated into male and female groups.
These total 98 DM Saudis patients comprised of 50 males and 48 females (male-female ratio of nearly 1:1). There ages were ranging from 30 to 56 years (mean 42.9 years in males and 40.4 years in females). There were 42 patients between 30 to 39 years, 32 patients between 40 to 49 years, and 24 patients more than 50 years.
Methods
Glucose
The glycemia values were obtained from the laboratory of Biochemistry of the Prince Abdurahman Al- Sodiry Hospital- Skaka.
Urea
Urea liquicolor Kit (Human) and a semi-automatic clinical chemistry analyzer (microlab 300) were used to determine the serum urea concentration in the samples.
Creatinine
Serum creatinine was measured by a liquicolor Kit (Human), using the compensated kinetic Jaffe assay. It’s a photometric colorimetric test for endpoint measurement of creatinine, method with deproteinisation.
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is an estimate of the filtering capacity of the kidneys. It is usually expressed as milliliters (mL) per minute (min) and adjusted to a “standard” body size with a surface area of 1.73 meters2. The normal GFR ranges between 95 -120 mL/min/1.73m2 but it varies depending on age, gender and body size.
There are many formulae for estimating GFR [18,19]. The two best known are the Cockcroft and Gault and the formulae derived from the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) study [20]. The Cockcroft and Gault estimate requires a weight, information is not routinely available in the biochemistry laboratory.
Cockroft-Gault formula:
(140 - age [yr]) x body wt [kg] x K/serum creatinine [mumol/L])
K = 1.23 for men, 1.05 for women
MDRD formula:
GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) = 175 x [serum creatinine (SI) x 0.011312]-1.154x [age}-0.203 x [1.212 if black] x [0.742 if female]
Estimated GFR was calculated using the MDRD equation and the MDRD-GFR Calculator program: (https://www.kidney.org/ professionals/KDOQI/gfr_calculator.cfm).
The numerical data was presented as mean and SEM. Results were considered statically significant if P-value is less than 0.05.
Results
Repartition of D. M. Patients According to Glucose Level
According to glucose levels, we have defined 3 groups of D.M patients: Group I: glucose level < 200 mg/dl, Group II: glucose level 200 – 300 mg/dl and Group III: glucose level > 300 mg/dl (Table I).
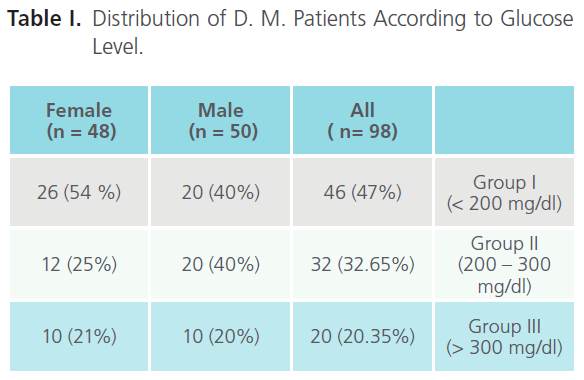
Table I: Distribution of D. M. Patients According to Glucose Level.
Table I summarize the repartition of D.M. patient, according to serum glucose levels. We observed that the group I had the largest number of patients, in the case of male and female. We note a difference between male and female, in the case of male the group I and II are the most representative, while group I in female.
Repartition of D.M. patients according to age
The patient’s ages range from 30 years to 56 years with a mean age of 41.65 (SD±11.16 years). For males, the mean age was 42.9 years, and for females, 40.4 years. There were 42 patients between 30 to 39 years, 32 patients between 40 to 49 years, and 24 patients more than 50 years. The study sample had a sex ratio of nearly 1:1.
According to age of the DM-patients, three groups were defined as follow: Group 1: 30-39 years, Group 2: 40-49 years and Group 3: ≥ 50 years.
As shown in table II, the majority of subjects in the sample involved in this study (n=98) are beyond middle age (n=42). According to age and sex of D.M. patients we observed that in the case of males, group-2 is the most representative group (22 patients), while in the female case group-1 (28 patients) was.
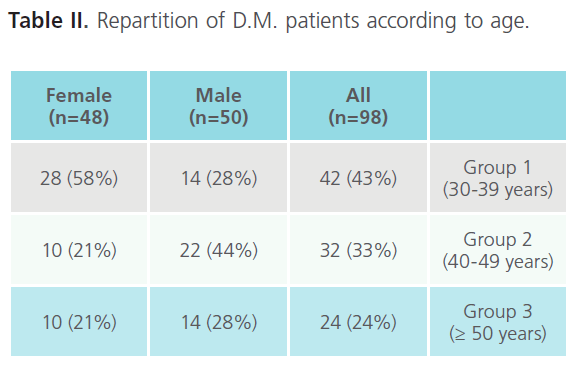
Table II: Repartition of D.M. patients according to age.
Prevalence of some biochemical variables according to glucose level
We have studied the prevalence of some biochemical variables in these 98 D.M. patients such as: serum glucose level, serum urea and serum creatinine.
The obtained results are summarized in Table III.
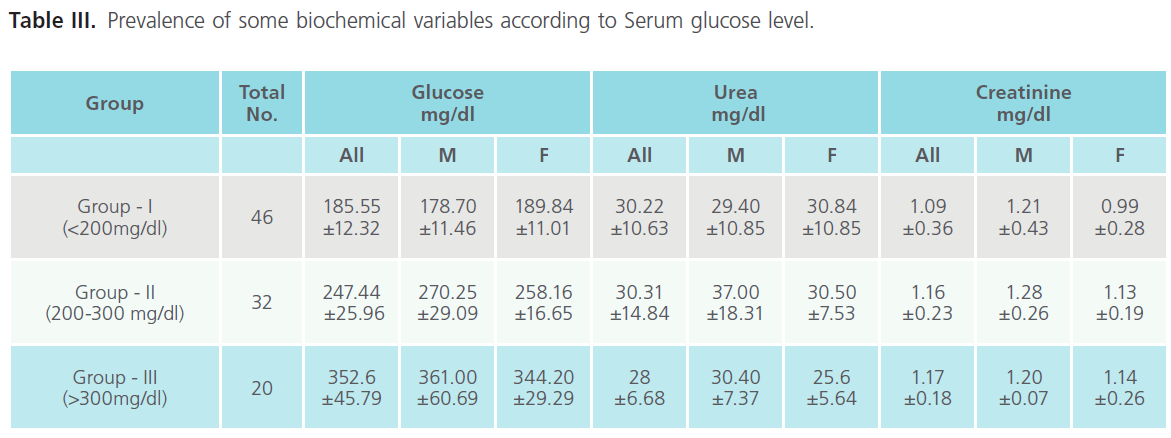
Table III: Prevalence of some biochemical variables according to Serum glucose level.
Regarding these results, we observed that:
1. The average value of serum glucose level is related negatively with the total number of patients. (As the serum glucose level increase the number of patients decrease).
2. The urea level in the three groups within a normal values ranging from (28-30.22 mg/dl). Group-III which presented the highest level of serum glucose level (352.6 mg/dL) presented the lowest value of urea (28 mg/dL).
3. In case of creatinine, all groups present above normal value. The creatinine values are positively correlated with serum glucose level.
Our results suggest that serum glucose level affects serum creatinine level in the case of diabetic patients.
4. The group-III which presents the highest value of serum glucose level is the most affected.
Our result suggests that as the serum glucose level increase the serum urea level decrease and the serum creatinine level increase. Interestingly, in the groups 1 and 2 we found that the males present higher serum urea and creatinine levels compared to females, but in the third group we observe the opposite result.
Prevalence of Some Biochemical Variables According to Age
The study of the prevalence of some biochemical variables in 98 D.M. patients according to age such as: serum glucose level, serum urea and serum creatinine are presented in table IV.
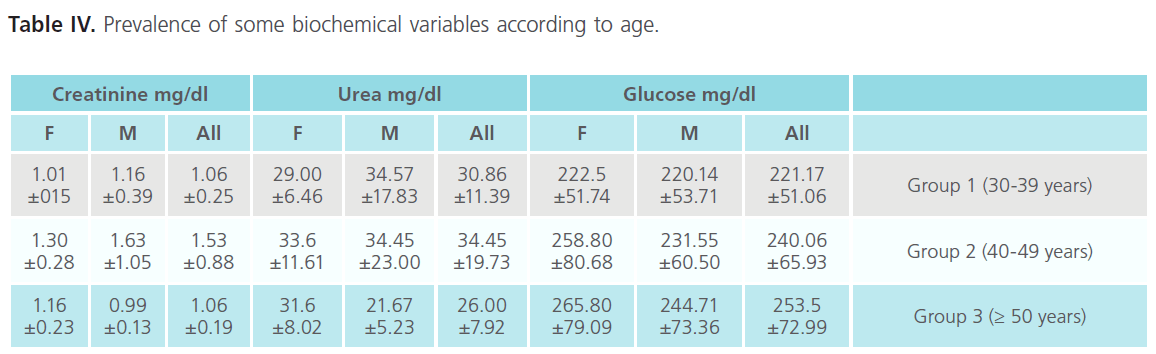
Table IV: Prevalence of some biochemical variables according to age.
Table IV shows that according to age the studied biochemical parameters are significant variable and some relationship can be established between them.
Based on the serum glucose level, we observed that:
1. The serum glucose level is positively correlated with age in the case of all, male and female groups. The oldest patients (group 3) present the highest value of serum glucose level.
2. All the female groups present higher values of serum glucose level than male groups.
3. the case of (All, Male and Female), group 2 present the highest value of urea (34.88 mg/dl) and group 3 the lowest value (26 mg/dl), while group 1 has a medium value (30.86 mg/dl).
4. In case of male, group 1 exhibit highest serum urea value (34.57 mg/dl) and group 3 the lowest value (21.67 mg/dl). We observe that there is no significant difference between group 1 (34.57) and 2 (34.45) while there is a significant difference with group 3 (21.67)
5. According to sex, male exhibit higher values than females in group 1 and 2, while in the group 3 female’s values are higher than males.
6. In all group, the group 2 present the highest value (1.53), while group 1 and 3 present same value (1.06).
7. In both male and female we observe that group 2 present the highest value (1.63, 1.30), so it is clear that males have higher value than females.
8. In the case of male, (group 3), and female (group 1) the lowest values of serum urea and creatinine levels are registered.
In spite of higher serum glucose level the urea value falls within normal range (10-50 mg/dl). Our result suggest that hyperglycemia has no effect on serum urea level so it seems that we cannot use it to evaluate renal function in the case of diabetic mellitus patients.
We observe that there is a positive correlation between creatinine and glucose. The group 2 presents the highest creatinine level, the same position was observed in case of male and female.
Our result shows that group 2 (40-49 years) present the higher value of both urea and creatinine, which seems to be due to renal function disorders.
Asses of Renal Function using eGFR
We have calculated the eGFR using the eGFR calculator program (https://www.kidney.org/professionals/KDOQI/gfr_calculator. cfm), in order to evaluate the effect of Diabetes Mellitus on the renal function.
Distribution of eGFR Values According to Glucose Level
It is clear from the table V below, as glucose level increase the eGFR decrease which increases the risk factor to CKD. Most patients fall in group I and II, where only one fifth of patients falls in group III. According to sex we observe that males present higher eGFR value than females.
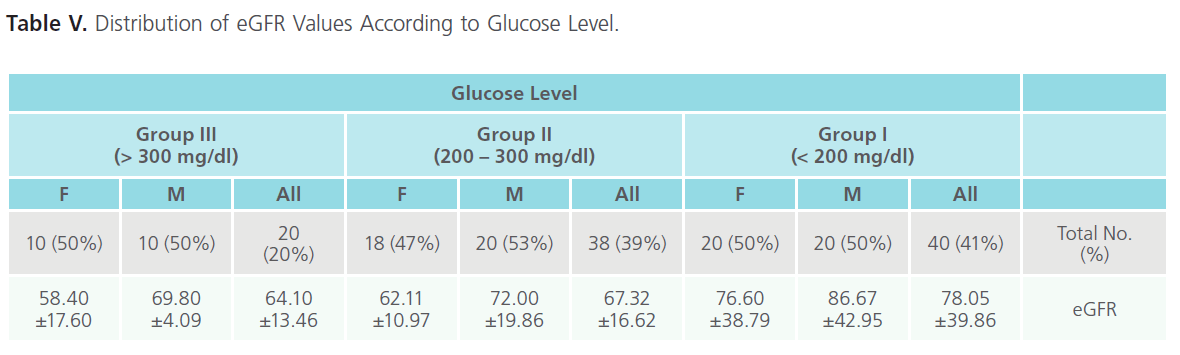
Table V: Distribution of eGFR Values According to Glucose Level.
Distribution of eGFR Values According to Age
According to age we observe that group 2 present the lowest eGFR value so it is more close to the CDK risk factor (Table VI).
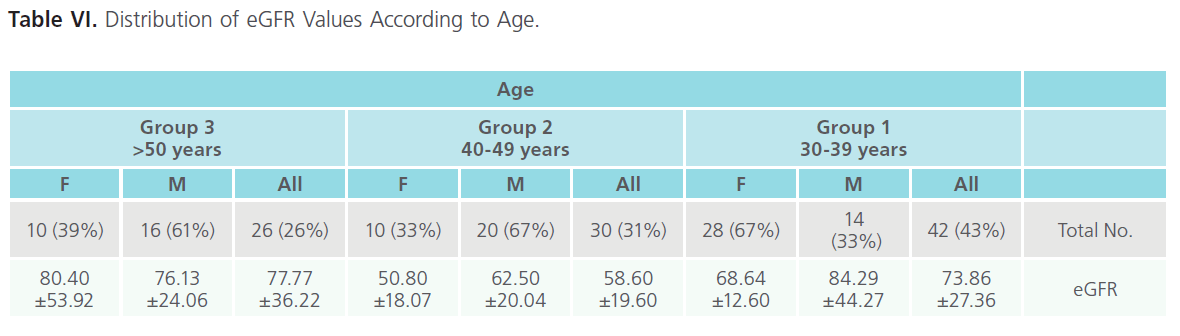
Table VI: Distribution of eGFR Values According to Age.
According to sex males have a significant higher values than females in group 1 and 2, while in group 3 no significant difference (Table VI).
Assess Renal Function According to staging CKD
More than half of the patients (55%) falls in CKD stage-2 (kidney damage with mildly reduced GFR), 16% in stage-1 (kidney damage with normal GFR), and 27% in stage-3 (moderately reduced GFR) (Table VII).
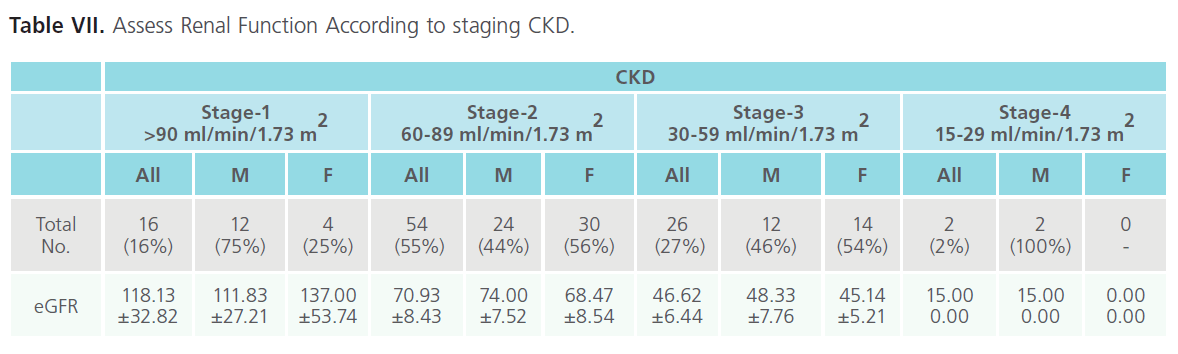
Table VII: Assess Renal Function According to staging CKD.
It is clear from our result that stage-2 more prevalence among the patients than other stages. According to sex, males exhibit more values than females in all stages except stage-1.
Discussion and Conclusion
Diabetes mellitus now is the major health problem in KSA. Changes in the life and eating habits of the population are important factor in the increase of its prevalence [8,9].
Multifaceted intervention programs aimed at delaying and preventing diabetic nephropathy using measures, such as screening, prevention, and the optimal treatment of hypertension and diabetes, are essential in the management of end state renal disease (ESRD). Lifestyle modifications are particularly important in KSA populations as they are at high risk of developing kidney disease because of increased social, environmental, and genetic factors, such as obesity, hypertension, cigarette smoking, and type II diabetes, as well as heightened responsiveness to increased salt intake. Screening and prevention programs need to be combined with initiatives in other areas, such as educational programs, improved access to healthcare, and policy changes to address societal issues and reimbursement.
There is no data available on the use of the eGFR in the hospital to assess the renal function in Saudis diabetics. What’s known is that the majority of Saudi diabetics entering dialysis (96%) are of type II [12].
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the renal function in the case of DM-patients using the eGFR. The results indicate that in the case of DM-patients, serum creatinine concentration an unreliable and insensitive marker for the presence of CKD. Our study has the advantage of revealing the magnitude of diabetes and CKD risk factors among this community.
According to serum glucose level, we note that the creatinine level, in all groups present above normal value, while in case of urea all groups within normal value. The creatinine values are positively correlated and urea values are negatively correlated with serum glucose level.
Kidney dysfunction affects the kidneys ability to clear creatinine from the blood. It would therefore seem reasonable to use serum creatinine concentration as an indicator of kidney function.
However, there is a wide range for serum creatinine in people with normal kidney function, because the production of creatinine is affected by: Age, Gender, Muscle mass and Diet [20].
This makes serum creatinine concentration an unreliable and insensitive marker for the presence of CKD. Using serum creatinine concentration alone to assess kidney function results in undiagnosed cases of CKD. Serum creatinine concentration, however, is useful for following the trend of kidney function, in an individual, over time [19,21].
Our results show that as glucose level increase, the eGFR decrease which. increase the risk factor to Chronic Kidney diseases (CKD) and males present higher eGFR value than females.
We have found that the serum urea level or creatinine can not be used alone to assess the renal function in the case of the DM patients, because the obtained levels are within normal values. We observed a decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) will result in an increased serum creatinine concentration.
Renal function, in nephrology, is an indication of the state of the kidney and its role in renal physiology. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) describes the flow rate of filtered fluid through the kidney. Creatinine clearance rate (CCr) is the volume of blood plasma that is cleared of creatinine per unit time and is a useful measure for approximating the GFR. Both GFR and CCr may be accurately calculated by comparative measurements of substances in the blood and urine, or estimated by formulas using just a blood test result (eGFR and eCCr) [22].
The results of these tests are an important gauge used in assessing excretory function of the kidneys. For example grading of chronic renal insufficiency and dosage of drugs that are primarily excreted via urine are based on GFR (or creatinine clearance).
It is commonly believed to be the amoun of liquid filtered out of the blood that gets processed by the kidneys. Physiologically, these quantities (volumetric blood flow and mass removal) are only related loosely. Clearance is a ratio of the mass generation and concentration at a steady state [22].
The rate of filtration across the glomerular membrane, the GFR, is the initiating step in many of the homeostatic functions of the kidney and it is widely accepted as the best overall measure of kidney function.
The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is an estimate of the filtering capacity of the kidneys. It is usually expressed as milliliters (mL) per minute (min) and adjusted to a “standard” body size with a surface area of 1.73 meters2. The normal GFR ranges between 95 -120 mL/min/1.73m2 but it varies depending on age, gender and body size.
Early in the course of diabetic nephropathy, changes in kidney hemodynamics and hyperfiltration lead to an increase in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) [23]. The progression of nephropathy involves characteristic pathologic changes, including accumulation of the extracellular matrix, widening of the glomerular basement membrane, arteriosclerosis, and some degree of interstitial fibrosis [24].
The results revealed that an eGFR calculated from serum creatinine is a practical way to detect, evaluate, and manage people with chronic kidney disease (CKD), especially people with risk factors for CKD-diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, or family history of kidney disease, in whom CKD might otherwise go undetected and untreated [25]. The use of the MDRD Study equation to estimate GFR is the best means currently available to more appropriately utilize serum creatinine values as a measure of kidney function.
The most effective way to assess renal function and gauge the need for further investigation or referral is by using eGFR, a formula-based calculation of GFR. Based on current evi dence, MDRD is the recommended equation, as it gives an estimate of GFR that is normalized to a body surface area of 1.73m2 and does not require the patient’s weight [20,26].
As Diabetic nephropathy are a major cause of death among people with diabetes and an important cause of morbidity and increased health care costs due to diabetes.
We recommended that laboratories calculate and report an eGFR using the MDRD formula with every request for serum creatinine concentration in adults. Automatic laboratory reporting of eGFR on each occasion a serum creatinine concentration is ordered, may significantly increase the likelihood of early detection of CKD. This will allow reducing the risks of kidney failure progression in D.M. patients.
1941
References
- Report of a WHO Consultation. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Geneva, World Health Organization 1999 (WHO/ NCD/NCS/99.2).
- Prevention of diabetes mellitus. Geneva, World Health Organization 1994; (WHO Technical Report Series, No. 844).
- International Diabetes Federation (2003). In: Diabetes atlas, 2nd ed. Brussels.
- Lloyd A, Sawyer W, Hopkinson P (2001). Impact of long-term complications on quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes not using insulin. Value Health, Sep; 4 (5):392-400.
- Thommasen HV, Berkowitz J, Thommasen AT, Michalos AC. Understanding relationships between diabetes mellitus and healthrelated quality of life in a rural community. Rural Remote Health Jul. 2005; 5 (3):441.
- Canadian Diabetes Association. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada. Canadian Journal of Diabetes 2007; 27 (Suppl. 2): 1-152. Available from: URL: https:// www.diabetes.ca/cpg2003
- US Renal Data System. USRDS 2000 Annual Report. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2000.
- Fatani HH, Mira SA, Elzubier AG. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in rural Saudi Arabia. Diabetes Care 1987; 10:180-3.
- Karim A, Ogbeid DO, Siddiqui S, Al-Khalia IM. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in Saudi community. Saudi Med J 2000; 21:438-42.
- El-Hazmi MAF, Warsy AS. Comparative study of hyperglycemia in different regions of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J.1989; 9:435-8.
- Al-Nozha MM, al-Maatouq MA, Al-Mazrou YY, Al-Harthi SS, Arafah MR, Khalil MZ. Diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 2004, Nov; 25 (11): 1603-10.
- Al-Khader Abdullah. Impact of diabetes in renal diseases in Saudia Arabia. Nenphral Dial Transplant 2001; 16: 2132-2135.
- El-Hazmi M, Warsy A, Al-Swailem A, Al-Meshari A. Diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in Saudi Arabia. Ann. Saudi Med. 1996; 16: 381-385.
- Nelson RG, Morgenstern H and Bennett PH. Birth weight and renal disease in Pima Indians with type 2 diabetes mellitus; Oct 1; 148 (7): 650-6.
- Atkins R. The epidemiology of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2005; 67 (suppl. 94): S14–S18
- Neugarten J, Acharya A, Silbiger S R. Effect of gender on the progression of nondiabetic renal disease: a meta-analysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000; 11(2): 319–329.
- Levey AS, Greene T, Kusek JW, Beck GJ. A simplified equation to predict glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000; 11:A0828.
- Rule AD, Larson TS, Bergstralh EJ, Slezak JM, Jacobsen SJ, Cosio FG. Using serum creatinine to estimate glomerular filtration rate: accuracy in good health and in chronic kidney disease. Ann Intern Med. 2004; Dec 21; 141 (12): 929-37.
- Johnson D, Usherwood T. Chronic kidney disease - Management update. Aust Fam Physician 2005; 34 (11): 915-923.
- National Kidney Foundation: Clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification and stratification. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 39 (Suppl. 1): S1–S266, 2002.
- Fioretto P, Steffes MW, Sutherland DE, Goetz FC. and Mauer M. Reversal of lesions of diabetic nephropathy after pancreas transplantation. New England Journal of Medicine 1998; Jul 9; 339(2):69-75.
- Chaiken RL, Eckert-Norton M, Bard M, et al. Hyperfiltration in African-American patients with type 2 diabetes. Cross-sectional and longitudinal data. Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:2129-2134.
- O’Callaghan C, Brenner BM. The Kidney at a Glance. London: Blackwell Science; 2000.
- National Kidney Foundation, “K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation classification and stratification”, Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002; 39 (suppl. 1): S1–266.
- Lamb E, Tomson C, Roderick P, “Estimating kidney function in adults using formulae”, Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2005; 42: 321–345.